Agriculture Test Von Thunen Model Shows agricultural activities in
advertisement

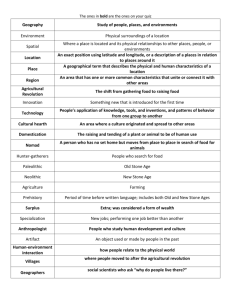
Agriculture Test 1. Von Thunen Model a. Shows agricultural activities in relation to market (central city) b. Balance transportation costs (based on weight and distance to market) and land costs (based on distance to market) c. Relevant in examining dairy in the U.S. (still near major cities in northeast) 2. Intensive agriculture a. Small land area b. High inputs of labor per acre c. High output of food d. High population density 3. Capital intensive a. High amounts of technology (machinery) 4. Labor intensive a. High amount of work/workers needed to produce food 5. Extensive agriculture a. Large land area b. Low inputs of labor per acre c. Low output of food d. Low population density 6. Subsistence Agriculture a. Food is produced for family’s consumption b. Seen in LDCs c. Types i. Shifting Cultivation 1. 25% of world’s land 2. Low population density 3. Rainforest areas in Brazil and Africa 4. Being taken over by cattle ranching (bigger money maker) ii. Pastoral nomadism 1. 20% of world’s land 2. Low population density 3. Practiced in dry/arid areas that can’t support agriculture (Northern Africa, Southwest Asia, Mongolia) 4. Transhumance: season migration iii. Intensive subsistence 1. High population density 2. VERY labor intensive 3. Dominated by wet rice 7. Commercial Agriculture a. Food is produced to make money b. Seen in MDCs c. Types i. Plantation 1. Seen in both LDCs and MDCs 2. Mostly cash crops (tobacco, sugarcane, coffee, cotton) ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. 3. In LDCs, plantations tend to be controlled by MDCs (core—periphery) Dairy 1. Located near major cities in U.S. (northeast) Mixed Crop and Livestock 1. Corn (corn belt) and soybeans grown for consumption by animals 2. Profits come from animal products Grain 1. Wheat, corn, etc. grown for consumption by humans Ranching 1. Low population density 2. Practiced in dry/arid areas that can’t support agriculture 3. Grazing of livestock Commercial gardening 1. Horticulture 2. Truck farming 3. U.S. east/southeast coasts, west coast Mediterranean 1. Horticulture 2. Practiced in California, Chile, and areas bordering Mediterranean Sea 3. Olives and grapes 8. Agricultural Revolutions a. First Agricultural Revolution i. Domestication of plants and animals ii. 10,000 years ago b. Second Agricultural Revolution i. Innovations in technology that helped spur Industrial Revolution ii. 200 years ago iii. Seed drill, enclosure movement c. Third Agricultural Revolution i. Green Revolution ii. Targeted areas with high populations and low development iii. Increased use of biotechnology, chemicals, irrigation, machinery to increase agricultural output iv. Developed new varieties of rice, corn, and wheat (high yields) v. Africa has not benefitted as much as Latin America and Asia 9. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) a. DNA of seeds are modified in labs b. People who support GMOs say like that GMO seeds can produce their own fertilizers and pesticides, can be grown on nutrient-lacking soils, can have high-yielding varieties and can be resistant to disease c. People who are against GMOs don’t like that we don’t know long term effects and that these foods are not labeled d. Recent experiments with GMOs to increase agricultural output in Africa e. Monsanto i. Huge biotechnology corporation ii. Produces herbicide Roundup and Roundup Ready soybeans iii. Suing farmers over patented seeds 10. Industrial Agriculture a. Agribusiness i. Farms are not isolated activities, but part of a large food production industry ii. Large corporations have become dominant players in this business b. Vertical integration i. Single firm takes control of all the stages in the production process (primary, secondary, tertiary) c. Factory farming i. CAFO/feedlots ii. Use of antibiotics and growth hormones iii. Corn fed beef 11. Sustainable agriculture a. Organic b. Sensitive land management c. Limited use of chemicals d. Better integration of crops and livestock e. Grass fed beef 12. Land survey systems a. Township and range i. Grid pattern/rectangular land division ii. Thomas Jefferson iii. Land Ordinance of 1785 b. Metes and bounds i. British ii. Found on eastern coast of U.S. c. Long lots i. French ii. Found in Louisiana and Quebec 13. Environmental problems a. Deforestation i. The cutting down of trees/forests to use land for other purposes such as cattle raising, logging, plantations ii. Brazil (Amazon) b. Desertification i. The expansion of deserts/arid areas (land that used to be fertile is becoming arid) ii. Caused by overgrazing of livestock and over farming iii. Sahel region of Africa 14. Agriculture maps a. Corn (think central U.S.) b. Wheat (think western U.S.) c. Chicken (think fried chicken in the south) d. Beef (overlaps corn, but is spread out more)