DIGESTION QUIZ
advertisement

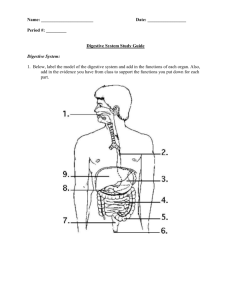
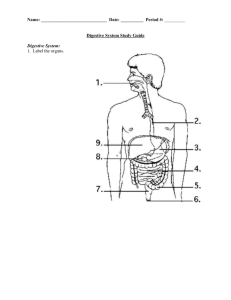
DIGESTION QUIZ 1. Which of the following is an advantage of a complete digestive system over a gastrovascular cavity? a. Food items are retained longer. b. Specialized regions are possible. c. Digestive enzymes can be more specific. d. Extensive branching is possible. e. Intracellular digestion is easier. 2. Some nutrients are considered “essential” in the diets of certain animals because a. only those animals use the nutrients. b. they are subunits of important polymers. c. they cannot be manufactured by the organism. d. they are necessary coenzymes. e. only some foods contain them. 3. Which of the following is TRUE of the mammalian digestive system? a. All foods begin their enzymatic digestion in the mouth. b. After leaving the oral cavity, the bolus enters the larynx. c. The epiglottis prevents food from entering the trachea. d. Enzymes production continues in the esophagus. e. The trachea leads to the esophagus and then to the stomach. 4. Which of these animals has a gastrovascular cavity? a. bird b. hydra c. mammal d. insect e. annelid 5. In general, herbivorous mammals have teeth modified for a. cutting b. ripping. c. grinding. d. splitting. e. piercing. 6. Cows are able to survive on a diet consisting almost entirely of cellulose because a. Cows are autotrophic. b. The cow, like the rabbit, reingests its feces. c. Cows can manufacture all 15 amino acids out of sugars in the liver. d. Unlike humans, the cow’s saliva has enzymes capable of digesting cellulose. e. Cows have cellulose-digesting, symbiotic microorganisms in their rumens. 7. All of the following statements about digestion are correct EXCEPT a. Digestion is catalyzed by enzymes. b. Digestion cleaves nucleic acids to nucleotides. c. Digestion cleaves fats into glycerol and fatty acids. d. During digestion the essential macromolecules are directly absorbed. e. During digestion polysaccharides and disaccharides are split into simple sugars. 8. What is peristalsis? a. A process of fat emulsification in the small intestine. b. Voluntary control of the rectal sphincters regulating defecation. c. The transport of nutrients to the liver through the hepatic portal vein. d. Loss of appetite, fatigue, dehydration, and nervous disorders. e. Smooth muscle contractions that move food through the alimentary canal. Use the following diagram to answer questions 9 – 13. 9. Agents that help emulsify fats are produced by a. 1. b. 2. c. 3. d. 8. 10. Where does the digestion of carbohydrates occur? a. 1 and 3 b. 1 and 4 c. 3 and 4 e. 9. d. 4 and 5 e. 5 and 7 11. Where are the enzymes maltase, sucrase, and lactase produced? a. 1 b. 3 c. 4 d. 8 e. 10 12. Where does the digestion of fats occur? a. 3 only b. 4 only c. 1 and 4 e. 1,3, and 4 d. 3 and 4 13. Where does the reabsorption of most of the water used in digestion occur? a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7 e. 8 14. Most enzymatic hydrolysis of the macromolecules in food occurs in the a. Small intestine. c. stomach. e. mouth. b. Large intestine. d. liver. 15. Which of the following is a CORRECT statement about pepsin? a. It is manufactured by the pancreas. b. It helps stabilize fat-water emulsions. c. It splits maltose into monosaccharides. d. It is activated by the action of HCl on pepsinogen. e. It is denatured and rendered inactive in solutions with low pH. 16. Blood sugar concentration is likely to vary MOST in which of these blood vessels? a. The abdominal artery b. The coronary arteries c. The pulmonary veins d. The hepatic portal vein e. The hepatic vein, which drains the liver The following questions (17 – 19) refer to the substances below. From the list, match the term that best fits each of the following descriptions. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a. nucleases b. chylomicrons d. lysine and leucine c. lipoproteins e. thiamine and niacin 17. Essential amino acids 18. Water-soluble vitamins. 19. Fat globules transported by exocytosis into the lacteals of the microvilli. 20. Which of the following terms could be applied to any organism with a digestive system? a. heterotroph b. autotroph c. herbivore d. omnivore e. bulk-feeder 21. In a variation of the game “twenty questions,” you are asked whether the animal being thought of is a suspension-feeder or not. Which of the following questions could NOT provide you with any useful information? a. Is it aquatic? b. Does it have teeth? c. Is it bigger than your biology book? d. Does it have claws? e. Does it have tentacles? 22. The process of intracellular digestion is usually preceded by a. hydrolysis. . c. absorption. e. secretion. b. endocytosis d. elimination. 23. To actually enter the body, a substance must cross a cell membrane. During which stage of food processing does this first happen? a. Ingestion c. hydrolysis e. elimination b. Digestion d. absorption 24. The body is capable of catabolizing many substances as sources of energy. Which of the following could be used as a source of energy but would be the last utilized for this purpose? a. Fat in adipose tissue b. Glucose in the blood c. Protein in muscle cells d. Glycogen in muscle cells e. Calcium phosphate in bone 25. How does the digestion and absorption of fat differ from that of carbohydrates? a. Processing of fat does not require any digestive enzymes, whereas the processing of carbohydrates does. b. Fat absorption occurs in the stomach, whereas carbohydrates are absorbed from the small intestine. c. Carbohydrates need to be emulsified before they can be digested, whereas fats do not. d. Most absorbed fat first enters the lymphatic system, whereas carbohydrates directly enter the blood. e. Fat must be worked on by bacteria in the large intestine before it can be absorbed, which is not the case for carbohydrates. 26. Which of the following terms could be used accurately to describe absorbed nutrients? a. macromolecules c. monomers e. peptides b. polymers d. enzymes 27. Digestive systems are not needed by a. heterotrophs c. herbivores. b. autotrophs. d. omnivores. e. carnivores. 28. Which of the following minerals in INCORRECTLY associated with its use in animals? a. Calcium – construction and maintenance of bone b. Magnesium – cofactor in enzymes that split ATP c. Iron – regulation of metabolic rate d. Phosphorous – ingredient of nucleic acids e. Sodium – important in nerve function 29. After ingestion, the first type of macromolecule to be enzymatically attacked in the human digestive system is a. protein. c. fat. e. glucose. b. carbohydrate. d. nucleic acid. 30. Increasing surface area facilitates which of the following digestive processes? a. hydrolysis c. ingestion e. both a and b b. absorption d. elimination 31. Secretin a. stimulates the release of alkaline products by the pancreas. b. stimulates the gastric glands. c. is released by the salivary glands. d. decreases the stomach’s churning activity. e. stimulates the release of digestive system.