pH calculations
advertisement

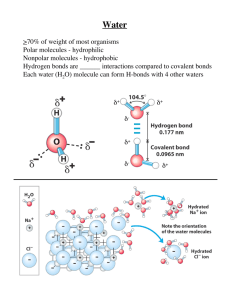
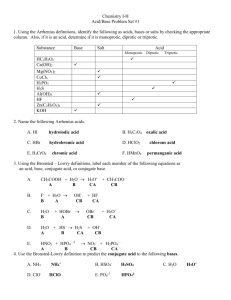
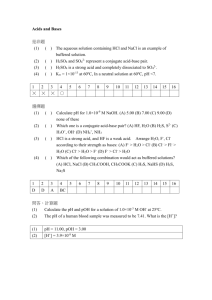
A Brief summary of pH calculations: 1. pH = -log[H3O+] pK = -logK pOH = -log[OH-] pKw = logKw = 14 lower case p means -log 2. H2O + H2O ⇆ H3O+ + OHKw = 1 x 10-14 = [H3O+][OH-] pKw = 14 = pH + pOH 3. Common strong acids: Common strong bases: HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4 LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2, NaNH2, CH3ONa What’s the pH of 0.1 M HCl? -log(0.1) = 1 What’s the pH of 0,1 M H2SO4? -log(0.1 x 2) = 0.7 What’s the pH of 0.1 M Ba(OH)2? pOH = -log(0.1 x 2) = 0.7. pH = 14 – 0.7 = 13.3 4. For any weak acid HA and its conjugate weak base AHA + H2O ⇆ A- + H3O+ Ka = [A- ][H3O+]/[HA] << 1 pKa = -logKa A- + H2O ⇆ HA + OH- Kb = [HA][OH-]/[A-] << 1 pKb = -logKb pKa + pKb = pKw FOR A PURE WEAK ACID IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION: pH ≅ pKa + p[HA] 2 FOR A PURE WEAK BASE IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION: pOH ≅ pKb + p[A-] . . 2 remember to convert pKa to pKb and pOH to pH if that’s what the question asks for! FOR A MIXTURE OF A WEAK ACID AND ITS CONJUGATE BASE: pH = pKa + log[A-]/[HA] FOR A MIXTURE OF A WEAK ACID AND A CONJUGATE BASE pOH = pKb + log[HA]/[A-] pH calculations: Find the pH of any weak acid, HA, anywhere along the titration curve. 1. A pure weak acid, HA: HA + H2O ⇄ A- + H3O+ H2O + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + OH- pH ≈ pKa + p[HA] 2 2. Somewhere along the curve: A mixture of HA and AHA + OH- ⇄ A- + H2O HA + H2O ⇄ A- + H3O+ H2O + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + OH- Moles HAeq = moles HAstart - moles OH- added Moles A-eq = moles OH- added pH = pKa + log[A-]/[HA] In this case, pH = pKa + log (0.25/0.75) 3. Half-way through the titration: Equal concentrations of HA and AHA + OH- ⇄ A- + H2O HA + H2O ⇄ A- + H3O+ H2O + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + OH- Moles HAeq = Moles A-eq pH = pKa + log[A-]/[HA] = pKa + log(1) = pKa 4. Somewhere along the curve: A mixture of HA and AHA + OH- ⇄ A- + H2O HA + H2O ⇄ A- + H3O+ H2O + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + OH- Moles HAeq = moles HAstart - moles OH- added Moles A-eq = moles OH- added pH = pKa + log[A-]/[HA] In this case, pH = pKa + log (0.75/0.25) 5. At the endpoint. A- + H2O PURE A- ⇄ HA + OH- H2O + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + OH- Ka x Kb = Kw pKa + pKb = pKw = 14.0 pOH = pKb + p[A-] 2 pH = pKw – pOH [H3O+] = 10-pH For a mixture of weak base and weak acid: A- + H2O ⇄ HA + OH- H2O + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + OH- pOH = pKb + log[HA]/[A-] How can you spot weak acids or weak bases? 1. Weak acids/bases are not in the short list of strong acids (HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4) or strong bases (LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2, CH3ONa) 2. Weak acids/bases will usually have the pKa listed. Since the Ka of a strong acid is >> 1, (and pKa is a negative number ) it is assumed that strong acids dissociate virtually 100% in water.