313absnotes
advertisement

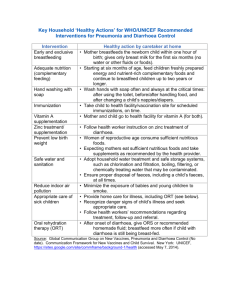
Notes on absorption unit 1 updated 04/08/2008 Absorption of the products of digestion Active transport Energy is used Transport against a concentration gradient. Protein pumps change their shape Pumps are specific May transport two molecules at once Active transport includes: Ca2+ pumps in muscles Active reabsorption in nephrons (the kidney) Absorption of the products of digestion Sugar loading into phloem Read Jones and Jones section 3.27 page 78 METHOD USES ENERGY USES PROTEINS SPECIFIC CONTROLLABLE Simple Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Absorption The stomach is not adapted for absorption but a few substances can pass through into the blood e.g. alcohol and aspirin. 1 Notes on absorption unit 1 updated 04/08/2008 The ileum is well adapted to absorption: …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Glucose is absorbed by indirect active transport. Sodium ions are pumped out of the cells into the lumen of the gut and then re enter the cells down their diffusion gradient carrying glucose molecules with them. There is a diagram of this p79 Jones and Jones. Copy it here: 2 Notes on absorption unit 1 updated 04/08/2008 More on cholera The cholera bacterium is an example of a prokaryotic organism. Draw and label a prokaryotic cell in this box: Vibrio cholerae produces several toxins. One of these is an enterotoxin. Definition = The enterotoxin has two parts – A and B. Part B binds to a receptor on the epithelial cells of the small intestine, then part A penetrates into the cell. It binds to a protein inside the cell called G protein, resulting in the stimulation of an enzyme called adenylate cyclase. This enzyme produces a molecule called cyclic AMP from ATP, which causes the cell to excrete chloride ions into the lumen of the small intestine through proteins called chloride channels. The secretion of chloride ions into the small intestine causes water to follow, down the water potential gradient by osmosis, resulting in a large amount of extra water being lost to the lumen of the small intestine. The large intestine cannot absorb this extra fluid quickly enough = diarrhoea. See diagram. If you are interested in some further research or reading: The symptoms of cholera are due to the effect of the toxin on chloride channels. Cystic Fibrosis is an inherited disease, people with CF have defective chloride channels. There is a suggestion that being a carrier of the CF gene may give some protection against cholera. How? 3 Notes on absorption unit 1 updated 04/08/2008 Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) What is oral rehydration therapy (ORT) and how does it work? If a person contracts cholera, it is imperative that they are treated as quickly as possible, since untreated cholera can have a case fatality rate as high as 50%. Fortunately, effective treatment can reduce this rate to less than 1%. ORT is the giving of fluid by mouth to prevent and/or correct the dehydration that is a result of diarrhoea. ORT does not stop the diarrhoea, but it replaces the lost fluids and essential salts. The glucose contained in ORS enables the intestine to absorb the fluid and the salts more efficiently (think about the glucose sodium co-transporter). Between 1980 and 2000, ORT decreased the number of children under five dying of diarrhea from 4.6 million worldwide to 1.8 million — a 60% reduction. How have more effective rehydration solutions been developed? For more than 25 years UNICEF and WHO have recommended a single formulation of glucose-based ORS to prevent or treat dehydration from diarrhoea. However, treatment with ORS does not reduce the amount or duration of diarrhoea. For this reason the ORS had less acceptance by mothers and health workers, preferring a treatment that causes diarrhoea to stop. During the past 20 years numerous studies have been undertaken to develop an 'improved' ORS. The goal was a product that would be at least as safe and effective as standard ORS for preventing or treating dehydration from all types of diarrhoea but which, in addition, would reduce diarrhoea. One successful approach was reducing the solution's glucose and salt (NaCl) concentrations. Some ORS have starch (such as rice flour) added instead of glucose. The starch is digested in the small intestine to give a steady supply of glucose for transport, but reduces the water potential of the mixture. This allows more water to be reabsorbed in the intestines, reducing the amount of diarrhoea. Drug testing ORS, like any drug, need to be tested before use. Use the green textbook and the internet to answer the following questions: 1. What are the stages in drug development? 2. How do drug trials follow a regulated set of ethical procedures? 4