AP Biology Chapter 27 Worksheets
advertisement

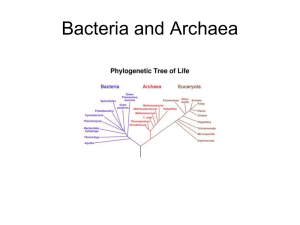
AP Biology Chapter 27 Worksheets Parts A-D 1. Give the 2 major branches of prokaryote evolution. 2. Explain the difference between the 2 branches. 3. Explain what a domain it and give the 2 prokaryote domains. 4. Explain what a colony is and the 3 most common shapes of prokaryotes. 5. What function does the cell wall have in prokaryotes? 6. What material makes up the cell wall of a prokaryote? Explain its structure…..do archaea have it? 7. Explain what a gram stain is, and the difference between gram positive and gram negative bacteria. 8. Explain what a lipopolysaccharide is and where it is found. 9. What are some characteristics of gram negative pathogenic bacteria? 10. Explain how anti-biotics work. 11. Explain the function of a capsule. 12. Explain what a pili is and its function. 13. Give the three methods of motility in prokaryotes. 14. Explain chemotaxis (positive and negative) and phototaxis. 15. Explain the structural differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 16. From a DNA standpoint how are they different? 17. Explain what a plasmid is. Do prokaryotes need them? Explain 18. Are all ribosomes the same? Explain 19. Do these differences help prokaryotes? Explain 20. Explain what binary fission is. 21. Explain the terms, transformation, conjugation and transduction. 22. How does a lack of meiosis help prokaryotes? 23. How do prokaryotes compete for space and nutrients? 24. Give the 4 categories of prokaryotes and how they are different. 25. Explain what a parasite is and give an example. 26. Explain what a saprobe is and give an example. 27. In terms of nitrogen, contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 28. Explain what nitrogen fixation is. 29. Explain the difference between aerobic bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. 30. Explain the difference between obligate and facultative anaerobes. 31. Summarize the probable evolution of photosynthesis. 32. How does the evolution of cyanobacteria coincide with the development of atmospheric oxygen? 33. How did the evolution of cyanobacteria change the earth? Section E 1. Explain how prokaryotes are classified based on molecular systematics. 2. Explain what a signature sequence is and how they are used. 3. Explain why phenotypic characters are poor ways to classify prokaryotes. 4. Explain what an SSU-rRNA comparison is. 5. In terms of lineage how are archae, prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms related? 6. Give at least 3 characteristics of archaebacteria. 7. Explain what an extremophile is and give a couple of examples. 8. Explain what a methanogen is and where they live. 9. Explain what halophile is and where they live. 10. Explain what bacteriorhodopsin is and how its formed. 11. Explain what a thermophile is and an example of where they live. 12. Give 2 new categories of prokaryotes and their characteristics. 13. Outline some of the unique metabolic capabilities of prokaryotes. 14. Explain what symbiosis, commensalisms, parasitism and mutualism are. 15. Explain what an opportunistic pathogen is. 16. Explain Koch’s work. 17. List Koch’s 4 postulates. 18. How do most pathogens cause illness? 19. Explain what an exotoxin is and give a couple of examples. 20. Explain what an endotoxin is and a couple of examples. 21. Where do most of our antibiotics come from? 22. Explain what lyme disease is, what causes it and how its treated. 23. Explain why bacteria are so antibiotic resistant in modern society. 24. Explain what bioremediation is. 25. How are bacteria used as metabolic factories?