Chapter 6
advertisement
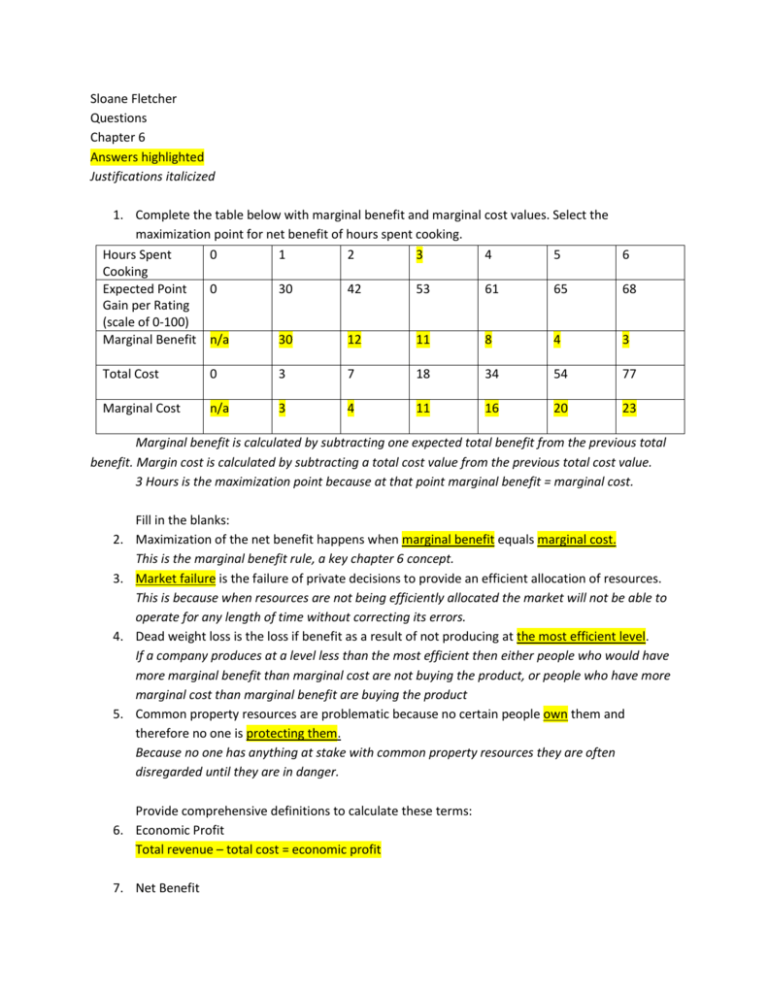
Sloane Fletcher Questions Chapter 6 Answers highlighted Justifications italicized 1. Complete the table below with marginal benefit and marginal cost values. Select the maximization point for net benefit of hours spent cooking. Hours Spent 0 1 2 3 4 5 Cooking Expected Point 0 30 42 53 61 65 Gain per Rating (scale of 0-100) Marginal Benefit n/a 30 12 11 8 4 6 68 3 Total Cost 0 3 7 18 34 54 77 Marginal Cost n/a 3 4 11 16 20 23 Marginal benefit is calculated by subtracting one expected total benefit from the previous total benefit. Margin cost is calculated by subtracting a total cost value from the previous total cost value. 3 Hours is the maximization point because at that point marginal benefit = marginal cost. 2. 3. 4. 5. Fill in the blanks: Maximization of the net benefit happens when marginal benefit equals marginal cost. This is the marginal benefit rule, a key chapter 6 concept. Market failure is the failure of private decisions to provide an efficient allocation of resources. This is because when resources are not being efficiently allocated the market will not be able to operate for any length of time without correcting its errors. Dead weight loss is the loss if benefit as a result of not producing at the most efficient level. If a company produces at a level less than the most efficient then either people who would have more marginal benefit than marginal cost are not buying the product, or people who have more marginal cost than marginal benefit are buying the product Common property resources are problematic because no certain people own them and therefore no one is protecting them. Because no one has anything at stake with common property resources they are often disregarded until they are in danger. Provide comprehensive definitions to calculate these terms: 6. Economic Profit Total revenue – total cost = economic profit 7. Net Benefit Benefit of an action – opportunity cost of that action = net benefit Describe the difference between the two terms: 8. Public Good v. Private Good Public goods can be consumed and used by everyone, because the marginal cost of adding another consumer is 0. Therefore, exclusion is not beneficial and in most cases almost impossible. A private good can be easily made only available to those that pay to use or consume it. Because there is no additional cost of having one more person be protected from terrorist attacks national defense it a public good. However, things like internet service are private because of the cost of managing accounts, installation etc. 9. External Cost v. External Benefit A cost that people not engaging in a market transaction incur is an external cost. An external benefit is when people outside of a market transaction incur benefits. Pollution is a large external cost, because people have to deal with the pollution but they are virtually unable to prevent it once a company has been allowed to make a certain amount. Parks could be considered an external benefit because they are usually constructed to keep parts of cities with some greenery and locations for events. However, they provide countless opportunities for people to use them at no cost. 10. Label the graph with the supply curve, demand curve, consumer surplus, producer surplus, maximized net benefit quantity Supply curve, demand curve, consumer surplus, producer surplus, maximized net benefit quantity as shown above Consumer surplus is when total benefit of consuming a good is larger than the price paid. Producer surplus is when total revenue received by sellers is larger than the total cost. Net benefit maximization quantity is shown where consumer surplus meets producer surplus.











