SURFACE ANATOMY OF THE THORAX
advertisement

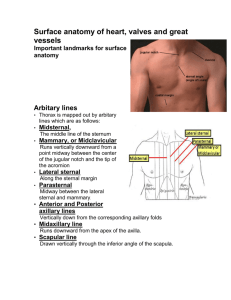
SURFACE ANATOMY OF THE THORAX WRITTEN BY : RAYAN S. ALBALLAA * ANTERIOR THORACIC WALL : - SUPRASTERNAL NOTCH is the superior margin of manubrium sterni , and it lies opposite to the lower border of T2 . - MANUBRIUM STERNI lies opposite to T3 & T4 . - STERNAL ANGLE ( ANGLE OF LOUIS ) is the angle between the manubrium and the body of the sternum forming a cartilaginous joint called MANUBRIOSTERNAL JOINT which has a small amount of movement possible during respiration . It lise between T4 & T5 . - XIPHISTERNAL JOINT is the joint between the xiphoid process ( which is a cartilage ) and the body of the sternum . It's a cartilaginous joint , and it fuses with the body of the sternum during middle age . It lies opposite to T9 . - SUBCOSTAL ANGLE is at the inferior end of the sternum ; between the sternal attachments of SEVENTH COSTAL CARTILAGES . - COSTAL MARGIN is the lower boundary of the thorax and is formad of 1- the costal cartilages of the 7th , 8th , 9th , ant the 10th ribs . 2- the ends of the cartilages of the 11th and 12th ribs . The loest part of it is formed by the 10th rib and lies at the lever of L3 * DIAPHRAGM : -THE CENTRAL TENDON lies behind the xiphisternal joint . -RIGHT DOME is HIGHER than the LEFT DOME . -RIGHT DOME is at the upper border of the 5th rib and left dome is at the level of lower border of the 5th rib . * NIPPLE : IN MALES , it's in the 4th intercostal space , but in females in differs . 1 * THE APEX OF THE HEART : - the apex of the heart is formed by the left ventricle . - the apex beat is caused by the apex of the heart being thrust ( pushed with a lot of force ) forward against the thoracic wall as the heart contracts . - you can feel the apex beat by placing the flat of your hand on the chest wall over the heart , and then determine the area of cardiac pulsation . after that , you place two fingers over the intercostal spaces and you keep moving till you find the point of maximum pulsation . - the apex is usually found in the 5th LEFT INTERCOSTAL SPACE 3.5 in ( 9cm ) from the midline . * THE AXILLARY FOLD : - THE ANTERIOR FOLD is formed by the lower border of PECTORALIS MAJOR while the POSTERIOR FOLD is formed BY THE TENDON THE LATISSIMUS DORSI as it passes around the lower border of TERES MAJOR . * POSTERIOR THORACIC WALL : - All the spines of the thoracic vertebrae can be palpated in the midline posteriorly . - C7 is the fist spine to be felt ( vertebra prominens ) . - you can not feel the spines of C1-C6 because the are covered by the LIGAMENTUM NUCHAE . * SCAPULA : - the superior angle lies opposite to the spine of T2 . - the root of the spine of the scapula lies at the level of the spine of T3 – the inferior angle lies at the level of the spine of T7 . * TRACHEA : - extends from C6 to T4 . 2 * LUNGS : - apex of the lung projects into the neck one inch above the clavicle . - the anterior border of the right lung begins at the sternoclavicular joint and runs downward almost reaching the midline behind the sternal angle . It then continues downward till it reaches the xiphisternal joint . - the anterior border of the left lung deviates laterally at the level of 4th costal cartilage and extends for a variable distance beyond the lateral margin of the sternum forming the cardiac notch . and then continues until it reaches the level of xiphisternal joint . - the lower margin of the left lung in midrespiration crosses the 6th , 8th , and 10th ribs . - the posterior border of the lung extends from the spine of C7 to T10 - READ ABOUT THE FISSURES ( pages 73 & 74 ) * PLEURA : - the lines that indicats the limits of the parietal pleura are called LINES OF PLURAL REFLECTION . - the cervical pleura ( cervical dome of the pleura ) extend upward into the neck about 1 in above the clavicle . ( READ THE CLINICAL NOTE ABOUT IT ) - the lower border of the pleura crosses the 8th in the midclavicular line and 10th in the midaxillary line and 12th adjacent to the vertebral column . - COSTODIPHRAGMATIC RECESS ( READ PAGE 87 ) . 3 * HEART : - the apex is found in the 5th left intercostal space 3.5 in ( 9cm ) from the midline . - the superior border , formed by the roots of the great vessels extends from a point on the 2nd left costal cartilage .5 in ( 1.3 cm ) from the edge of the sternum to a point on the 3rd righr costal cartilage .5 in ( 1.3 cm ) from the sternum . - the right border , formed by the right atrium , extends from a point on the 3rd right costal cartilage to a point on the 6th right costal cartilage .5 in ( 1.3 cm ) from the sternum . - the left border , formed by left ventricle , extends from a point on the 2nd left costal cartilage .5 in ( 1.3 cm ) from the the sternum to the apex of the heart ( 5th left inercostal space ) . - the inferior border , formed by right ventricle and the apical part of the left ventricle , extends from the 6th right costal cartilage .5 in ( 1.3 cm ) from the edge of the sternum to the apex beat . - the position of the margins of the heart can be determined by percussion . - THE : 1-ARCH OF AORTA 2- ROOT OF BRACHIOCEPHALIC ARTERY 3-COMMON CAROTID ARTERY 4-SUPERIOR VENA CAVA 5-TERMINAL PARTS OF RIGHT & LEFT BRACHIOCEPHALIC VEINS . lie behind the manubrium sterni . - THE INTERNAL THORACIC VESSELS run down vertically ,5 in ( 1.3 cm ) lateral to the sternum as far as the 6th intercostal space . - THE MAMMARY GLAND in young adult female overlies THE 2nd to the 6th ribs . THE END 4