Teacher notes
advertisement

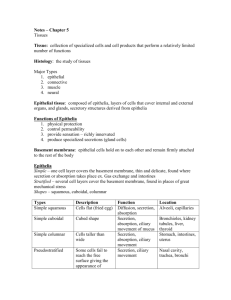
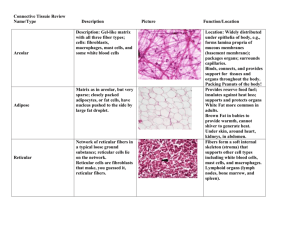
Teacher notes- Tissues Tissue – a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue: 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial – lines and protects the body and organs. Connective – connects, supports, and protects the body. Nervous – sends signals throughout the body. Muscle – allows for movement- voluntary/ involuntary 1. Epithelial Tissue General Characteristics: - Found throughout the body, covers all body surfaces both inside and out. - Main glandular tissue. - Attached to underlying connective tissue by noncellular nonliving basement membrane. - Usually has no vascular tissue - blood supply - Cells reproduce rapidly (rapid healing). - Cells tightly packed together Functions: Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, sensory perception Six Specific types of epithelial tissue - categorized based on the shape of the cells and the layers of cells. A. SIMPLE SQUAMOUS - single layer (simple) of very thin, flattened cells (squamous). Function: diffusion and filtration.. Found in: air sacs of lungs, walls of capillaries. B. SIMPLE CUBOIDAL - single layer, cube-shaped cells. Function: Secretion and absorption. Found: Lining of kidney tubules, ducts of glands, covering surface of ovaries C. SIMPLE COLUMNAR - single layer, elongated cells with their nuclei in about the same position in each cell (usually near the basement membrane). Function: Protection, secretion, absorption. Found in the lining of digestive tract and uterous D. STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS - muli-layered, squamous cells. Thicker tissue. Functions in protection. Found lining body cavities like the mouth and outer layer of skin E. PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR - appear "stratified" but really a single layer with nuclei at various levels giving the appearance of layered cells. - Function: secretion and cilia-aided movement - Location: lining air passages like the trachea and tubes of the reproductive system F. TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM - thick, layered cuboidal cells. "Stretchable" tissue, also forms barrier to block diffusion. Found: lining of urinary bladder. 2. Connective Tissue General Characteristics: -Most abundant tissue in your body, found throughout -Binds structures together -Provides support, protection, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces blood cells, fights infection, and helps repair tissue. -Composed of more scattered cells with abundant intercellular material ' matrix -Made up of a ground substance (fluid, semi-solid) and fibers -Most has a good blood supply -Cells can reproduce Three common types of cells: 1. mast cells (prevents blood clots) 2. macrophages (phagocytic) and 3. fibroblasts (most abundant, produce fibers) Main types of fibers: -collagenous fibers - thick, made of protein collagen, major structural protein in the body, appear in long parallel bundles. Strong, flexible, but not very elastic, also known as white fibers. (bones, ligaments, tendons) - elastic fibers - microfibrils in protein elastin, yellow fibers. Not as strong, but very elastic (respiratory and vocal cords) CATEGORIES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE A. LOOSE C.T. or AREOLAR TISSUE - binds skin to underlying organs and organs to organs, space between muscles B. ADIPOSE TISSUE - aka FAT, beneath skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, abdominal membranes. Function: Protective cushion, insulation to preserve body heat, stores energy, cells are called adipocytes C. FIBROUS C.T. - dense tissue, closely packed, thick collagenous fibers and fine network of elastic fibers. Few cells, poor blood supply, thus slow healing. Tendons - connect muscles to bones Ligaments - connect bones to bones CARTILAGE (all cartilage cells are called chondrocytes) D. HYALINE CARTILAGE - very fine white (collagenous) fibers. Most common cartilage. Covers ends of bones and joints, noise, respiratory passages. E. ELASTIC CARTILAGE - more flexible and elastic, external ear and larynx F. FIBROCARTILAGE - very tough, large numerous collagenous fibers. Intervertebral disks, menisci G. BONE TISSUE - Osseus tissue. Rigid due to mineral salts. Layers - lamellae, haversian canals, osteocytes H. BLOOD TISSUE - circulates throughout the body 3. Muscle Tissue A. Skeletal - skeletal muscles - voluntary (striated) B. Smooth - in hollow organs, stomach - involuntary C. Cardiac - wall of the heart 4. Nerve Tissue - Found in brain, spinal cord, nerves A. Neurons - transmit signals B. Neuroglia - protection, support Student notes- Tissues Tissue – ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ There are 4 major types of tissue: 1. 2. 3. 4. ______________________ – lines and protects the body and organs. ______________________ – connects, supports, and protects the body. ______________________ – sends signals throughout the body. ______________________ – allows for movement- voluntary/ involuntary 1. Epithelial Tissue General Characteristics: - Found throughout the body, covers all body surfaces both inside and out. - Main _______________________. - Attached to underlying connective tissue by noncellular nonliving basement membrane. - Usually has ________________________________ - blood supply - Cells _____________________________________ (rapid healing). - Cells ___________________________ together Functions: _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Six Specific types of epithelial tissue - categorized based on the ___________________________ and _________________________________. A. SIMPLE SQUAMOUS ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Function: _____________________ and ______________________.. Found in: _________________________ and, __________________________. B. SIMPLE CUBOIDAL - single layer, _________________________ cells. Function: __________________________ and ______________________. Found: ___________________, _____________________________, ____________________________________________. C. SIMPLE COLUMNAR - single layer, __________________________ with their __________________________ in about the ________________________ in each cell (usually near the basement membrane). Function: __________________, ___________________, _________________. Found in the lining of _________________________ and __________________ D. STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS - _________________, squamous cells. _____________________ tissue. Functions in _________________________. Found lining body cavities like the _______________ and __________________ E. PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR - appear "__________________" but really a __________________________ with nuclei at various levels giving the appearance of _____________________________. - Function: _____________________ - Location: lining air passages like the __________________ and tubes of the ________________________________________________ F. TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM - _____________________, layered _____________________ cells. "________________________" tissue, also forms barrier to ___________________________. Found: lining of __________________________. 