How Plants “See” - MrsRowlandScience
advertisement

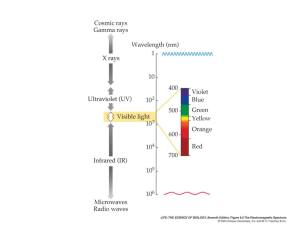
How Plants “See” By Marcelo J. Yanovsky and Jorge J. Casal Natural History, September 2004, p. 32 - 37 Name: Extra Credit 1. What question were the researchers in Argentina trying to answer? 2. State their hypotheses: 3. Do plants only use light for photosynthesis? 4. How do plants measure light? 5. How do plants measure time? 6. Is chlorophyll a molecule? 7. Are chlorophyll only found in leaves? 8. What color wavelengths of visible light do green leaves absorb? 9. What color wavelengths are transmitted? 10. What color wavelengths are reflected? 11. Can plants “see” beyond the visible spectrum? 12. What can plants measure? 13. What did the research team do to the “treated” plants? 14. Were the plants “tricked” into growing? 15. True or False. Plants can “see” their competitors long before their competitors cast a shadow on them. 16. What time of the day should a farmer plow if they want to minimize the growth of weeds? 17. Do plants have organs to perceive or focus light? 18. What to photoreceptors sense? 19. What are the two parts of the molecule of photoreceptors? 20. What are the 3 classes of photoreceptors? 21. Photochromes “inactive” forms absorb ___________ light and the “active” forms absorb _______________. 22. Darwin and his son studied the bending of plants toward ___________ light. 23. What is circadian rhythm? 24. What synchronizes the light-dark cycle? (The rest of this article becomes fairly complex. Skim the article to find the remaining question. There is an error in the paper from p. 36 to 37 – just keep reading) 25. Were the researchers able to make plants bloom on short days when they normally only bloom on long days? 26. What protein concentration change can cause this? (the name of the protein)