BIOS 1710 SI WORKSHEET 18 SI Leader: Helene Shai 14 Oct 2014
advertisement

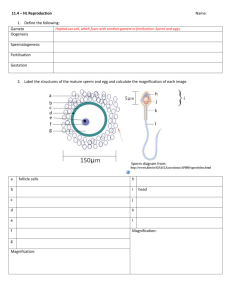
BIOS 1710 SI WORKSHEET 18 SI Leader: Helene Shai 14 Oct 2014 Chapter 42: Animal Reproduction and Development, continued 1. Draw and compare/explain the graphs of LH versus FSH, Estradiol versus Progesterone, and the uterine lining throughout the days of the menstrual cycle. Also, draw the stages of follicle development. Compare the changes in these hormones over time, with the different stages of development. What does each change cause? 2. How do hormone-based birth-control methods work? 3. Suppose someone was injected with a high estradiol concentration at day 10 of the menstrual cycle. What is the major effect? a. Estradiol would cause LH levels to fall b. Estradiol would cause progesterone to rise c. Ovulation would occur d. Estradiol would cause both FSH and LH levels to fall 4. What is gametogenesis? 5. What is spermatogenesis? 6. What is oogenesis? 7. What are diploid cells called in the male and female gonads? How do these c 8. What are stem cells? 9. Draw, label, and explain the process of spermatogenesis. 10. Where does the above process occur? 11. True/False: spermatogenesis begins at birth and continues throughout life. 12. True/False: the process of spermatogenesis takes 5-6 months from start to finish. 13. Draw, label, and explain the process of oogenesis. 14. Compare gametogenesis in males and females. 15. Which statement is true regarding human gametogenesis? a. Oogenesis occurs throughout life. b. Spermatogenesis occurs throughout life and meiosis of a primary spermatocyte eventually results in four mature gametes. c. Oogenesis eventually results in four mature gametes from each primary oocyte. d. Spermatogenesis produces haploid sperm; oogenesis produces diploid eggs. e. Spermatogenesis produces polar bodies; oogenesis does not. f. None of the above. 16. Explain internal fertilization. 17. What is an acrosomal reaction? 18. What is an acrosome? 19. What is polyspermy? How is this prevented? 20. How is a diploid zygote formed? 21. What is cleavage? Draw and detail/explain the process. When does cleavage occur? 22. What is a blastula? What does it consist of? 23. Summarize what occurs during the first week. 24. What is the placenta? 25. Summarize what occurs during gastrulation. 26. Summarize what occurs during gastrulation. 27. Summarize what occurs during weeks 2 and 3. 28. During what stage of human development does implantation in the uterus occur? a. During the first cleavage. b. During the morula stage. c. At the blastula stage. d. During early gastrulation. 29. Summarize what occurs during the first trimester. 30. What is organogenesis? When does this occur? Explain in detail. 31. What does each layer become? 32. When is sex determined? How? 33. True/False: a fetus is most vulnerable to toxins, drugs, and infections during the second trimester. 34. True/False: sex determination is mainly caused by hormones. 35. The second and third trimesters are focused on ______________ ________________ and ______________. 36. What characterizes the third trimester? 37. If a baby is born prematurely, what can occur? 38. How long does a total pregnancy last? 39. Summarize childbirth. What hormone is important in this process? Why? Where does it come from? 40. How is labor induced? 41. True/False: the baby being delivered head first, face down, allows the easiest passage.