Sociology 7
advertisement

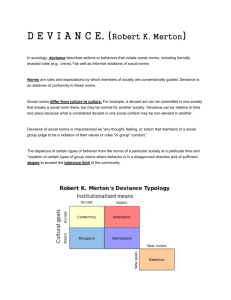
Deviance—Behavior that violates a norm Who decides what is deviant? Answer: each society decides based on morals etc As a threat—unpredictable Society needs norms Why? Stigma-- POSITIVE NEGATIVE Over-conformity to norms Rejection of norms Idealize norms Ignore norms Unaware of norms Ex: anorexia, Singapore & cleanliness Ex: crime Costs of Deviance Benefits of Deviance •$ for police; social workers etc •Erodes trust •Clarifies norms •Promotes social change; •Creates unity INTERNAL EXTERNAL -inside of individual -group -learn thru socialization -learn thru rewards & punishments -internalize norms—”what to do” -desire to be “good” people -integrity; fear of punishment -positive & negatives “Shaming” Example—shoplifting Which type of control is more effective? Deviance depends on the bonds between society & individual ◦ Social bonds: 1-attachment 2-commitment 3-involvement 4-belief **Bonds control individual behavior THE MORE BONDS YOU HAVE---THE MORE INTERNAL SOCIAL CONTROL YOU HAVE Anomie—the strain people feel when they are blocked in their attempt to achieve societies goals Strain Theory by Merton ◦ Gap between goal and means of attaining the goal ◦ Forces people to be deviant 1-conformity 2-innovation 3-ritualism 4-retreatism 5-rebellion **key criticism—just being “frustrated” doesn’t CAUSE deviance Cloward & Ohlin Social classes have different styles of crimes Illegitimate opportunities— ◦ Opportunities for crimes—part of social life Urban poor ◦ Hustles—drug dealing, robbery, gambling, prostitution Prison time Death penalty Reasons: ◦ Lack $ ◦ Crimes against whites punished more ◦ Victim discounting— Don’t care about crime if it is done to someone of a lower status High status people do crimes usually as they do their jobs ◦ Insider trading ◦ Tax evasion ◦ Embezzlement Huge $ to economy Usually treated better ◦ Less jail time ◦ “country club” prisons—ex-Governor Blagojevich 1-Differential Association Who you associate with makes you more deviant ◦ Learned behavior- ◦ Age of exposure to deviance makes a difference ◦ “friends determine your behavior” 2-Labeling “scarlet letter-A=adulteress” Self-fulfilling prophecy Label people as deviant—then they will do deviant things ◦ Ex: Teen pregnancy Who gets labeled??? SAINTS & ROUGHNECKS Sykes & Matza—people resist labels ◦ Denial—of victim, injury, responsibility, ◦ Appeal to loyalty ◦ Condemnation-- Some groups like the label of “deviant” ◦ Ex: motorcycle gangs, street gangs Primary Secondary Occasional breaking of norms Life & identity centered around norm breaking Juvenile record, but no adult record Master status Ex: teens or college age Drink when not 21 Ex-gang members; career criminals Deviance 1-threatens status quo (or norm) 2-challenge beliefs 3-who makes rules??? Who decides on what is deviance? Agree/Disagree: The death penalty is cruel and unusual punishment and should be abolished in the US. Explain your view.