Deviance & Crime
advertisement

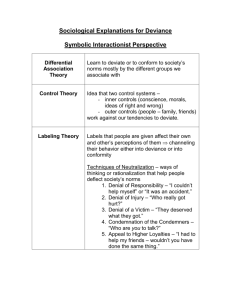
Deviance & Crime Deviance A behavior that violates significant norms Can be criminal or non-criminal Examples: Talking to yourself loudly in public Drag racing Using illegal drugs Cross-dressing Assault with a deadly weapon Changes in deviance Deviance has changed throughout history and culture Divorce used to be considered deviant in the US but has become accepted by society. In the Philippines, divorce is illegal Stigma A mark of social disgrace that sets the deviant apart from the rest of society Examples: In ancient Greece, they would burn or cut signs into the bodies of criminals in order to warn others of their deviance Prison inmates have dress codes and numbers that must be worn daily More examples of stigma Hester Prynne and her “scarlet letter”. During the Holocaust, they would tattoo the Jews and other non-Aryans in the concentration camps. And/or they would have badges denoting their status. Functions of Deviance 1. Clarifying Norms Deviance serves to define norms How do we know what’s wrong until someone else does it? We know what society accepts or doesn’t by people pushing the limits Functions of Deviance 2. Unifying the Group Serves as a way for a community to bond Separates the conformers from the non-conformers or “outsiders” Functions of Deviance 3. Diffusing Tension In some cases, minor acts of deviance serves as a safety valve. It allows people to act out and get out tension and stress Functions of Deviance 4. Promoting Social Change When large numbers of people violate a particular norm, it usually means that something needs to be changed in society Example: people who strike in order to change working conditions Functions of Deviance 5. Providing Jobs Because deviance exists, it requires people to control it Police, lawyers, judges, prison workers, etc All these people help control an important part of society Crime Three parts to what defines a crime are: Any act that is labeled as such by those in authority Is prohibited by law Is punishable by the government Types of Crimes 1. Violent Crimes Make up a small percentage of the population Examples: murder, forcible rape, robbery, aggravated assault Occurs every 22 seconds in the US Every 2 minutes, someone is sexually assaulted in the US Most victims of violent crimes are African American Types of Crimes 2. Crimes against property Examples: burglary, larceny (theft other than auto), car theft, arson, tagging Involve stealing someone else’s property or intentionally damaging it Rate of larceny and burglary has declined since the 1990’s Types of Crimes 3. Victimless Crimes Examples: prostitution, illegal gambling, illegal drug use, vagrancy “victimless” because they supposedly harm no one but the person committing the act Types of Crimes 4. White-collar crimes Describes offenses committed by individuals of high social status in the course of their professional lives Examples: misrepresentation, fraud, tax evasion, embezzlement, price-fixing, toxic pollution, insider trading, political corruption Cost the US over $300 billion each year FBI Most Wanted - White Collar Crimes Martha Stewart Money Laundering & Fraud Obstruction of Justice & Conspiracy Bernie Madoff Fraud Convicted to 150 years in prison Types of Crimes 5. Organized Crime Crime syndicate – a large scale organization of professional criminals that controls some vice or business through violence or threat of violence Operate in many areas of business including legal businesses often as “fronts” for their criminal activities Types of Crimes They reinvest their money through legal channels Examples: drug trafficking illegal gambling unfair labor practices hijacking of merchandise loan-sharking (lending money at very high interest rates) FBI — Famous Cases & Criminals