Midterm II Physics 231
advertisement
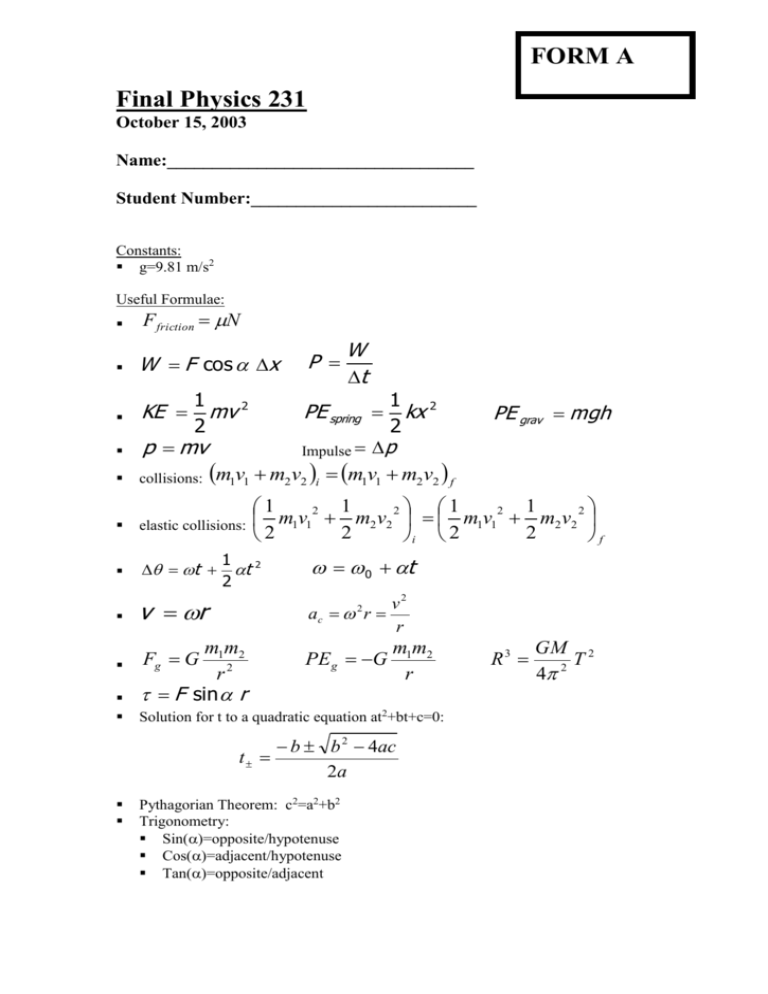
FORM A Final Physics 231 October 15, 2003 Name:__________________________________ Student Number:_________________________ Constants: g=9.81 m/s2 Useful Formulae: F friction N W F cos x 1 2 1 2 p mv Impulse p collisions: m1v1 m2 v2 i m1v1 m2 v2 f elastic collisions: t W t PE spring kx 2 KE mv 2 P 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 m1v1 m2 v2 m1v1 m2 v2 2 2 2 i 2 f 1 2 t 2 0 t v r v2 ac r r m1m2 r2 F sin r PEg G Fg G 2 m1m2 r Solution for t to a quadratic equation at2+bt+c=0: b b 2 4ac t 2a PE grav mgh Pythagorian Theorem: c2=a2+b2 Trigonometry: Sin()=opposite/hypotenuse Cos()=adjacent/hypotenuse Tan()=opposite/adjacent R3 GM 2 T 4 2 General comment: I think that some of the questions are too difficult. Adding some hints will help (problems 1,2,4), but especially 3,5 and 8 are beyond what they typically did in LON-CAPA. 1) A grasshopper jumps 10.2 cm high. If the angle with which the grasshopper jumps is at 45o with the horizontal, what is its total initial speed. (hint: consider first the vertical direction only). a) 4.0 m/s b) 2.0 m/s c) 4.0 m/s2 d) 1.4 m/s e) smaller than 1.0 m/s answer b) comments: change text (see above) and add hint. 2) Two objects are connected by a light string passing over a light frictionless pulley. The 5.00 Kg object is released from rest at a point 4.00 m above the floor...(delete 2 dots) Which of the flowing statements is true? a) The speed of the 5Kg mass when it reaches the floor is 4.43 m/s. b) The speed of the 3 kg mass when it reached the floor is 8.85 m/s. c) The speed of the 5Kg mass when it reaches the floor is 8.85 m/s d) The speed of the 5Kg mass when it reaches the floor is 19.6 m/s e) None of the above. Answer a) Comments: small errors (see above) Add hint: Use conservation of mechanical energy 3) A bullet is fired with an initial speed v into a block that is initially at rest at the edge of a table of height 1.00 m. The bullet remains in the block, and after the impact the block lands 2.00 m from the bottom of the table. If the mass of the block of 50.0 g and the 1g mass of the bullet is 1.00 g, what was the initial speed v of the 50g bullet? a) 442 m/s b) c) d) e) 221 m/s 4.42 m/s 2.21 m/s 0.49 m/s answer: b) although I find 226 m/s, I think you neglected the 1 g of the bullet??? I think problem 3 is much too difficult. In midterm I only 25% had the problem with parabolic motion correct. This involves even more steps. Even though they saw this in Lon-capa, I don’t think many students can do this in a reasonable amount of time. 4) A 600 Kg satellite is in circular orbit around the Earth at a height equal to the Earths mean radius. What is the speed at which the satellite is orbiting? (G=6.67x10-11 Nm2, ME=5.98x1024 Kg, RE=6.38x106 m) a) 3.05 m/s b) 7.91 x103 m/s c) 5.59 x103 m/s d) 5.60x10-8 m/s e) 11.2x103 m/s answer: c) Again, I think this is a difficult problem and probably a hint is a good idea. Also small type 5) Aliens in planet X intend to launch a rocket. What is its escape speed from the unknown planet X, if the mass is 7.36x1022 Kg and radius R is 9.82x106 m? a) 1.00 x103 m/s b) 7.07 x103 m/s c) 2.00 x103 m/s d) 0.32 m/s e) It cannot be calculated because the mass of the rocket is not given. I think this is much too difficult….They had no real practice with escape speed (in lon-capa for example). You would have to give the exact equation for escape speed on the equation sheet and then this problem just becomes a fill-in exercise. 