AEC 2102 4206 RURAL DEVELOPMENT
advertisement

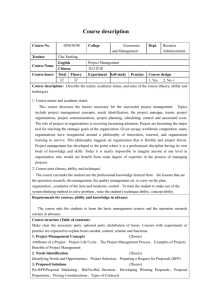
AEC 2102 4206 RURAL DEVELOPMENT 2. INSTRUCTOR(s): ASS. PROF. THEODORA SHUWU HYUHA(BA Economics, Simon Fraser University, British Columbia, Canada, Msc. Agricultural Economics, University Alberta, Edmonton, Canada and PhD, Makerere University, Uganda.) 3. COURSE TYPE: ELECTIVE (BSC AGRIC 1V, BAEE, BSC FORESTRY, BA RURAL ECONOMY AND ABM 11). 4. COURSE STRUCTURE (Credit Units: 30 lecture hours and 15 tutorial hours) 5. COURSE DESCRIPTION: Rural development encompasses a range of issues and hence, it is not possible to cover them all in one semester. Therefore, a selection of topics will be made for this session. The topics will include: meaning of development and rural development, theories of economic and rural Development, Approaches to Rural Development and theories of Agricultural Development and belief appraisal of approaches adopted to effect rural development. 6. COURSE OBJECTIVES: General objective The main objective of this course is to introduce students to some theories of rural and agriculture development. At the end of the course the student should be able to appreciate the past and current efforts taken in Uganda to effect rural development and appraise its relevance in the current Uganda in order to contribute positively to rural transformation. Specific Objective To provide students with a range of theories propounded in the past suggesting multiple paths to development. To make students appreciate different strategies countries confronted with rural underdevelopment can take to get out of vicious circle poverty. To make students better prepared to work in rural areas. 7. SELECTED REFERENCES Chambers, R (1989). Rural Development, Putting the Last First. Essex: Longman Group of Companies. Hayami Y. and Luttan V.W, (1985). Agricultural Development Baltimore: The John Hopkins University Press. Todaro, M, (1994), Economics for Developing World, an introduction to Principles, Problems and Policies for Development, London: Longman. Meier, G.M. (1995) Leading Issues in Economic Development, 6th Edition. Tomich, T.P.; Kilby P, and Johnson B. F. (1995). Transforming Agrarian Economies Opportunities Seized, Opportunities Missed. Ithaca: Cornell University Press Stevens, R, D and Jabara, C. L. (1988). Agricultural Development Principles, Economic Theory and Empirical Evidence. 8. COURSE CONTENT, METHODS OF INSTRUCTION, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED TOPIC CONTENT METHOD OF TOOLS/ INSTRUCTION/ EQUIPMENT TIME ALLOCATED NEEDED 1.Meaning of Lecture Chalk/ Markers/ What is development Development 3hours LCD/Laptop Core values of development Framework of underdevelopment 2.Meaning of Rural Interactive Lecture Chalk/ Markers/ Definition Development 3hours LCD/Laptop 3.Nature and causes of rural development 4.Theories Economic development of 5.Theories Economic development 6.Ruralmigration of urban 7.Popualation Issues 8. Population issues 9.Theories Agricultural Development of 10Theories Agricultural Development of How outsiders view rural poverty Who is poor Causes of rural poor Integrated rural poverty Growth stage theories (Rostow’s five -stage theories). Leading sector model Dualistic models(sociological dualism) Dualistic models (Dynamic dualism(Arthur Lewis’s model, FeiRannis and Jogenson) Fei-Rannis model Jorgenson An expected income model of rural urban migration. Generalized theory of rural -urban migration Policy implications for rural development Why study population Structure of Population in LDCs and Uganda and its implication on development Interactive Lecture Chalk/ Markers/ 2hours LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hour Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours The diffusion model The Schultz High-payoff Tutorial 1hour Input model Investment in Human capacity Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Theory of demographic transition Malthusian population trap The role of Agriculture in development The Resource Exploitation model Conservation model The Location model 11 Theories of Institutional Change 13 Approaches to Rural development 14 Approaches to Rural development 15 Course 16-17 Induced Innovation in Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Agriculture Mechanism of inducement in both public institution (research centres) Complete model of Induced innovation Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Lecture 2hours Tutorial 1hour Chalk/ Markers/ LCD/Laptop Different paths to agricultural transformation ( Japan and USA) Community Development Integrated rural development Decentralization Continuous Course assessment quizzes 3 Continuous Course paper assessment quizzes 3 Revision time Final Exam 9. SUMMARY OF TIME NEEDED Lectures 30 Hours Tutorials 15 Hours 10. COURSE ASSESSMENT Continuous There will be 3 quizzes arising from lectures and 20% Assessment(quizzes) tutorials During week 5, 8 and 13 Midterm 20% University Exam Final Exam in 16-17 60% Electives (At least one relevant course) FOM 4201 LAND USE POLICY & LAW - MISSING