Chapter 8 Deviance coreobj 2014
advertisement

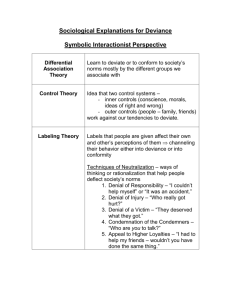
Chapter 8 Deviance __________________________________________________________ Objectives: After studying this chapter the students will be able to: A. Define “deviance” and understand why deviance is relative from a sociological perspective (190) B. Know why human groups need norms to exist and consequently, develop a system of social control for enforcing norms (190-19) C. Describe some of the sanctions human groups use to enforce norms, including shaming and degradation ceremonies (192, 196) D. Differentiate between biological, psychological, and sociological explanations for why people violate norms. (192-193) E. Discuss deviance from the symbolic interactionist perspective, describing and applying the various components of differential association theory, control theory, and labeling theory. (193-195) F. List and discuss the five techniques of neutralization (197) G. From the Functionalist Perspective, know which functions deviance fulfills for society. (199-204) H. Understand strain theory and discuss its social implications (199-201) I. Discuss the role power plays in defining and punishing deviance while discussing, from the conflict perspective, how the criminal justice system legitimates and perpetuates social inequality. (201-204) J. Describe the different ways street crime and white collar crime are perceived by the public and treated by the criminal justice system. (201-206) K. Address the ramifications of the growing prison population in the U.S.; examine how the way society addresses crime is related to the conflict perspective. (205-208) L. Talk about the gender, social class, and racial –ethnic bias with regard to the death penalty. (210-212) M. Explain why crime statistics may be misleading and should be interpreted with caution. (214) N. Know what is meant by the “medicalization of deviance” and why some sociologist view mental illness as more of a social, rather than biological condition.(214-216) O. Explain why the United States needs to develop a fairer and more humane approach to dealing with deviance. (216) Chapter 8 Core List/Top Ten degradation ceremonies street crime rehabilitation hate crimes labeling theory deterrence Strain theory control theory positive sanctions negative sanctions ******************************************************************************************** crime genetic predisposition Institutional Means criminal justice system Cultural Goals police discretion marginal working class stigma deviance differential association personality disorder illegitimate opportunity structure techniques of neutralization white-collar crime medicalization of deviance recidivism rate serial murder working class incapacitation retribution social order social control