Fetal Pig Dissection prelab
advertisement

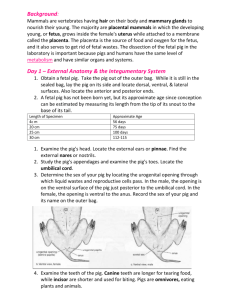
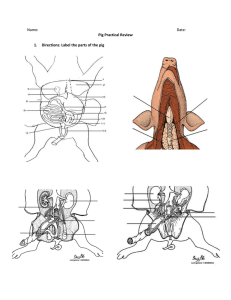
Fetal Pig Dissection Pre-Lab Name___________________________ How old is your pig? The age of a fetal pig is determined by its length. Measure body length along the back following the spine from the tip of the snout to the start of the tail. Length of Fetus cm mm 1.1 11 1.7 17 2.8 28 Approximate Age (days) 21 35 49 Length of Fetus cm mm 4.0 40 22.0 220 30.0 300 Approximate Age (days) 56 100 Full Term 112-115 Our fetal pig measures ________ cm (_______ mm) in length. It seems to be approximately _______ days old. 1. 2. Why do you think we are dissecting pigs while we are studying the human body? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Use the Internet to determine the taxonomy of the fetal pig and a human: Fetal Pig Human Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species 4. Pigs and humans are both mammals. What are two major characteristics that set mammals apart from other classes of vertebrates? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Use the internet to determine whether pigs and humans are quadrupeds or bipeds. Pigs: ______________________ Humans: ________________________ 6. Look at the pig in the bag. Record at least six observations. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 7. How many toes are present on each foot? ___________________________________________ 8. Are the hooves split or fused? _____________________________________________________ 9. What is the sex of your fetal pig? How do you know? ___________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Label Figure 1 and Figure 2: Anatomical Terminology Directions or Positions Anterior (Cranial) Posterior (Caudal) Dorsal (Superior) Ventral (Inferior) Lateral Medial Proximal toward the head toward the tail toward the backbone toward the belly toward the side toward the midline lying near the point of reference Planes or Sections Through the Body Transverse (Cross Section) Sagittal Frontal (Coronal) perpendicular to the long axis of the body a longitudinal section separating the body into right and left sides a longitudinal section dividing specimen into dorsal & ventral parts