Sociological Explanations for Deviance
advertisement
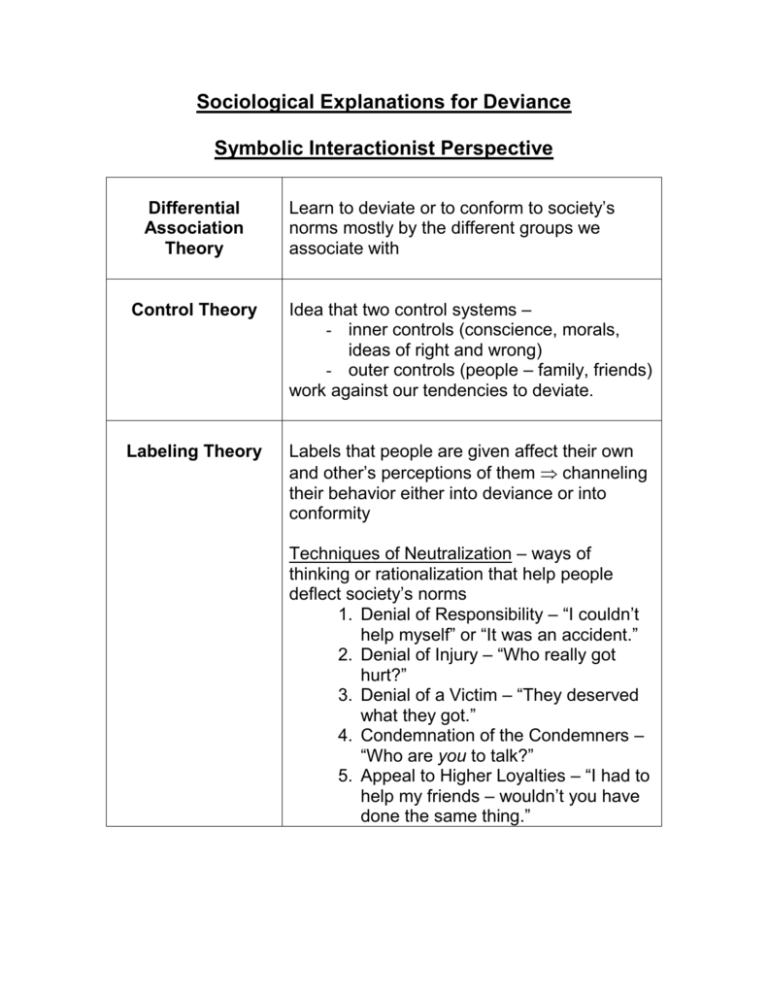
Sociological Explanations for Deviance Symbolic Interactionist Perspective Differential Association Theory Learn to deviate or to conform to society’s norms mostly by the different groups we associate with Control Theory Idea that two control systems – - inner controls (conscience, morals, ideas of right and wrong) - outer controls (people – family, friends) work against our tendencies to deviate. Labeling Theory Labels that people are given affect their own and other’s perceptions of them channeling their behavior either into deviance or into conformity Techniques of Neutralization – ways of thinking or rationalization that help people deflect society’s norms 1. Denial of Responsibility – “I couldn’t help myself” or “It was an accident.” 2. Denial of Injury – “Who really got hurt?” 3. Denial of a Victim – “They deserved what they got.” 4. Condemnation of the Condemners – “Who are you to talk?” 5. Appeal to Higher Loyalties – “I had to help my friends – wouldn’t you have done the same thing.” Sociological Explanations for Deviance Functionalist Perspective Deviance has three main functions: 1. Deviance clarifies moral boundaries and affirms norms 2. Deviance promotes social unity 3. Deviance promotes social change Strain Theory People who feel strain are likely to feel anomie – a sense of normlessness (mainstream norms don’t seem to be getting them anywhere, can’t identify with the norms of society) Illegitimate Opportunity Structures Opportunities that are woven into the texture of life Illegal opportunities are available to different social classes to reach the institutionalized means/success Ex. Street Crimes – robbery, prostitution, gambling, drugs White Collar Crimes – bribery of public officials, false advertising, embezzlement Sociological Explanations for Deviance Conflict Perspective Class, Crime, and Group in power imposes its definition of the Justice System deviance on other groups (Capitalists vs. Working Class) Law is an instrument of oppression by the ruling class – to keep the less privileged in their place. Ruling class uses the criminal justice system to punish the poor, while diverting/protecting their crimes. Ex. sentences for white collar crimes vs. street crimes











