Marketing Exam 2 pre.. - Jeeves Green Computer Repair Service
advertisement

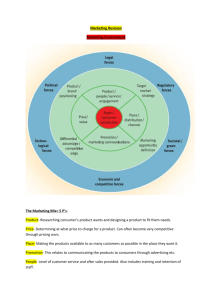
Steven Green CH 5,6,7,9 Marketing Exam 2 prep Ch 5 Gross domestic product (GDP) – The total market value of all goods and services provided in a country’s economy in a year by both residents and nonresidents of that country BirthRate – The number of babies per 1,000 people Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) – an integrated economic and social unit with a large population nucleus Real income – income that is adjusted to make out the effects of inflation on purchasing power Disposable income – income that is left after taxes Discretionary income – whatever is left of disposable income after paying for necessities Empty nesters – people whose children are grown up and who are now able to spend their money in other ways. Senior citizens – people over 65 Ch 6 Economic buyers – people who know all the facts and logically compare the choices to get the greatest satisfaction from spending their time and money Economic needs – Needs concerned with making the best use of a consumer’s time and money – as the customer judges it. Needs – the basic forces that motivate a person to do something Wants – needs that are learned during a person’s life Drive – a strong stimulus that encourages action to reduce a need Physiological needs – Biological needs such as the need for food, drink, water, rest, sex…ect Safety needs – needs concerned with protection and physical well-being Personal needs – an individual’s need for personal satisfaction unrelated to what others think or do Perception – how we gather and interpret information from the world around us Selective exposure – our eyes and mind seek out and notice only information that interests us Selective perception – people screen our or modify ideas, messages, and information that conflict with previously learned attitudes and beliefs Selective retention – people remember only what they want to remember Learning – a change in a person’s thought process caused by prior experience Cues – Products, signs, ads, and other stimuli in the environment Response – an effort to satisfy a drive Reinforcement – occurs in the learning process when the consumer’s response is followed by satisfaction – that is, reduction in the drive Attitude – a person’s point of view toward something. Belief – a person’s opinion about something Expectation – an outcome or event that that a person anticipates or looks forward to. Psychographics – the analysis of a person’s day-to-day pattern of living as expressed in that person’s activities, interests, and opinions – sometimes referred to as AIOs or lifestyle analysis Lifestyle analysis – same as psychographics Social class – a group of people who have approximately equal social positions as viewed by others in the society Reference group – the people to whom an individual looks when forming attitudes about a particular topic Opinion leader – a person who influences others Culture – the whole set of beliefs, attitudes, and ways of doing things of a reasonably homogeneous set of people Extensive problem solving - the type of problem solving consumers use for a completely new or important need – when they put much effort into deciding how to satisfy it. Limited problem solving – when a consumer is willing to put some effort into deciding the best way to satisfy a need Routinized response behavior – when consumers regularly select a particular way of satisfying a need when it occurs Low-involvement purchases – purchases that have little importance or relevance for the consumer Dissonance – tension caused by uncertainty bout the rightness of a decision Adoption process – the steps individuals go through on the way to accepting or rejecting a new idea Ch 7 Business and organizational customers – any buyers who by for resale or to produce other goods and services Purchasing specifications – a written (or electronic) description of what the firm wants to buy ISO 9000 – a way for a supplier to document its quality procedures according to internationally recognized standards Purchasing managers – buying specialists for their employers Multiple buying influences – several people share in making a purchase decision – perhaps even top management Buying center – all the people who participate in or influence a purchase Vendor analysis – formal rating of suppliers on all relevant areas of performance Requisition – a request to buy something New-task buying – when an organization has a new need and the buyer wants a great deak of information Straight rebuy – a routine repurchase that may have been made many times before Modified rebuy – the in-between process where some review of the buying situation is done --- though not as much as in new-task buying or as little as in straight rebuys Competitive bid – terms of sale offered by different suppliers in response to the buyer’s purchase specifications Just-in-time delivery – reliably getting products there just before the customer needs them Negotiated contract buying – agreeing to a contract that allows for changes in the purchase arrangements Outsourced – when the buying organization chooses to contract with an outside firm to produce goods or services rather then producing them internally North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes – codes used to identify groups of firms in similar lines of business Open to buy – a buyer has budgeted funds that he can spend during the current time period Resident buyers – independent buying agents who work in central markets for several retailer or wholesaler customers based in outlying areas or other countries Foreign Corrupt Practices Act – a law passed by the US Congress in 1977 that prohibits US firms from paying bribes to foreign officials Ch 9 Product – Quality – Product assortment – Product line – Individual product – Branding – Trademark – Service mark – Brand familiarity – Brand rejection – Brand non-recognition – Brand recognition – Brand preference – Brand equity – Lanham Act – Family brand – Licensed brand – Individual brands – Generic products – Manufactured brands – Dealer brands – Private brands – Battle of the brands – Packaging – Universal product code (UPC) – Federal Fair Packaging and Labeling Act – Warranty – Magnuson-Moss Act – Consumer products – Business products – Convenience products – Staples – Impulse products – Emergency products – Shopping products – Homogeneous shopping products – Heterogeneous shopping products – Specialty products – Unsought products – New unsought products – Regularly unsought products – Derived demand – Expense item – Capital item – Installations – Accessories – Raw materials – Farm products – Natural products – Components – Supplies – Professional services -