The main source of energy for life is the sun
advertisement

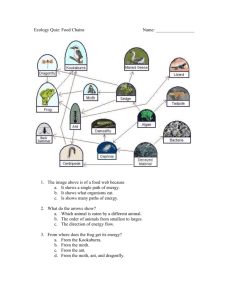
The main source of energy for life is the sun. The energy flow in an ecosystem is quite complex. Organisms give off different amounts of energy depending on their level in the energy pyramid. Plants are organisms that use the energy from the sun to make energy rich compounds. These plants are known as producers, or autotrophs, which are organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis. Some examples of producers are grasses, shrubs, trees and aquatic, photosynthetic plants. Energy is transferred to the next level when the plants are eaten by heterotrophs. These organisms cannot make their own food, and have to consume other organisms in order to get energy. These organisms are classified as herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. A couple examples of herbivores are deer, turtle, and fish. These first order heterotrophs, or herbivores, are eaten by second order heterotrophs, or carnivores, which only feed on meat or first order heterotrophs. Carnivores can be animals such as lions, bears, snakes, and tigers. The third order heterotrophs eat plants as well as animals. These organisms are called omnivores. Omnivores are for the most part people. Finally, all the organisms are broken down by decomposers like bacteria and fungi which help release nutrients back into the ecosystem. Through every step of this process the energy that is transferred is 90% less than the last time. This is known as the rule of 90. The energy is lost because of heat and other processes that drain the energy from the organism. The most energy starts with the plants and the least is with the third order heterotrophs. Since the Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be lost nor gained, the energy that is not transferred to the next level is changed into heat energy when it enters the environment. An easy way to show how energy moves through an ecosystem is known as a food chain. Each organism in a food chain represents a trophic level, or a feeding step. A way to show all the possible feeding relationships between animals and plants in different biomes, is called a food web. By: Kyle Gresh, Gina Medbery, Tyler Mench