Test 3 Review
advertisement

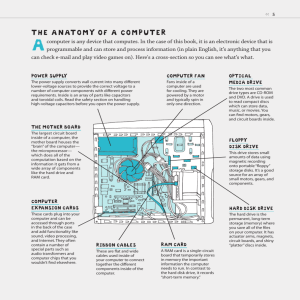
Test 3 Review Chapter 7 Storage holds data, instructions and information for future use. Every computer uses storage to hold software, to start up, a computer locates an operating system in storage and loads it into memory. Different type of user has different requirement for storage. A storage medium is the physical material on which a computer keeps data, instructions and information. A storage device is the computer hardware that records and /or retrieves items to and from storage media. Storage devices access time is in milliseconds. Reading is the process of transferring these items from a storage medium into memory and it function as a source of input; writing is process of transferring items from memory to a storage medium and it functions an output. Capacity is the number of bytes a storage medium can hold. Nonvolatile storage media include floppy disks, PC cards, microfiche, tapes, and so on. A floppy disk is portable, inexpensive storage magnetic medium that uses magnetic particles to store items in tracks and sectors. A floppy disk drive is a device that reads from and writes on a floppy disk. It can write to floppy disk only if the write-protect notch is closed. It stores data on both sides of disks, and each side has 80 tracks, each track has 18 sectors. If the user seldom uses floppy disk, you can buy an external floppy disk drive. A zip disk is a type of portable magnetic media that can store up to 500 times more than a standard floppy disk. It is a little bit larger than floppy disk and twice thicker than floppy disk. It is easy to transport many files or large items. A hard disk is a storage device that contains one or more inflexible circular platters. Each platter has two read/write head, one for each. The capacity of a hard disk is determined from the number of platters it contains, together with the composition of the magnetic coating on the platters. While the computer is running, the platters rotate at 5400-7200 rpm. It spins much faster than floppy disk and usually spins constantly. The spinning creates a cushion of air between the platters and the read/write heads. A head crash occurs when a read/write head touches the surface of a platter, usually resulting in a loss of data. The storage capacity is 40-160GB. First hard disk drive is called drive C. For the external hard disk and removable hard disk have some advantages over fixed hard disk(sharing a drive with multiple computers, adding storage space to a notebook computer, transporting a large number of files). platter Figure track sector read/write head platter sides actuator Hard disk interface for internal use: SATA, EIDE, and SCSI. The primary advantage of each kind of interface. CD and DVDs are type of optical media that store items. Laser light is used to read from (lower-power laser is used) and write to (high power laser is used) discs. A DVDROM is an extremely high capacity optical disc. DVD –ROM uses a different technique to improve the storage capacity, it can have an extremely high capacity optical disc capable of storing 4.7GB to 17GB. Not only is the storage capacity of it greater than that of a CD-ROM (because DVD-ROMs use different storage techniques: using two layers of pits, using double sides, making the disc more dense by packing the pits closer together), a DVD-ROM’s quality also far surpasses that of a CD-ROM Proper care CD and DVDs makes them have a long life time. Transfer rate can be measured by the original transfer rate (such as 50X = 50x150= 7500KBps). We need to protect the CDs and DVDs so that they will have a long life time (do not stack disks, do not touch the underside of a disc, do not expose disks to any type of contaminant). CD-RW and CD-R are popular for creating audio CDs. Tape is a magnetically coated ribbon of plastic capable of storing large amounts of data and information at low cost. It no longer is used as a primary method of storage but is used most often for long-term storage and backup. The tape drive access type is called sequential access type, other storage devices such as CD, DVD use direct access type. A PC card is a thin, credit card size device that fits into a PC Card slot to add storage or other capabilities to a desktop or notebook computer, it is portable. When the user buys digital cash, the amount of money is withdrawn from the user’s bank account. A smart card is similar in size to a credit card or ATM card and can store data on a microprocessor embedded in the card. Microfilm and microfiche are used widely. The use of microfilm and microfiche provides a number of advantages. They greatly reduce the amount of paper firm mush handle. Chapter 8 Operating System((OS)(sometimes called the platform) coordinates all activities among computer hardware resources. In single user/multitasking, user works on two or more programs that reside in memory at the same time. Foreground contains application you are using, background contains programs that are running but are not in use. Utility program is system software that performs maintenance-type tasks such as managing files and viewing graphics files, uninstalling programs and diagnosing problems, backing up files and defragmenting files, and so on. Cross-platform application runs identically on multiple operating systems. Booting is Process of starting or restarting a computer. Cold boot turns on computer that has been powered off. Warm boot restarts computer that is powered on. For the Windows XP, a warm boot can be performed by pressing a combination of keyboard keys (CTRL+DEL+ALT), pressing reset button on the computer, selecting a button or an opting from a list in a dialog box. Recovery disk, also called boot disk, contains system files that will start computer when computer cannot boot. Single user/multitasking can work on two or more programs that reside in memory at same time. The application that is being used is called the foreground, others are in background. Spooling sends print jobs to buffer instead of directly to printer, print jobs line up in queue. Disk defragmenter is to reorganizes files and unused space on hard disk so programs run faster. Diagnostic utility compiles technical information about hardware and some software and then prepares to report outlining problems. Backup utility copies selected files or entire hard disk onto another disk or tape. Most compress files during backup to require less storage space. Windows XP is Microsoft’s fastest, most reliable Windows operating system, available in three editions: Home Edition, Professional Edition, and Tablet PC Edition. Device driver is program that tells operating system how to communicate with device, each device on a computer has its own specialized set of commands and this requires its own driver. When you boot a computer, the OS loads each device’s driver. These devices will not function without their correct drivers. If you want to attach a new device to a computer, you have to install its driver before you can use the device. File compression utility shrinks size of files to free up room and improve performance. Compressed files are sometimes called zipped files, which has .zip extension. Two popular utilities: PKZIPTM and WinZip® Chapter 9 Communication is process in which two or more computers or devices transfer data, instructions, and information via cables and wires or wirelessly mainframe computers. Web Services are tools that enable programmers to create applications that run on Internet or internal network, one platform for implementing Web services is Microsoft’s .NET. Groupware is software that allows people to share information. An online meeting lets users share documents with others in real time. Network is Collection of computers and devices connected via communications devices and transmission media. Local Area Network(LAN) is Network in limited geographical area such as home or office building, Metropolitan area network (MAN) connects LANs in city or town, wide area network (WAN) is network that covers large geographic area using many types of media and Internet is world’s largest WAN. Network topology: Bus networks are all computers and devices connect to central cable, or bus. It is easy to implement, but has Bus traffic, Bus failure. Ring networks are cable forms closed ring, or loop, with all computers and devices arranged along ring, can span a long distance and disadvantage is one node fail, all network down. Star networks are all devices connect to a central device, called hub. It is easy to install and disadvantage: If the hub fails, the network becomes inoperable. Communication software includes programs that help users establish connection to Internet, other network, or another computer; programs that help users manage transmission of data, instructions, and information; and programs that provide an interface for users to communicate with one another. Router connects computers and transmits data to correct destination on network Routers forward data on Internet using fastest available path. Hub is device that provides central point for cables in network. Channel is Transmission media on which data travels in communications system. Transmission media are materials capable of carrying one or more signals. Bandwidth is amount of data that can travel over channel. For the best performance of a communications channel bandwidth should be high, latency should be low. Physical transmission media is wire, cable, and other tangible materials used to send communications signals. Features of fiber-optic cable: Fast, expensive, more secure, smaller size, hard to install Microwave transmission, sometimes called fixed-point wireless, involves sending signals from one microwave station to another. Client/server network: One or more computers act as server and other computers, or clients, access servers, can support more than 10 computers. Peer-to-peer network is simple network that connects fewer than 10 computers and each computer, or peer, has equal capabilities. ISDN and DSL are communications devices that send and receive digital ISDN and DSL signals. For the small business and home user, an ISDN line provides faster transfer rates than dial-up telephone lines, but ISDN requires that both ends of the connection have an ISDN modem. Bluetooth is short-range radio waves transmit data between Bluetooth devices (0 to 10meters). IrDA specification allows data to be transferred wirelessly via infrared light waves (0 to1 meter). Communication satellite is space station that receives microwave signals from earthbased station, amplifies signals, and broadcasts signals back to any number of earth-based stations. Transmission from a satellite to an earth-based station is downlink, transmission from an earth-based station to a satellite is uplink.