Guided Notes - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement
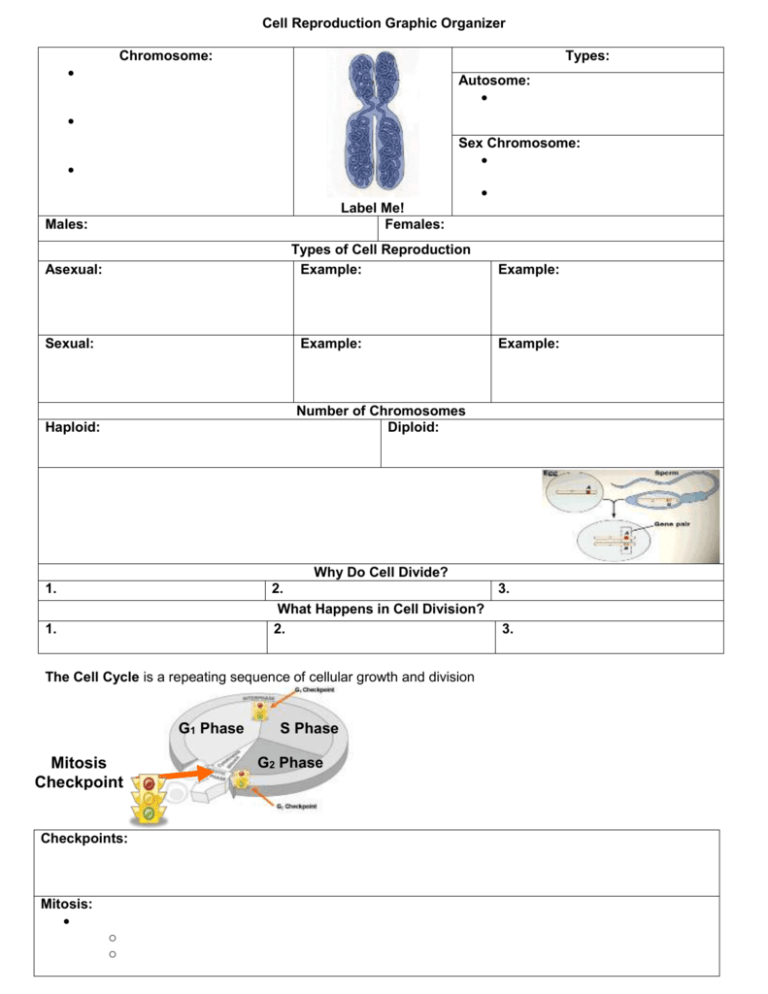
Cell Reproduction Graphic Organizer Chromosome: Types: Autosome: Sex Chromosome: Label Me! Females: Males: Types of Cell Reproduction Example: Asexual: Sexual: Example: Haploid: Number of Chromosomes Diploid: Example: Example: Why Do Cell Divide? 2. 3. What Happens in Cell Division? 2. 3. 1. 1. The Cell Cycle is a repeating sequence of cellular growth and division G1 Phase Mitosis Checkpoint Checkpoints: Mitosis: o o S Phase G2 Phase MITOSIS MEIOSIS Meiosis is Mitosis twice without interphase in between Interphase: Interphase 1. 2. 3. Prophase: Prophase I Metaphase I Metaphase: Anaphase I Telophase I Anaphase: Prophase II Metaphase II Telophase: Anaphase II Telophase II Cytokinesis : Meiosis: 1 cell becomes 4 cells which are called gametes Male gametes = _______________ Female gametes = _________________ The Difference Meiosis is _____________________ twice _______________________ interphase in between. Mitosis is in my________________, but Meiosis is in my ___________________! Why Meiosis? --Fertilization –Union of ____________________________ (n) –____________ is formed (2n) •The chromosome number is _______________, so at fertilization there is _____________________________________________________________ •Cuts chromosome ______________________________ ( 2n—n) •Creates ________________________________________ •Makes offspring ________________ Meiosis Creates variation in 3 ways. 1. Law of Segregation: 2. Law of Independent Assortment: 3. Crossing Over: Mitosis or Meiosis Diploid (2N) •Cells ________________________________________________________________________ •Human body cells have ___________ chromosomes each = (diploid or 2N # is 46) Haploid (N) •Cells ________________________________________________________________________ •Human sperm & eggs have ____________ chromosomes = (haploid or N # is 23) The Differences Mitosis Meiosis 1 cell becomes … Cell Types… In my… Phases… Haploid or Diploid Why-- Importance Diagram In my … Karyotype Notes: How do We look at Chromosomes? _______________________________ Steps: 1. Get cells from ________________ 2. Treat with chemicals and stain 3. Photograph Chromosome Abnormalities 4. _________________________________________ 5. Arrange from ______________ to ____________ 6. __________________________________________ Types Monosomy: Drawing Nondisjunction: (Not Coming Apart) Example: Trisomy: Example: Mutations: Deletion: Duplication: What is happening during Meiosis that that causes Trisomy or Monosomy? CANCER Cancer is mutations______________________________________________________________________ Increasing your risk: 1. 4. 2. 5. 3. SOME GENES THAT CONTROL CANCER: 1. Proto-Oncogenes: ________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Oncogenes: ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Tumor Suppressor Genes: ________________________________________________________________________________________ Why don’t we all get cancer? a. ______________________________________________________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________________________________________________








