st-gde-ch1-2-AGRESTI
advertisement

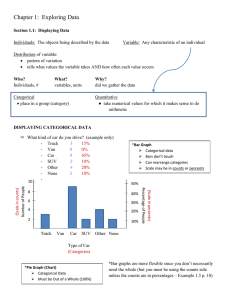
Math 116 and Math 116A– Study Guide for Chapters 1 and 2 Section 1.1 Data Statistics Design Description (Descriptive Statistics) Inference (Inferential Statistics) Section 1.2 Subjects Population Sample Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics Parameter Statistic Random samples Randomness in experiments Section 1.3 TI-83,84 graphing calculator Minitab StatCrunch Section 2.1 Individuals Variable Quantitative variable (discrete, continuous) Categorical or qualitative variable Frequency Tables Frequencies Proportions or relative frequencies Mode Section 2.2 Graphs for categorical data Pie chart Bar graph Pareto Charts Graphs for quantitative data Dot plots Stem and leaf plots Histograms Time plots Shape of a distribution Unimodal Bimodal Symmetric Skewed to the left Skewed to the right 1 Section 2.3 Measures of the center of quantitative data Mean Median Mode Outliers Comparing mean and median Resistant Section 2.4 Measures of variability of quantitative data Range Standard deviation Variance Empirical rule Potential outliers rule (more than 3 standard deviations from the mean) Section 2.5 Measures of position Percentiles Quartile Interquartile range Detecting potential outliers, the 1.5 IQR rule Box plot The five-number summary Box plot compared to histogram Side by side box plots z-scores to identify position and potential outliers Section 2.2: In the Multimedia Book for chapter 2 - Within Active Stats 1. Listen to Attributes of Distribution Shape (animated Activity) 2. Listen to “Learn About Stem and Leaf Displays” (animated activity) – 3. Listen to “Meaning of Distribution Shape” – Does the shape of a distribution change if we add or multiply a number to each of the observations? 4. Listen to “Practice describing the Center” – Describe shape, number of modes, and deviations from pattern 2