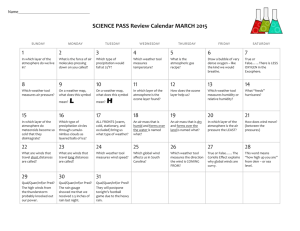
7. CLIMATE Glossary
advertisement

CLIMATE a glossary Acid rain: rain or other forms of precipitation that is unusually acidic. Climate change: any long-term change in weather statistics over decades or millions of years. Carbon dioxide: the most abundant greenhouse gas (CO2) emitted from fossil fuels. Drought: an extended period when a region receives very little rain. Ecosystem: a natural area/environment where interdependent organisms (plants, animals and micro-organisms) are functioning together. Emission Standards: requirements that set specific limits to the amount of pollutants that can be released into the environment. Fahrenheit: a temperature scale in use in the USA. 0C (Celcius) = 32F (Fahrenheit). Flood: an overflow or accumulation of an expanse of water that submerges land. Forecasting: the process estimating future weather patterns. “Prediction” is a similar term. Global warming: the increase in the average temperature of the Earth near-surface, air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. Greenhouse gas: gases in the atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation. The greenhouse effect is the heating of the surface of the Earth due to the presence of greenhouse gases. Meteorology: the scientific study of the atmosphere. Precipitation: rainwater (atmospheric water vapor deposited on the surface of the Earth.) Storm: disturbances of the atmosphere with severe weather, marked by strong wind, thunder (thunderstorm) and lightning, heavy precipitation, with ice (ice storm), strong winds (as in a dust storm, snowstorm, hailstorm, etc.) Tide(s): the rising of oceans caused by tidal forces of the Moon and the Sun. Weather: a set of all the phenomena occurring in the atmosphere at a given time. Wetland: an area of land soil saturated with moisture either permanently or seasonally. Winds: cyclone, hurricane (start in the tropics), typhoon (Pacific Ocean), tornado (mostly in US), monsoon (typically in Indian Ocean and Southern Asia), jet stream (rapidly moving air) www.papajoop.com