Module B1: The Statistical System
advertisement

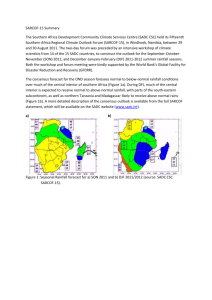
Basic Module B1 Module B1: The Statistical System Synopsis This module provides an overview of statistics as a discipline and its application within the National Statistical System (NSS) in your country. It also introduces students to different data collection techniques through the study of how data are collected to generate statistics that are used to help in decision making. Objectives The National Statistical System Successful students will Be familiar with the functions of the National Statistical Office and relevant parts of other institutions that make up the National Statistical System in their country. Be aware of the content of the National Statistical Act in their country. Be able to find statistical information about their country. Be aware of the main statistical series that are produced in their country, the methods used to collect them, the frequency of the collections, and their uses. Statistics Successful students will: Be able to explain what is statistics as a discipline Be able to explain the importance of statistical information for decision making at local, national and international level. Be able to explain what should happen at different stages of the cycle of statistical production including: specific definition of information needs, design of data collection, data gathering, data management, data processing and data presentation. Data collection Successful students will SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 1 Basic Module B1 Be able to explain the differences between data collection techniques including census, surveys and experiments. Be able to choose an appropriate data collection technique depending on the objectives of the collection. Be able to identify the likely errors and their sources in data collection Be able to propose options for reducing the incidence of errors during data collection. Be able to write simple field reports describing the experience of a data collection exercise. Expected outcome Successful students will have awareness of the work carried out by the different institutions that form the National Statistical System in their country. They will be able to find information and help others finding information available to the general public. Students will have an appreciation of the practical uses of local, regional and national statistics as an important element in decision making. Pre-requisites Enthusiasm SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 2 Basic Module B1 Contents Part A: The National Statistical System Successful students will: Be familiar with the functions of the National Statistical Office and relevant parts of other institutions that make up the National Statistical System in their country. Be aware of the content of the National Statistical Act in their country. Be able to find statistical information about their country. Be aware of the main statistical series that are produced in their country, the methods used to collect them, the frequency of the collections, and their uses. Session 1. Examples of Statistics At the end of this session students will be able to: List a minimum of 10 areas of application of statistics in their country Explain how statistics is used to promote development Give examples of how such statistics are used in his/her country Session 2. The role of statistics in Evidence Based Policy Making At the end of this session students will be able to: Explain the role of statistics in evidence-based policy-making. Give examples of uses of statistics for evidence-based policy-making at different levels Session 3. The National Statistical System: At the end of this session students will be able to: Explain what is statistics Explain what is the National Statistical System (NSS) Explain what is the composition of the NSS in their country Explain what is the National Strategy for the Development of Statistics (NSDS) Explain what are the essential components of a NSDS SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 3 Basic Module B1 Session 4a. The NSO, the National Statistics Act At the end of the session students will be able to: Locate and summarise salient features of the Statistics Act of their country Define the functions of the National Statistical Office as defined in the Statistics Act Identify the competences of the National Statistical Office from the Statistics Act Make comparisons of the Statistics Acts of the member states of SADC Session 4b. The 10 Principles of Official Statistics At the end of the session, students will be able to: List the 10 Principles of Official Statistics Assess how their country has implemented the 10 Principles of Official Statistics and compare that with what has happened in other member states of SADC Part B: Statistics in Practice Session 5. The Swaziland Agricultural Survey as an example of a large national survey At the end of this session students will be able to: Explain what is the Swaziland Agricultural Survey Describe how the data for the SAS is collected and how often is collected Explain the way that the SAS is organised throughout the year Explain how fields are selected for the crop cutting survey Describe how the results of the survey are used Give examples of three national scale surveys that are carried out regularly in their own country Session 6. CPI as an example of a regular data collection At the of this session students will be able to: Describe the CPI, and its uses Discuss some of the issues that affect the compilation and calculation of the CPI Calculate the inflation rate SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 4 Basic Module B1 