Chemistry I
advertisement

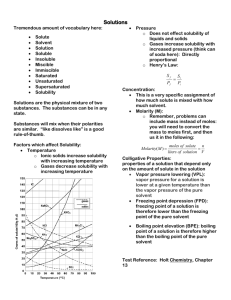
Chemistry I Chapter 13 – Solutions Test review TEST: Wednesday, April 4, 2007 Planned format: All multiple choice o Part I; 2 points each (12) o Part II; 4 points each (12) Bonus problem, solve for the molar mass of a compound (See problems 121-122 in the text.) Bonus problem, converting from molarity to molality, or vice-versa Topics for MC: Solutions o What can be said of the attractive forces between the solute and solvent (See Fig. 13.1) o Terms: Solute, Solvent o Solution, homogeneous mixture Different types Gas, gas (air) Gas, liquid (pop) Liquid, liquid (diluted antifreeze) Solid, solid (brass – penny lab) Etc. o Electrolyte solutions – those that will form ions in solution and therefore conduct current Solubility o What types of solutes dissolve well in water? o What does “like dissolves like” refer to? o Solubility of solids in water As temperature increases the solubility of solids … Predict if a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated, based on available data ( a chart (page 434) or provided information or description of the solution) Concentration of ions in solution o Solubility of gases in water As temperature increases the solubility of gases in water… As pressure increases the solubility of gases in water… Concentration units o Calculate the mass percent of a solution o Use mass percent to determine how much of a solute is needed. o Calculate the molarity of a solution given the mass of solute and volume of solution. o Calculate volume of solution of given molarity that can be made from a given amount of solute. o Calculate and describe the preparation of a specific molarity solution. o Use molarity or molality to determine how much of a solute is needed. o Calculate the molality given the mass of solute and volume of water (density of 1.00 g/mL). o Given a balanced chemical equation, calculate the grams of product produced from … o Given a balanced chemical equation, calculate the volume of reactant needed … Dilution o Calculate the final molarity of a solution that has been diluted from a more concentrated solution. o Calculate the volume of concentrated solution need to make a more dilute solution. Colligative properties o Depends on what? – The number of particles in solution… o Affects what properties Vapor pressure lowering Freezing point (FP) depression, equation given; calculate the freezing point Boiling point (BP) elevation, equation given; calculate the boiling point Osmotic pressure (OP), equation given; calculate the osmotic pressure Being able to describe the flow that occurs in an osmosis situation. o Van’t Hoff factor Bea able to figure it out Be able to use it as part to predict FP, BP, OP calculations. Information given on the test: All of the molar masses needed for this test will be given in order to save you time and some possible mistakes in calculating these values. Equations Tf = i∙m∙Kf Tb = i∙m∙Kb = i∙M∙R∙T M1V1 = M2V2