Ecology Powerpoint
advertisement

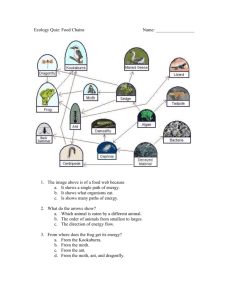
Chapters 3-6: Ecology Ecology • study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environment Biosphere • Part of the Earth that holds all living things • Air, land, and sea • Living things affected by nonliving and living things • Abiotic factors – Nonliving parts of an environment – Temperature, moisture, light, soil…etc • Biotic factors – All living organisms that inhabit an environment – Plants, other animals – Depend on others directly or indirectly • Food, shelter, reproduction, protection Levels of Organization • Organisms make up population – Group of organisms of the same species – Interbreed and live in the same area – Can compete for food, water, mates • # of populations make up community –Made up of interacting populations –Change in a population can affect entire community • Populations + abiotic factors make up ecosystem – Terrestrial (land): forests, meadows – Aquatic (water): oceans, lakes, ponds, rivers • Niche: all the ways and • Habitat: place adaptations a species where an organism uses in its environment lives • How it meets its • Can change or needs for food, disappear shelter, survival, because of reproduction natural and – Biotic + abiotic parts human causes of the environment Predation • consumers • Eat plants and animals • Eat prey (animals that predators eat) • Fight for survival Symbiosis • Relationship where there is a close and permanent association between different organisms • Means “living together” • 3 kinds Mutualism • Both species benefit (+,+) Commensalism • one benefits and the other does not benefit or is harmed (+,o) Parasitism • one benefits and the other is harmed (+,-) How Organisms Get Energy • Sun is the ultimate form of energy and source for energy • Producers: autotrophs –Uses light to make own food (photosynthesis) and energy • Ex: grass, trees, green algae Consumers • Heterotrophs • Eat other organisms to get energy • CANNOT make its own food Herbivores • Only eat plants Carnivores • Only eat animals Omnivores • Eat both plants and animals Scavengers • Eat on dead organisms Decomposers • break down and release nutrients from dead organisms Flow of Matter and Energy • You consume matter when you eat food –Carbon, nitrogen, other elements • Energy flows through levels of the entire ecosystem –Only some energy is transferred from 1 energy level to the next Food Chains • show how matter and energy move through an ecosystem – Nutrients and energy move from autotrophs to heterotrophs and then decomposers – Ex: grass rabbit wolf – Arrows indicate the direction energy is transferred from one organism to the next Ecological Pyramid • shows how energy flows through an ecosystem – Energy that is transferred from one trophic level to the next is only 10% Trophic Level • A feeding step in passing of energy and materials Heterotroph Heterotroph Herbivore Autotroph Food Webs • all the possible relationships at each trophic level of a community Chapter 3-6 Review #1: 1. Which of the following types of heterotrophs eat other animals? a. omnivores & carnivores c. carnivores only b. herbivores & omnivores d. carnivores & herbivores 2. Which of the following types of heterotrophs would bacteria and fungi be classified as? a. detritivores b. herbivores c. carnivores d. decomposers 3. What is the one-way flow of energy in an ecosystem called? a. food chain b. energy pyramid c. food web d. biomass pyramid 4. What is each step in a food chain or food web called? Limiting Factors • Affect an organism’s ability to survive in its environment • Ex: water, food, predators, temperature • Density-dependent: disease, competition, parasites, food – Depend on the density of a population • Density-independent: affects all populations regardless of their density – Temperature, storms, floods, drought, and habitat disruption Succession • Natural changes and species replacement that takes place in communities in an ecosystem – Occurs in stages • Primary succession – Colonizing bare land where there are no organisms – Pioneer species: 1st species in an area Climax Community • Stable, mature community that has little or no changes in species Secondary Succession • Changes that occur when existing community is disrupted by natural disasters or human actions Biomes • Large group of ecosystems that share the same type of climax community • Terrestrial or aquatic – Aquatic: marine, estuaries, freshwater, swamps – Terrestrial: tundra, taiga, desert, grassland, rain forest, temperate forest Population Growth • Organisms can grow exponentially • Exponential growth: as a population gets larger, it also grows faster – J-shaped curve (diagram): • Growth will be limited at some point by limiting factors • Food availability, disease (ex: AIDS, influenza, TB, Dutch Elm disease, Pfiesteria), predators, lack of space • Results in an S-shaped curve • Diagram: • Carrying capacity: the number of organisms of a species that an environment can hold Define these terms: • Birth rate • Death rate • Emigration • Immigration • Zero population growth Biological Diversity • Biodiversity: the variety of species in a specific area • Loss of biodiversity is increasing • Extinction: disappearance of a species when the last organism dies • Ex: • Endangered species: # of species become low that can lead to extinction • Ex: • Threatened species: population likely to become endangered • Ex: Cycles in Nature • Matter is constantly being recycled Water Cycle • Water evaporates from lakes and oceans to become water vapor in the air • Water vapor in the air condenses to form clouds • More water condensation leads to precipitation, falling as rain, ice, or snow back to the ground • Cycle repeats constantly • Problems with the cycle: Carbon Cycle • Starts with autotrophs – Makes carbon molecules from CO2 during photosynthesis • Heterotrophs feed on autotrophs, getting those carbon molecules • Release CO2 back into the atmosphere Problems with Cycle • Global Warming: –Greenhouse effect –Gases that lead to global warming Nitrogen Cycle • Lightning and some bacteria convert nitrogen in the air into a usable form • Plants use nitrogen to make proteins • Herbivores eat plants – Convert nitrogen-containing plant proteins into animal proteins • Humans eat plants – Convert animal proteins to human proteins • Excess nitrogen in animals released in urine – Returned to water or soil • Nitrogen molecules return to the soil when animals die – Re-used by plants – Bacteria put nitrogen back into the air Phosphorous Cycle • All organisms need phosphorus for growth and development • Plants get phosphorus from the soil • Animals get phosphorus by eating plants –Decompose when they die, returning phosphorus to the soil Problems: • Eutrophication Impact of Human Activities on the Environment • Population growth • Pollution • Global warming • Burning fossil fuels • Habitat destruction • Introducing nonnative species Chapter 3-6 Review #2: 1. A lone elephant joining another herd of elephants is an example of a. emigration c. immigration b. parasitism d. exponential growth 2. What term is used to describe a species whose population is rapidly shrinking and might disappear completely? a. endangered c. extinct b. threatened d. invasive