Intermolecular Forces- PRACTICE Test
advertisement
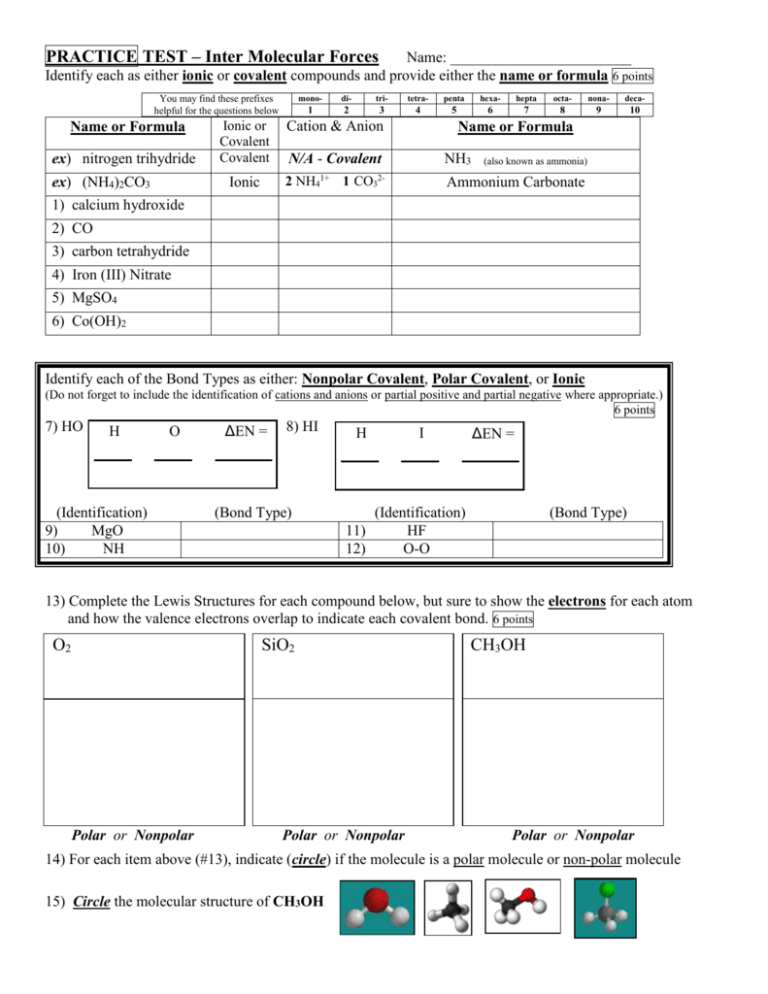
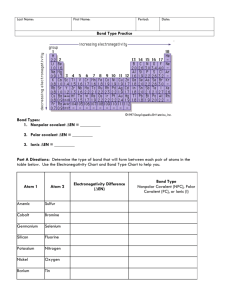
PRACTICE TEST – Inter Molecular Forces Name: ________________________ Identify each as either ionic or covalent compounds and provide either the name or formula 6 points You may find these prefixes helpful for the questions below Name or Formula ex) nitrogen trihydride ex) (NH4)2CO3 mono- di- tri- tetra- penta hexa- hepta octa- nona- deca- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ionic or Covalent Covalent Cation & Anion N/A - Covalent NH3 Ionic 2 NH41+ 1 CO32- Ammonium Carbonate Name or Formula (also known as ammonia) 1) calcium hydroxide 2) CO 3) carbon tetrahydride 4) Iron (III) Nitrate 5) MgSO4 6) Co(OH)2 Identify each of the Bond Types as either: Nonpolar Covalent, Polar Covalent, or Ionic (Do not forget to include the identification of cations and anions or partial positive and partial negative where appropriate.) 6 points 7) HO H O (Identification) 9) MgO 10) NH ΔEN = 8) HI H (Bond Type) 11) 12) I ΔEN = (Identification) HF O-O (Bond Type) 13) Complete the Lewis Structures for each compound below, but sure to show the electrons for each atom and how the valence electrons overlap to indicate each covalent bond. 6 points O2 SiO2 Polar or Nonpolar Polar or Nonpolar CH3OH Polar or Nonpolar 14) For each item above (#13), indicate (circle) if the molecule is a polar molecule or non-polar molecule 15) Circle the molecular structure of CH3OH 18) Explain “how” atoms become partially positive and partially negative in a polar bond. 2 points Match each item (a-o) with the correct statement below. (NOTE: each item (a-o) may be used once, more than once, or not at all). a. b. c. d. e. cation anion electrostatic force electronegativity dipole (polar molecule) f. g. h. j. k. ionic bond polar covalent bond nonpolar covalent bond intramolecular force intermolecular force 10 points l. Van der Waals force m. London dispersion force (LDF) n. dipole-dipole interaction (DDI) o. hydrogen bond (HF) ____ 19. the force of attraction between a positive and negative charge ____ 20. the electrostatic force between atoms – (covalent bond between atoms) ____ 21. the electrostatic force between molecules – cause molecules to stick to each other ____ 22. atom or group of atoms having a positive charge ____ 23. intermolecular force between molecules that have permanent dipoles that are attracted to each other ____ 24. the relative ability of a bonded atom of an element to attract the electrons from the another element participating in the bond. ____ 25. a molecule that has two electrically charged regions (a slightly positive region and a slightly negative region) ____ 26. these forces are present in all molecules, whether they are polar or nonpolar. ____ 27. the electrostatic force of attraction binding oppositely charged ions together ____ 28. a covalent bond between two atoms of significantly different electronegativities – (bonding occurs when the electrons are shared unequally.) ____ 29. atom or group of atoms having a negative charge ____ 30. a covalent bond between atoms where the bonding electrons are shared equally. ____ 31. intermolecular force between an instantaneous dipole and an induced dipole. (Caused by the motion of the electrons) ____ 32. this type of intermolecular force is found between molecule of water (H2O) ____ 33. the dipole-dipole interactions experienced between molecules when H is bonded to N, O, or F ____ 34. in a polar covalent bond, the atom with the higher ___________ will become partially negative ____ 35. the weak attractive forces that hold molecules together (includes London dispersion, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonds) ____ 36. the force of attraction within ionic, metallic, and covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, London dispersion forces, and even between protons & electrons is due to ________. Identify each of the following as either intermolecular or intramolecular 4 points 37) _____________ Polar Covalent Bond 40) _____________ Ionic Bond 38) _____________ Hydrogen Bond 41) _____________ Dipole-Dipole Interact 39) _____________ London Dispersion 42) _____________ Van der Waals 42) For each box below, identify (label) the intermolecular and intramolecular attractions 4 points ____ 