Chapter 6
advertisement

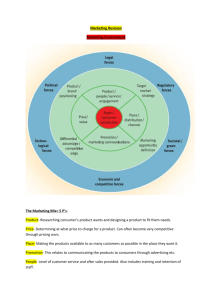
Define the business market and explain how business markets differ from consumer markets Identify the major factors that influence business buyer behavior List and define the steps in the business buying decision process Compare the institutional and government markets and explain how institutional and government buyers make their buying decisions Market Structure and Demand Nature of the Buying Unit Types of Decisions and the Decision Process Nature of the Buying Unit Types of Decisions and the Decision Process Let’s look at Dow Plastics straight rebuy modified rebuy new task Users Influencers Buyers Deciders Gatekeepers Most B-to-B marketers recognize that emotion plays an important role in business buying decisions Environmental Factors Organizational Factors Interpersonal Factors Individual Factors “When doing business in a foreign country and a foreign culture—particularly a nonWestern culture—assume nothing,” “Take nothing for granted. Turn every stone. Ask every question. Dig into every detail. Because cultures really are different, and those differences can have a major impact.” Business-to-business e-procurement yields many benefits. First, it shaves transaction costs and results in more efficient purchasing for both buyers and suppliers. Reduces the time between order and delivery. And a Web-powered purchasing program eliminates the paperwork associated with traditional requisition and ordering procedures and helps an organization keep better track of all purchases. Frees purchasing people from a lot of drudgery and paperwork. Sources suppliers to reduce costs and develop new products Institutional market consists of schools, hospitals, nursing homes, prisons, and other institutions that provide goods and services to people in their care. In the United States federal, state, and local governments contain more than 82,000 buying units that purchase more than $1 trillion in goods and services each year A deeper look at the marketing mix: the tactical tools that marketers use to implement their strategies and deliver superior customer value. Define product and the major classifications of products and services Describe the decisions companies make regarding their individual products and services, product lines, and product mixes Identify the four characteristics that affect the marketing of services and the additional marketing considerations that services require Discuss branding strategy—the decisions companies make in building and managing their brands Levels of Product and Services Consumer products Convenience products Shopping products Specialty products Unsought products Materials and parts include raw materials and manufactured materials and parts Person marketing Place marketing Ideas Social marketing Product Quality Product Features Product Style and Design Branding helps buyers in many ways. Brand names help consumers identify products that might benefit them. Brands also say something about product quality and consistency—buyers who always buy the same brand know that they will get the same features, benefits, and quality each time they buy Labeling Product Support Services Product Line Decisions Product Mix Decisions The Nature and Characteristics of a Service Brand Equity Brand Positioning