6) A window has a glass surface of 1.60x103 cm2 and a thickness of 3.00 mm. The thermal conductivity of the glass is 0.84 J/s m 0C. Determine the rate of energy transfer by conduction through this pane in the summer, when the temperature of the inside surface of the glass is 70 0 F and the outside temperature is 90 0 F is: a) There is no thermal conduction through the window. b) 8.98 x103 J/s c) 896 J/s d) 4.98 x103 J/s e) 498 J/s answer e) I would suggest converting at least the cm2 and mm into m2 and m so that they only have to worry about the Fahrenheit (conversion must be on equation sheet) 7) Consider the following PV diagrams. Which of the following statements is correct: a) The work performed to take the gas from the initial to the final state is the same in all cases. b) The heat transferred to the gas is the same in all cases. c) Diagram (c) can represent an isothermal process. d) Diagram (b) consists of an isobaric process followed by an isovolumetric process. e) Diagram (a) consists of an isothermal process followed by an adiabatic process. Answer c). I would change the phrasing of answer d) or the intro for the problem, so that it is more clear that it is important to consider the direction of time. 8) In one cycle, a heat engine absorbs 500 J from the hot reservoir and expels 300 J to the cold reservoir. If the efficiency of this engine is 60% of the efficiency of a Carnot engine, what is the ratio of the temperatures of the hot reservoir and the cold reservoir of this Carnot engine? a) 2/3 b) 1/3 c) 2/5 d) 5/2 e) 3/5 answer b) Wow, you are hurting them! This is much more difficult than anything in LON-CAPA and involves ratios and percentages….. 9) A pendulum clock that works well on Earth is taken to a different planet. Knowing that the clock in the unknown planet ticks at twice the speed, what is the planet’s gravitational acceleration compared to that of earth (g)? a) 2g b) 4g c) g/2 d) g e) g/4 answer b) small change to text 10) The snapshot of two waves, A and B, is represented in the figure. Which of the following statements is correct? a) The amplitudes of the waves are the same. b) The wavelength of A is twice the wavelength of B B. c) The period of oscillation of A is the same as that of B. d) The speed of wave A is smaller than the speed of wave B e) None of the above. Answer a). It might be wise to indicate that the waves are moving (arrow or so…) 11) A long open pipe is 1.715 m long. Pressing the mouth against the pipe and blowing air into it, produces a sound (the speed of the sound is v=343m/s) that consists of the superposition of the several harmonics of the pipe. What are the frequencies of the first three harmonics? a) 100 Hz, 200 Hz, 300 Hz. b) 200 Hz, 400 Hz, 600 Hz. c) 100 Hz, 300 Hz, 500 Hz. d) 50 Hz, 100 Hz, 150 Hz. e) 50 Hz, 150 Hz, 250 Hz. Answer a) 12) You are patiently waiting for a train to arrive to Lansing. Suddenly the train approaches at high constant speed, blowing the whistle, and just passes straight through the station. What happens to the sound you hear? a) As the train approaches the frequency of the sound increases and the intensity decreases. b) As the train approaches both the intensity and the frequency of the sound decreases. c) As the train approaches the intensity of the sound decreases whilst the frequency remains constant. d) As the train approaches both the intensity and the frequency remain constant. e) As the train approaches both the intensity and the frequency increase. Answer e) I would rephrase the question to something like: A train approaches the station at constant velocity (does not intend to stop) while blowing its whistle. A person standing on the platform notices that: