Mesoamerican Civilizations: Review Questions & Review Sheet
advertisement

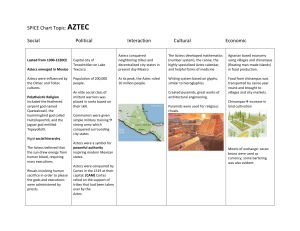
Name:____________________________ Date:_________________ Unit 4, Section 1: Mesoamerican Civilizations Directions: Read Unit 4, Section 1 (pages 143-149) and answer the following questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. Define/Identify: a. Olmecs b. Mayas c. Aztecs d. Incas e. Terraces f. Quipus 2. How where prehistoric people able to settle in the Americas? 3. What types of things did the Olmecs build? What contributions did they make to other societies? 4. What did men do in Mayan society? What did women do? 5. Describe the social structure of Mayan civilization. 6. What is one contribution/accomplishment of Mayan society? 7. How did the Aztecs expand their empire? 8. How was Aztec social structure different from the Maya’s? 9. What roles did the King play in Incan society? 10. Name two contributions/accomplishments of the Incas. Name:____________________________ I. Date:_________________ Unit 4, Section 1: Mesoamerican Civilizations Vocabulary a. Olmecs: Mesoamerican people that lived from 1400 to 500 BC in tropical rainforests along the gulf coast of present day Mexico b. Mayas: Mesoamerican people that lived from 400 to 600 AD in southern Mexico and much of Central America c. Aztecs: Mesoamerican people that settled in the Valley of Mexico by 1200 and by 1400 had constructed a large empire in Central America d. Incas: Mesoamerican people that built a huge empire during the 1400 and 1500s Pacific coast of South America e. Terraces: strips of flat land cut into mountainsides for farming f. Quipus: Inca system of knotted, colored string used for record keeping II. Geography a. During last ice age a land bridge from Asia to the Americas allowed prehistoric people to cross over b. Hunter gatherers followed herds and spread eastward and southward throughout the Americas c. Geography varies: woodlands, fertile plains, mountain ranges and rainforests d. Between 8500 and 2000 BC Americans learned to cultivate crops e. Like elsewhere in the world agriculture led to the development of cities and civilization III. Olmecs a. 1400 to 500 BC b. Emerged in the tropical rainforests along the gulf coast of present day Mexico c. Built pyramid shaped temples and vuildings d. Invented a calendar and a system of writing e. Spread influence through trade IV. Mayas a. 400 to 600 AD in southern Mexico and much of Central America b. Agriculture i. Most population were farmers ii. Men cultivated the crop, women turned it into food iii. Taxes (in the form of food) was collected to support local temples iv. Accumulated great wealth through trade c. Religion i. Priests occupied exalted place in social order ii. They alone could conduct rituals that they believed brought success in farming and battle d. Social Structure i. Each city-state had ruling chief ii. Under chiefs were nobles that served as officials and military leaders iii. Women sometimes hold power iv. Most people were farmers e. Contributions i. Built pyramids and temples with paintings and carvings ii. Cleared rainforests, built raised fields to hold rainwater iii. Developed picture system of writing, an elaborate calendar and number system f. Decline Name:____________________________ Date:_________________ i. Around 900, Mayas abandoned cities ii. Warfare or overpopulation may have caused failure in agriculture or revolts V. VI. Aztecs a. Late 1200s migrant group settled in the Valley of Mexico; by 1400 a powerful empire was constructed b. Expansion i. Founded Tenochtitlan in 1315 ii. Formed alliances with neighbors to build an empire iii. Grew wealthy off of tribute from defeated nations iv. By 1500s Aztec empire covered most of Mexico and included 30 million people c. Social Structure i. Ruled by emperor, who chose a council of nobles and priests ii. Nobles were officials, judges, provincial governors iii. Warriors and traders were beneath nobles iv. Farmers were under warriors/traders, slaves were under farmers d. Religion i. Priests were important as leaders of rituals ii. Aztec priests offered many thousands of human sacrifices e. Contributions i. Devised accurate calendar, established schools, recorded historical events and had practiced medicine ii. Capital city of Tenochtitlan was architectural marvel iii. Created farmland by converting swamps and creating artificial “floating” islands Incas a. 1400s emerged from Andes mountains and conquered a huge area in South America along the Pacific coast b. Centralized government i. Ruled by an emperor who lead army in battle and owned all people, land, herds and mines; also chief religious leader ii. Nobles ran the provinces while other officials collected taxes and enforced laws c. Roads i. Empire was linked by a series of roads ii. Runners carried news from all parts of the empire d. Religion i. Religion was a large part of life ii. Many gods worshiped iii. Rituals and festivals were common e. Agriculture: Used stone walls to improve existing terraces to farm crops f. Communication: knotted colored string was used to keep records g. Science: Practiced advanced medicine