1 - Chemistry-i

SIBio3 Lab Practice I for Final exam spring 2009 made by P.Kim updated: 05/19/09
1. What type of root system are you seen? Monocot? Eudicot?
A) Tap root (Eudicot) B) Fibrous root (Monocot)
2. What type of root system is Dr. Hughey pointing and give rise from stem? Adventitious root
3. What are the three regions in root? Region of maturation,Region of Elongation,Apical meristem(Region of Cell
Division)
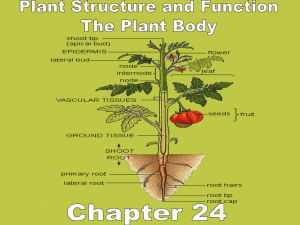
4. Label
A: Region of maturation E: Ground meristem
B: Region of Elongation
C: Apical meristem(Region of Cell Division)
D: Protoderm
F:
G:
Procambium
Apical meristem
H: Promeristem
I: Rootcap
5. Nam e of tubular extension? Root hair What is the function? facilitate absorption.
Name of the region where the tubular extension is present? Region of maturation
6. Name of the thimblelike mass of parenchyma? Region? Function?
Rootcap; Region of cell division(Apical meristem); Covers the root and secretes mucigel
7. What is the name of structure penetrating the cortex? What is the name of part where the structure originates? Lateral root; Pericycle
8. Monocot? Eudicot? How do you know? Monocot; Vascular cylinder in ring with pith.
What is the name of structure which the arrow indicates? What is the name of part where the structure originates? Lateral root; Pericycle
9. Monocot? Eudicot? How do you know? Eudicot; Vascular cylinder solid.
10. Monocot root? Eudicot root? Eudicot root
Label.
A: Pericycle D: Metaxylem
E: Protoxylem (first-formed primary xylem) B: Primary Phloem
C: Endodermis
11. Monocot root? Eudicot root? Can you see secondary growth? Monocot root; No Only primary growth
Label.
A: Endodermis
B: Protoxylem (first-formed primary xylem)
D: Pericycle
E: Early metaxylem
F: Late metaxylem C: Primary Phloem
12. Label.
A: Protoderm
B: Leaf promordium
C: Procambium
D: Ground meristem
E: Bud primordium
F: Apical meristem
G: Node
SIBio3 Lab Practice I for Final exam spring 2009 made by P.Kim updated: 05/19/09
13. Label. Monocot? Eudicot? How do you know? Can you see secondary growth? No Only primary growth
A: Vascular bundle B: Pith (ground tissue)
Eudicot ; the vascular tissues forms of discrete strands
14. Label. Monocot? Eudicot? How do you know? Can you see secondary growth? No Only primary growth
A: Vascular bundle B: Pith (ground tissue)
Dicot ; the vascular bundles appear scattered throught the ground tissue.
15. What type of plants has the structures you are seeing? How do you know? Label.
Hydrophyte ; Large intercellular spaces for buoyancy
A: Upper Epidermis
B: Vein(vascular tissue)
C: Stoma
D: Palisade parenchyma
E: Spongy parenchyma
F: Trichome
G: Intercellular space(buoyant)
H: Lower epidermis
I: Bundle sheath
16. What type of plants has the structures you are seeing? How do you know? Label.
Xerophyte ; Thick waxy cuticle, stomatal crypts
A: Cuticle
B: Vein(vascular tissue)
C: Upper epidermis
D: Palisade parenchyma
E: Spongy parenchyma
F: Lower epidermis
G: Trichome
H: Guard cell
I: Stomatal crypts
J: Bundle sheath
17. What type of plants has the structures you are seeing? Label.
Mesophyll
A: Xylem
B: Upper epidermis
C: Palisade parenchyma
D: Spongy parenchyma
E: Lower epidermis
F: Stoma
G: Phloem
H: Trichome
I: Bundle sheath
18. You are look at a zone of a leaf. What is the name of zone of the leaf? There are two layers in the zone. What are they? Function in each? Abscission (the normal separation of the leaf from the stem.)
Separation layer – the break occur; Protective -forms a leaf scar
19. Monocot? Eudicot? How do you know?
A) Eudicot- random stomata B) Mocot - parallel stomata
20. You have a Purple starch cone(F1 generation). Purple(R) is dormant over yellow (r). Starch endosperm(Su) is dormant over sweet one(su). a) What is possible combinations of alleles will be carried? RRSuSu, RrSuSu, RrSusu.
b) What is possible genotypes ?
RRSuSu, RrSuSu, RrSusu.
c) What are the possible dihyrid crossing? Show the parents’ phenotype and genotypes.
Phenotype: Purple starch
Genotype: RrSuSu -RRSuSu,
RrSuSu -Rrsusu
SIBio3 Lab Practice I for Final exam spring 2009 made by P.Kim updated: 05/19/09
21. a) What internal stimulus in a plant can cause different height and lateral length as shown in the two pictures?
Auxin(hormone)
b) Which one is the stronger internal stimulus? Right tree
c) How the internal stimulus works? Auxin inhibits axillary(lateral) buds
d) Name of term of this phenomenon by the internal stimulus? Apical dominance
22. If you cut the blade and then put IAA(Auxin) in lanolin on it in the plant A, only lanolin on it in the plant B, and put nothing on it in the plat C.
a) What happens in each: Plant A, B, & C
Plant A; Abscission does not occurs.
Plant B; Abscission occurs.
Plant C; Abscission occurs.
b) What is effect of IAA(Auxin)? Prevent abscission.
c) What is effect of lanolin? No effect
23. You are doing experiment of hormone auxin. You prepare two pots and plant dicot and eudicot in each pot.
You forget to put a label in each. After 3 weeks, you saw the result of the experiment. Which pot has been treated with
2,4 D(synthetic Auxin)? How do you know? A: Because auxin acts as an herbicide
24. You are looking at same species.
a) What external stimuli cause different height? mechanical stimuli.
b) What is the name of ?
Thigmomorphogenesis
25. What Hormone can cause different height in a same species? Effect of the hormone?
Gibberellin causes hyperelongation of shoots by stimulating cell division and elongation.
26. a) What is the name of phenomenon you are seeing in shoot? Negative Gravitropism
b) What external stimulus cause the shoot grow upward? Gravity
c) Is the growth in the root same as the shoot? No; the roots grow downward .
d) What is the name of phenomenon in root? Positive Gravitropism
27. What type of tropism is in each picture A, B, C? Write the external stimulus in each.
A- Phototropism; sunlight B- Thigmotropism; solid object CHeliotropism; Sunlight
28. In the picture C, which part is involved by the movement (solar-tracking) of sunflower? Explain how the part works to move the flower. Pulvini; Turgor pressure changes of the Pulvini.
29. a) What is the name of phenomenon you are seeing? Thigmonasty
b) What is the external stimuli? Touch c) Which part is involved by the movement? Pulvini; Turgor pressure changes of the Pulvini.
30. a) What are the name of square equipment and thread(or like ruler)? Square - Quadrats Thread- Transects b) What are they for? For study or measurement of the distribution or abundance of plants or other organisms in an area.