L Memory Notes with Blanks
advertisement
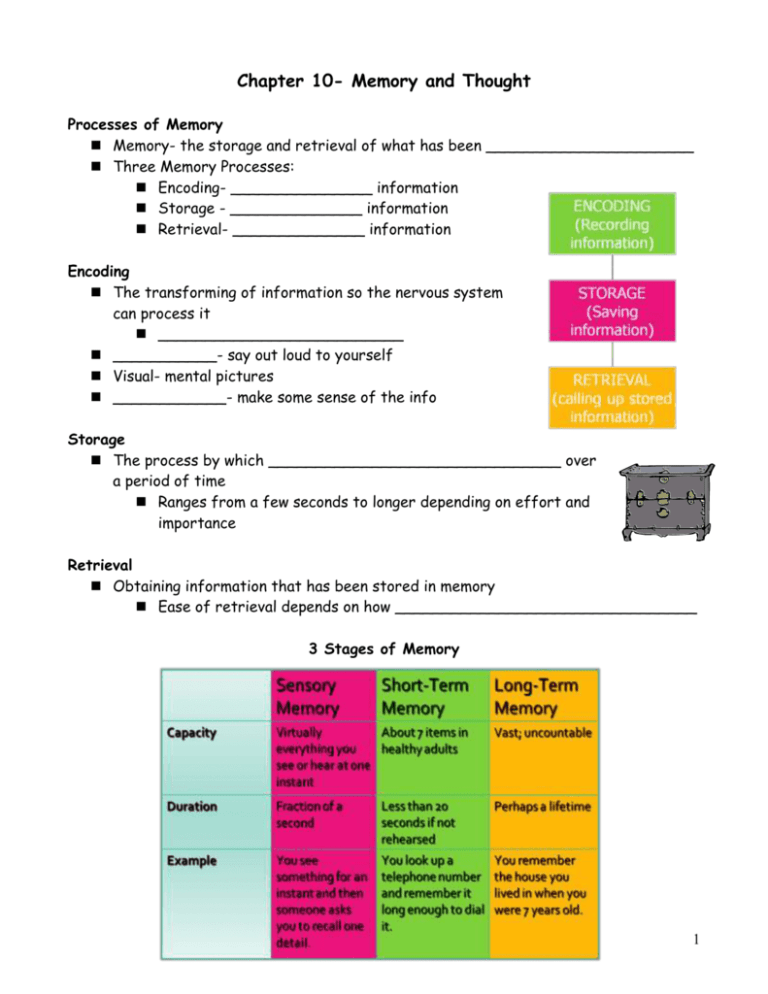
Chapter 10- Memory and Thought Processes of Memory Memory- the storage and retrieval of what has been ______________________ Three Memory Processes: Encoding- _______________ information Storage - ______________ information Retrieval- ______________ information Encoding The transforming of information so the nervous system can process it __________________________ ___________- say out loud to yourself Visual- mental pictures ____________- make some sense of the info Storage The process by which _______________________________ over a period of time Ranges from a few seconds to longer depending on effort and importance Retrieval Obtaining information that has been stored in memory Ease of retrieval depends on how ________________________________ 3 Stages of Memory 1 Sensory Memory Very brief memory storage immediately following _______________________________ Senses hold info for a fraction of a second before it disappears Gaps between frames in movies Sensory Memory- Sperling’s Experiment Used a tachistoscope to present a group of letters and numbers to people for a 20th of a second. In the past if you presented people this… 7 1 V F X L 5 3 B 7 W 4 They would remember ___________. Sperling believed this was because the stimulus created a ___________________ and only a few could be read back before the image faded- ________________________ (Visual Sensory Memory) Sperling told participants that after he flashed the letters, he would present a tone. Upon hearing a high tone, participants were to tell him the top row Medium tone= ____________ Low tone= _____________ Sperling’s Results Once people learned this system, they were able to remember about _____ of any one row if asked to recall immediately This proved that the participant _______________________________ and can still read off the items in the correct row after the picture has left the screen Echoic- auditory sensory memory (held for _________________) Three Functions of Sensory Memory 1) Prevents you from being __________________________________________ 2 2) Gives you enough decision time to figure out if __________________________- automatically transferred to short term memory 3) Allows for _______________________ Short-Term Memory Memory that is limited in capacity to about _________________ and in duration by the subject’s active rehearsal Does not necessarily involve ____________________ AKA __________________- processing and working with new information STM + Recalled LTM Maintenance Rehearsal A system for remembering that involves _______________________________ without attempting to find meaning in it ________________ lead to losses in STM STM measured by seeing how long a participant can retain information without rehearsal About _______________ Chunking ST Memory- only _________________________ Chunking- the process of grouping items together to make them ______________________ Usually items are either related or rehearsed Miller- if a collection is packaged into a chunk, it is ________________________ Radio station names, phone numbers, initials, etc. Memorizing trick- chunk ASAP 555-6794 instead of 5-5-5-6-7-9-4 Even with chunking, no more than __________________ without rehearsal. Must be rehearsed to transfer to LT memory with ____________________. Primary-Recency Effect We are better able to recall information presented at ________________________________ Primary- ______ Recency- ______ 3 Long-Term Memory The storage of information over ______________________________ Not like a filing cabinet- you reconstruct what you must recall when you need it Capacity appears to be _________________ Only ______________ are maintained (i.e. movies) Types of Long-Term Memory Semantic vs. Episodic (Tulving) ____________ vs. ___________________ Declarative vs. Procedural (Squire) ___________________________ vs. ___________________________ Memory and the Brain What happens when we remember? Change in ____________ structure Change in ____________ structure Evidence that procedural memories are formed in the __________ in the frontal cortex and declarative memories occur in the _____________ (words, facts, events) and the ____________ (emotions) Retrieving Information Stored information is useless unless ___________________ Human brain has to be extremely well-organized Recognition A person ____________ an object, idea, or stimulation as one he or she has not experienced before. Multiple choice tests A single item of information may be indexed under ______________________ Identifying musical instruments regardless of the song A person’s features: more files, easier to retrieve Recall Reconstructing __________________________ Searching for and finding information In a ____________, each word and bit of information must be retrieved separately Involves knowledge, attitudes, and inferences 4 Influenced by __________________- alteration of a recalled memory that may be ___________ or ___________ depending on experiences, attitudes, or references _______________- act of filling in memory gaps if our reconstruction is incomplete, sometimes in terms of our schemas Schema- ___________________________________________ _________________- ability to remember with great accuracy based on ST exposure (5% of children but _____________ in adults) State-Dependent Learning Recalling information easily when you are in _______________________________________ as you were when you encoded the information Studying Relearning Both declarative and procedural memory Learn more quickly _________________________ Forgetting __________- fading away over time Not certain if long term memories can ever decay- can sometimes be remembered by ________________________________________________ _________________- blockage of a memory by previous or subsequent memories Proactive- earlier memory prevents you from __________________________ Retroactive- a later memory or new information blocks remembering ____________________________ May sometimes erase memories permanently but sometimes _____________________________ ___________- people may subconsciously block memories- ____________ Amnesia A ___________________ that may occur due to brain damage, drug use, or severe psychological stress Infant amnesia- the relative lack of ___________________________ Freud- infancy is filled with ___________________ 5 Because infants do not yet understand language, their memory is _______________ The ________________ is not mature enough to spark memories Improving Memory Meaningfulness and Association Elaborate rehearsal- relate the information to ________________________ Rearranging: DFIRNE-FRIEND Use of ________________ __________________ to prevent interference- rehearse even when you know it Avoid studying ________________________ Space out your learning Mnemonic Devices 6