Ch - Paint Valley Schools
advertisement

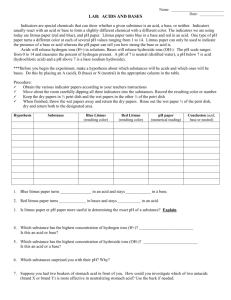
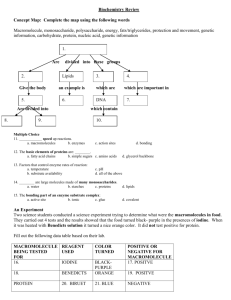
Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Ch. 2-3 Test Review Advanced Biology Know the following vocabulary words: atom, proton, neutron, electron, nucleus, element, enzyme, compound, mass number, atomic number, pH, acid, base, neutral, organic, macromolecule, reactant, product, chemical reaction, monomer, and macromolecule, protein, carbohydrate, nucleic acid, lipid, monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide, triglyceride, phospholipid, fatty acid, nucleotide, DNA, and RNA. (Ch. 2 and 3 Triple Entry Vocabulary) Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons for Chlorine. Draw a Bohr model showing the proper placement and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. (See journal and Ch. 2-3 Chemistry Quiz) List the characteristics of acids, bases, and neutrals. (pH lab and science journal) If you had an acidic substance, what color would blue litmus paper turn? Red litmus paper? (pH lab) If you had a basic substance, what color would red litmus paper turn? Blue litmus paper? (pH lab) Household bleach, a strong base, turns red to blue when using litmus paper to determine the concentration of OH- ions. What would you predict the pH of household bleach to be? (pH lab) What is the pH of a substance that shows no color change with blue litmus or red litmus paper? (pH lab) Give the monomer units for the following organic compounds: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. (Ch. 3 Biochemistry- Molecules of Life Concept Map) What elements on the periodic table are important to living things? (science journal) Compare and contrast DNA to RNA. (Ch. 3 C Map) What type of chemical bonding is formed as a result of electrons being shared between differing atoms? (Ch. 2 C Map) What type of chemical bonding does the following example illustrate? (Ch. 2 C Map & Quiz) 12. Na + Cl ------------- Na----Cl What types of chemical tests are used to determine if a food substance contains sugar, protein, starch, and/or lipid? (Detecting Compounds in Foods Lab) 13. 14. Be able to construct a graph given a data table. (pH lab) Which type of fat, saturated or unsaturated, is bad for you? (Ch. 3 C Map) 15. Know the four types of macromolecules. (Ch. 3 C Map) 16. Which type of macromolecule do DNA and RNA belong to? Know what each of these molecules function to do in the human body. (Ch. 3 C Map) What type of protein is responsible for speeding up the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs? (Enzyme Cornell Notes) How can you speed up the efficiency of an enzyme? (Enzyme Cornell Notes) 17. 18. 19. What types of changes can occur in the human body that could denature/destroy enzymes? (Enzyme Cornell Notes & Enzyme Lab) 20. List the properties of water that make it so important to living things. (science journal) Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ 1. 2. 3. Ch. 2-3 Test Review Advanced Biology Define the following vocabulary words: atom, proton, neutron, electron, nucleus, element, enzyme, compound, mass number, atomic number, pH, organic, macromolecule, reactant, product, chemical reaction, monomer, and macromolecule. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons for Chlorine. Draw a Bohr model showing the proper placement and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 17 Cl protons = 17 35 neutrons = 35 – 17 = 18 electrons = 17 List the characteristics of an acids and bases. Acids Bases Give off H+ in solution Give off OH- solution taste sour taste bitter Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ pH from 0 to 6.9 turn blue litmus paper red pH from 7.1 to 14 turn red litmus blue 4. If you had an acidic substance, what color would blue litmus paper turn? Blue litmus paper would turn red if you had an acidic substance. Red litmus paper? Red litmus paper would not turn color if you had an acidic substance. If you had a basic substance, what color would red litmus paper turn? Red litmus paper would turn blue if you had a basic substance. Blue litmus paper? Blue litmus paper would not turn color if you had a basic substance. 5. Household bleach, a strong base, turns red to blue when using litmus paper to determine the concentration of OH- ions. What would you predict the pH of household bleach to be? The pH would be somewhere in the 7.1 to 14 range. 6. What is the pH of a substance that shows no color change with blue litmus or red litmus paper? The pH of this substance would be 7. 7. Give the monomer units for the following organic compounds: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Substance Monomer Unit Protein Amino Acid Lipid 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ Nucleic Acid Nucleotide 8. What elements on the periodic table are important to living things? Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur 9. Compare and contrast DNA to RNA. DNA is double-stranded, has deoxyribose sugar, and contains the genetic code for an individual. RNA is single-stranded, has ribose sugar, and functions in protein synthesis. 10. What type of chemical bonding is formed as a result of electrons being shared between differing atoms? A covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms. For example, H2O has covalent bonds. 11. What type of chemical bonding does the following example illustrate? Na∙ + Cl ------------- Na----Cl Ionic bonding Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ 12. What types of chemical tests are used to determine if a food substance contains sugar, protein, starch, and/or lipid? To test for sugar, you would use Benedict’s solution and if the food has a simple sugar it would turn red, orange, yellow, or green. To test for the presence of starch, you would use iodine and if the food turns blue-black, it is positive. To test for protein, you would use Biuret’s solution and if it turns brown, it is positive for protein. You would use a brown paper bag to test for lipid. If the food leaves a greasy spot, it is positive for lipid. 13. Be able to calculate the total fat, carbohydrate, or protein calories of a food substance when given the total fat, carbohydrate, or protein content. When looking at a nutritional label for a NutriGrain Bar, you determine that there are 25 g of carbohydrate and 10 g of fat (lipid). Calculate the total number of carbohydrate and lipid calories in this cereal bar. Carbohydrates have 4 calories per gram. Total carb grams = 10 grams, so 25 grams X 4 calories per gram = 100 calories of carbs. Fats have 9 calories per gram. Total fat grams = 10 grams, so 10 grams X 9 calories per gram = 90 calories Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ of fats. 100 carb calories + 90 fat calories = 190 total calories! 14. Be able to construct a graph given a data table with the appropriate features that I have been teaching you in class. 15. Which type of fat, saturated or unsaturated, is bad for you? Saturated fats and trans fats are the bad fats. 16. Know the four types of macromolecules. The four macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. 17. Which type of macromolecule do DNA and RNA belong to? They are nucleic acids. Know what each of these molecules function to do in the human body. DNA functions to provide one’s genetic code (instructions). RNA functions to make protein. 18. What type of protein is responsible for speeding up the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs? An enzyme is responsible for speeding the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. 19. How can you speed up the efficiency of an enzyme? The efficiency of an enzyme can be sped up by having more substrate available and having more enzyme available. Name __________________ Date ________________ Period _______ # _____ 20. What types of changes can occur in the human body that could denature/destroy enzymes? A change in pH, a change in temperature, and a change in the amount of salt the cell is exposed to are all ways an enzyme can be denatured (misshapen). 21. Water is a polar molecule that looks like Mickey Mouse’s head. The ears are the hydrogen atoms which are slightly positively charged while the face is the oxygen atom which is slightly negatively charged. This polarity allows water to expand as it freezes (ice is less dense than liquid water), has a high surface tension (adhesion, cohesion, and capillarity), and has the ability to dissolve most substances (universal solvent).