Find the latest national data Explain how it is compiled Session 7. Climate variability and change At the end of this session, you will be able to: Explain why climate issues are included in this statistics course Relate issues of climate change and climate variability to risk assessment and productivity in agriculture Understand the data requirements for a climate variability/change problem concerning planting dates Interpret a graph of planting dates to begin to assess the evidence for climate change Explain what role, if any, they can play in the climate debate Session 8. Using alternative energy for cooking At the end of this session, you will be able to: Explain the potential importance of solar energy in Africa Explain the potential importance of solar cooking Describe a case study of solar cooking Identify aspects of the adoption of solar cooking where statistical skills are useful Explain whether aspects of solar cooking are useful locally Session 9: School enrolment and the MDGs At the end of this session students will be able to: State at least 3 of the MDGs State at least 1 indicator corresponding to education issues Identify the difference between a census and a sample Give objectives for the education census both in relation to the MDGs and to other needs of the country. Provide at least 2 other examples where a country routinely collects administrative data that is also used for statistical purposes. Identify the information needed from the survey for Indicator 6 of the MDGs Session 10. Statistics on Business At the end of this session students will be able to: Explain why business statistics are important SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 5 Basic Module B1 Discuss the difficulties in counting businesses Define the meaning of value added Identify key points in a table of business statistics Part C: Methods used for collecting data Session 11. Methods used for collecting data and the data cycle At the end of this session students will be able to: Describe the data cycle Define what is a census Define what is a survey Define what is an experiment List the main characteristics of a survey, a census and an experiment Choose between the use of a census, a survey or an experiment depending on the characteristics of the study at hand Session 12. Ask the right questions in the right way At the end of this session students will be able to Write simple questions following good practice recommendation in writing questions for questionnaires Session 13. Qualitative methods for data collection At the end of this session, participants will be able to Argue the case for an integrated approach to evidence gathering that combines qualitative and quantitative approaches Discuss the importance of participatory methods as one of the approaches that has become part of the mainstream of the methods used for gathering evidence Session 14. Choosing an appropriate methods for data collection At the end of this session, participants will be able to Explain how the objectives of a study determine the choice of a suitable method for data collection SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 6 Basic Module B1 Give examples of when a survey, a census, and experiement, a qualitative study or a combination of any of these are appropriate methods for data collection Part D: Special topics Session 15. Identifying and reducing sources of error in data collection At the end of the session students will be able to: Explain that data collected through surveys and censuses is not perfect but prone to errors. Identify the two types of errors in statistical data. Identify the sources of the two types of errors. Propose methods of minimising or reducing the incidence of errors in statistical data. Provide the necessary information to users and producers of statistics on the quality and limitations of survey data. Session 16. Rules for enumerators At the end of the session students will be able to: Explain the importance of an enumerator in the Statistical Data Collection process List the equipment required by enumerators in field work operations Identify the desirable characteristics of a good enumerator, and Explain how enumerators should behave in the execution of their duties Session 17. Developing skills to capture errors in data At the end of the session students will be able to: Explain the importance of an enumerator in the Statistical Data Collection process List the equipment required by enumerators in field work operations Identify the desirable characteristics of a good enumerator, and Explain how enumerators should behave in the execution of their duties Session 18. Principles for Drawing and Reading a Map At the end of this session, the student should be able to Read and be able to navigate using a map Understand the principles behind drawing a map and be able to draw a basic map Appreciate the benefits of using maps in designing studies SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 7 Basic Module B1 Session 19. Preparing a structured field report At the end of this session, you will be able to: Outline the structure/contents of a field report. Outline the importance of such reports in an institution producing statistics. Identify the future use of these field reports, if any, in their areas of work. Design a structured field report for any survey that they are familiar with. Session 20. Ethical issues in the collection of statistics At the end of the session students will be able to: Define ethics Identify and explain the main ethical challenges that arise in Official Statistics Explain how to address ethical issues that arise in Official Statistics SADC Course in Statistics Module B1 – Page 8