43) Which of the following covalent bonds is the most polar? a. H—F b. H—C c. H—H d. H—N ____ 44) Which of the following atoms acquires the most negative charge in a covalent bond with hydrogen? a. C b. N c. O d. S ____ 45) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? a. dipole-dipole interaction b. London dispersion c. hydrogen bond d. single covalent bond ____ 46) Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other c. to become more polar b. to gain a higher electronegativity d. to attain a full valence energy level ____ 47) A bond formed between a silicon atom and an oxygen atom is likely to be ____. a. ionic b. coordinate covalent c. polar covalent d. nonpolar covalent ____ 48) What is thought to cause the London dispersion forces? a. attraction between ions c. sharing of electron pairs b. motion of electrons d. differences in electronegativity ____ 50) Why is hydrogen bonding only possible with hydrogen? a. Hydrogen’s nucleus is electron deficient when it bonds with an electronegative atom. b. Hydrogen is the only atom that is the same size as an oxygen atom. c. Hydrogen is the most electronegative element. d. Hydrogen tends to form covalent bonds. Identify the primary type of Van der Waals Forces that exist between each type of molecule: LDF = London Dispersion Forces, DDI = Dipole-Dipole Interaction, HB = Hydrogen Bonds 51) C2H5OH- ______ 52) CH3Br- ______ 53) HI- ______ 54) CCl4- ______ 55) CH3NH2 -______ 56) CO2- ______ 57) Ar- ______ 58) HF - ______ 59) C2H4O - ______ 60) Br2- ______ 10 points 63) List and explain the two factors that affect the force of attraction in London dispersion forces? 2 points 64) Explain how London dispersion forces cause molecules to be attracted to one another. 2 points 65) Rank the following FOUR molecules from lowest to highest boiling points: EXPLAIN CH4 CBr4 CCl4 CF4 2 points 66) Rank the following THREE molecules from lowest to highest boiling points: EXPLAIN 2 points 67) Rank the following THREE molecules from lowest to highest boiling points: EXPLAIN 2 points 68) What is the difference between a hydrogen bond and a polar covalent bond involving hydrogen? 69) Complete the table below using the following terms: (Solid, Liquid, Gas, Exothermic, Endothermic) Phase Change From To Endothermic or Exothermic Deposition Gas Solid Exothermic (Gas is losing energy) Sublimation Freezing Melting Condensation Vaporization 4points 70) TRUE or FALSE: Gases have an indefinite shape and a definite volume. 71) TRUE or FALSE: The motion/speed of the particles increases as the temperature of particles decreases. 72) TRUE or FALSE: Because the shape of a solid never changes, the particles of the solid do not move. 73) TRUE or FALSE: Particles can stick together because of the intermolecular forces between the particles. 74) TRUE or FALSE: It is possible to heat pure water to a temperature of 127 °C. 75) TRUE or FALSE: Energy is either absorbed (Exothermic) or released (Endothermic) during a phase change. 76) TRUE or FALSE: The temperature of a substance changes during a phase change (melting/boiling). 77) TRUE or FALSE: The freezing point of and the melting point of a substance is the same temperature. 78) You put your recently washed, wet clothes into the dryer and start the machine. Forty-five minutes later, your clothes are dry. What happened to the water? ENERGY moves Causing the SPEED from the _____________ of the particles to to the _______________ This will cause the particles to Resulting in a PHASE CHANGE become more (held together, from a (s,l,g) to (s,l,g) which is called move (slower, faster) separated). (ATTRACTION) _______________ and is (Endo, Exo) 79) A piece chocolate is sitting on the dashboard of your car on a hot sunny day. ENERGY moves Causing the SPEED from the _____________ of the particles to to the _______________ This will cause the particles to Resulting in a PHASE CHANGE become more (held together, from a (s,l,g) to (s,l,g) which is called move (slower, faster) separated). (ATTRACTION) _______________ and is (Endo, Exo) 80) After taking a hot shower, the mirror in the bathroom is all steamy (covered in water droplets). Explain how the mirror became wet. (Be sure to use the proper scientific terms in your response) 81) EXPLAIN what is happening at the atomic level when a substance undergoes a phase change? Details required.