Unit 2 Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
advertisement

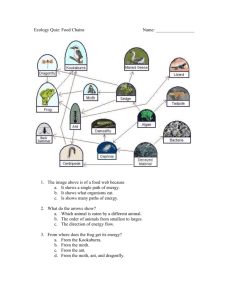
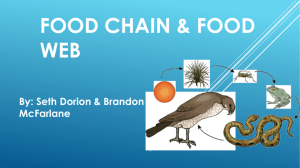
Principles of Ecology Unit 2 Chapter 2 What is ecology? Ecology: study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environment Biosphere the portion of the Earth that supports living things Ex: ocean, forest, atmosphere. Abiotic vs. Biotic factors Abiotic = nonliving parts of the environment Ex: light, air, temperature, soil Biotic = living parts of the environment Ex: bacteria, protist, fungus, plant, animal Levels of organization from smallest to largest Individual Population Community Ecosystem Individual made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows, and develops Population group of organisms all of the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time Community interacting populations in a certain area at a certain time Ecosystem interacting communities and abiotic factors Habitat vs. Niche Habitat: place where organism lives Niche: role or position a species has in its environment Habitats are capable of changing. What can lead to changes in habitats? Symbiosis: interactions between two species Mutualism: both benefits Commensalism: one benefits, the other unaffected Parasitism: one benefits, one is harmed Mutualism Clownfish is protected, while providing a lure for the anemone. Some say that this relationship can be commensalistic. Commensalism Volcano sponge using the crinoid sponge as a “lift” for increased filtration but the crinoid sponge is unaffected. Parasitism Head lice How organisms obtain energy Autotroph (producer): photosynthetic or chemosynthetic, makes own food Heterotroph (consumer): “eat” other organisms, cannot make own food Decomposer: breaks down dead or decaying organisms, recycles matter Autotroph Heterotrophs - scavengers Scavengers: feed off of dead or decaying living things but do not recycle matter back into the ecosystem Heterotrophs - herbivores consume only vegetative matter mostly primary consumers. Heterotrophs - carnivores obtain energy from eating other consumers Secondary and tertiary consumers Decomposers Typical examples: fungus and bacteria Food chain shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem (one route) berries → mice → black bear Food web shows interactions between organisms (all possible routes) Energy pyramid Pyramid of Energy Heat Shows how much energy is available at each trophic (energy) level Heat 0.1% Consumers 1% Consumers 10% Consumers Heat Heat Autotrophs Third-order heterotrophs First-order heterotrophs Second-order heterotrophs Decomposers Four cycles in nature Water cycle Carbon cycle Nitrogen cycle Phosphorus cycle Water cycle Carbon cycle Nitrogen cycle Phosphorus cycle