7.8 thoracic cage
advertisement

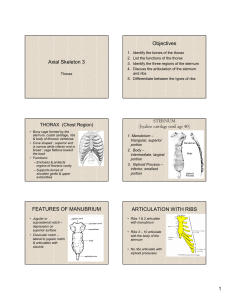
Thoracic Cage Functions Protects vital organs within the thorax Supports thorax during respiration, Supports shoulder girdles and upper limbs Provides attachment points for back, chest and shoulder muscles. Parts Composed of thoracic vertebrae (dorsal) Ribs (laterally) Sternum with costal cartilages (anteriorly). Ribs and costal cartilages There are 12 pairs of ribs. All 12 attach posteriorly to vertebral column. Pairs 1 – 7 and true ribs (attach directly to sternum by costal cartilages) 8 – 12 are false ribs (attach indirectly or lack a sternal attachment completely). 8 – 10 attach indirectly by a common cartilage. 11 and 12 are floating ribs and do not attach to sternum at all. Rib Cage Sternum Divided into three parts, manubrium, body and xiphoid process. A flat bone approximately 6 inches long. Manubrium (superior) is shaped like a knot in a necktie. Articulates with clavicle at clavicular notches. Sternum Body Forms the bulk of the sternum. Sides are notched where it articulates with cartilages of the second to seventh ribs. Body Xiphoid process Forms inferior end of sternum. Is hyaline cartilage in youth, but ossifies in adults. Articulates only with sternal body and serves as attachment point for diaphragm and some abdominal muscles. Sternal landmarks Jugular notch Sternal angle Xiphisternal joint Jugular notch Visible as a central indentation in the upper border of manubrium. Is generally in line with the disc between T2 and T-3. Is also in line with the point where the left common carotid artery issues from the aorta. Sternal angle Found where the manubrium joins the sternal body. Sternum is slightly angled at this point. Can be felt as a horizontal ridge across across front of sternum. Landmark position for 2nd rib and the disc between T-4 and T-5. Xiphisternal angle Where sternal body and xiphoid process fuse. Lies opposite ninth thoracic vertebrae.