2. Connective Tissue General Characteristics: -Most abundant tissue in your body, found throughout -Binds structures together -Provides _____________________, _________________________, ____________________, _________________________, _______________________, ___________________________, _________________________, and helps _____________________________. -Composed of more _______________________________ with abundant intercellular material ' matrix -Made up of a ground substance (fluid, semi-solid) and fibers -Most has a good blood supply -Cells can ___________________________ Three common types of cells: 1. _________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________ Main types of fibers: -collagenous fibers - thick, made of protein collagen, major structural protein in the body, appear in long parallel bundles. Strong, flexible, but not very elastic, also known as white fibers. (bones, ligaments, tendons) - elastic fibers - microfibrils in protein elastin, yellow fibers. Not as strong, but very elastic (respiratory and vocal cords) CATEGORIES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE A. LOOSE C.T. or AREOLAR TISSUE - binds skin to ________________, and organs to organs, and binds the space between muscles B. ADIPOSE TISSUE - aka FAT, beneath skin, around ______________ and ____________________, abdominal membranes. Function: Protective cushion, insulation to preserve body heat, __________________________, cells are called adipocytes C. FIBROUS C.T. - dense tissue, closely packed, and fine network of elastic fibers. Few cells, poor blood supply, thus slow healing. Tendons - connect ______________ to ________________ Ligaments - connect ______________ to ________________ CARTILAGE (all cartilage cells are called ____________________________) D. HYALINE CARTILAGE - very fine white (collagenous) fibers. Most common cartilage. Covers ends of bones and joints, noise, respiratory passages. E. ELASTIC CARTILAGE - more flexible and elastic, external ear and larynx F. FIBROCARTILAGE - very tough, large numerous collagenous fibers. Intervertebral disks, menisci G. BONE TISSUE - Osseus tissue. Rigid due to mineral salts. Layers - lamellae, haversian canals, osteocytes H. BLOOD TISSUE - circulates throughout the body 3. Muscle Tissue 1. Skeletal - __________________ muscles - voluntary (striated) 2. Smooth - in hollow organs, ___________________ – involuntary 3. Cardiac - wall of the _____________________ 4. Nerve Tissue - Found in brain, spinal cord, nerves A. Neurons - _________________________________ B. Neuroglia - _________________, and __________________ Tissue worksheet #1 TISSUE TYPES MAJOR TISSUE SPECIFIC TYPES OF TISSUE WHERE ITS FOUND IN YOUR BODY Lining of air sacs in the lungs SIMPLE CUBOIDAL Digestive tract (intestinal wall) Air passages (trachea, etc) Outer layer of skin TRANSITIONAL Binds skin to internal organs Layer beneath the skin FIBROUS CONNECTIVE TISSUE Covers ends of bones at joints CONNECTIVE TISSUE ELASTIC CARTILAGE FIBROCARTILAGE Skeleton Circulates throughout body RETICULOENDOTHELIAL Muscles connected to bones Walls of many internal organs Walls of the heart NERVE TISSUE NERVE TISSUE Name _______________________ CONNECTIVE TISSUE MATRIX Coloring Instructions collagen fibers [A] yellow. fibroblasts [B] blue. mast cells [C] purple . macrophages [D] orange elastic fibers [E] green (shade over the line) blood vessel and blood cells [F] red. fat cells [G] pink. Match the structure to the function (use letters) 1. ____ Store energy 2. ____ Production of fibers 3. ____ Consume debris and foreign objects 4. ____ Fiber that makes up tendons 5. ____ Prevention of blood clots Epithelial Tissues Introduction Epithelia are tissues consisting of closely apposed cells without intervening intercellular substances. Epithelia are avascular, but all epithelia "grow" on an underlying layer of vascular connective tissue. The connective tissue and the epithelium are separated by a basement membrane. Epithelium covers all free surfaces of the body. Epithelium also lines the large internal body cavities, where it is termed mesothelium. Furthermore, the internal surfaces of blood and lymph vessels are lined by epithelium, here called endothelium. Epithelia are classified on the basis of the number of cell layers and the shape of the cells in the surface layer. * If there is only one layer of cells in the epithelium, it is designated simple. * If there are two or more layers of cells, it is termed stratified. * Cells in the surface layer are, as a rule, described according to their height as squamous (scale- or plate-like), cuboidal or columnar. Psuedostratified epithelia appears to be layered (stratified) because the cell nuclei occur in two or more levels in a row of aligned cells Name:____________________________ Date Due:_____________________ Epithelial Tissues Assignment 1. Epithelia are classified by the number of cell layers and the ___________________________ of the cells. (1 mark) 2. Distinguish between simple and stratified. (2 marks) 3. Describe the 3 main shapes of epithelial cells: (3 marks) 4. Scientific Drawings (review how to make an illustration of the slides). (12 marks) Label each drawing with the type of tissue, its location and function Identify any important structures (nuclei ...etc) on your drawings Type of tissue, location, function Type:__________________ Found in:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ Function:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Type:__________________ Found in:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ Function:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Scientific drawing Type:__________________ Found in:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ Function:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Type:__________________ Found in:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ Function:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Type:__________________ Found in:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ Function:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Type:__________________ Found in:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ Function:_______________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________