Unit 2 notes - Grant Community High School
advertisement

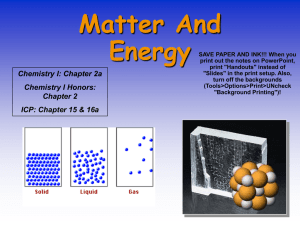
Unit 2: Matter and Energy Notes Matter Chemistry is the study of properties and characteristics of matter and materials. Matter is anything that takes up space, has mass, and shows inertia. An atom is the basic unit of matter. The atom can be broken down into smaller parts called subatomic particles. Subatomic particles include: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Proton: positively (+) charged subatomic particle. Electron: negatively (-) charged subatomic particle. Neutron: Neutral charged subatomic particle. Nucleus: center of atom made of protons and neutrons. When 2 or more atoms are chemically bonded together it’s called a molecule. states of matter solid liquid plasma gas molecules slide past each other but are close together definite volume but no definite shape molecules vibrate in a relatively fixed position definite shape & volume extreme temperatures strip electrons from protons "soup of ions" large distance between collisions no definite shape or volume The phase a substance is in is called its state of matter. In a solid, molecules vibrate, but are locked in place. In a liquid, molecules can shift around but are still very close together. In a gas, molecules are so far apart there is no definite shape or volume. Plasma is a special state of matter in which electrons are stripped off of atoms. This usually happens at high temperatures and creates a soup of positive and negative ions. Examples are stars, the sun, and fluorescent light bulbs The melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. Below this temperature the substance will be a solid. Above this temperature the substance is a liquid The boiling point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. Below this temperature the substance will be a liquid. Above this temperature the substance is a gas melting SOLID boiling LIQUID freezing GAS condensing Pure Substances: Elements and Compounds A pure substance is made up of one material only. It can be an element or a compound. If it’s an element you can find it in the periodic table. The substance has unique physical & chemical properties. An element is a simple pure substance made of only one kind of atom. Diatomic gases are atoms that are always found as molecules. Examples are H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2 Allotropes are different molecular forms of the same element. A compound is formed when 2 or more different elements are chemically joined in whole number ratios. A molecular compound is made of neutral molecules joined together. An ionic compound is made up of 2 or more ions (charged particles) Mixtures: Heterogeneous vs. Homogenous A mixture is a physical combination of 2 or more substances. The separate parts can be physically separated. There are no new substances formed. There are no chemical reactions. A heterogeneous mixture doesn’t look uniform; you can tell it’s a mixture. The components are not uniformly distributed. Different regions of the mixture can have different properties. Examples are orange juice & chocolate chip cookies. A homogenous mixture looks uniform, you can’t tell it’s a mixture. The components are uniformly distributed. Examples are air, gasoline, and 14-carat gold. A solution is a homogeneous mixture. It’s made of a solute dissolved in a solvent. You can’t separate the solute and solvent by filtering. The solute won’t settle out. An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of different metals. Mixing metals can change the properties, making the metal stronger, or lighter. All phases of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) can be in a homogeneous mixture. Ex: air, gasoline, 14-karat gold Homogeneous metals are called alloys. Homogeneous liquids are called solutions. Solutions cannot be separated through a filter. Mixtures vs. Compounds Mixtures are physical combinations, compound are chemical combinations. Compounds have their own unique properties, mixtures have the combined properties of their components. Atoms in compounds always combine in whole number ratios; mixtures can vary. To separate a compound into the pure substances that make it up you must use some kind of chemical change. A mixture can be separated into its parts by using a physical process (aka physical separation method) Mixtures are physical combinations. Compounds are chemical combinations. Compounds change properties, while mixtures have a combined property. Physical vs. Chemical Chemists study physical and chemical properties. Physical properties are properties that can be measured without changing the chemical nature of a substance. Physical properties can be intensive or extensive. Extensive physical properties depend on the amount of matter. Examples of extensive properties are mass, volume, size, and length. Intensive properties don’t depend on how much stuff you have. Examples are boiling point, melting point, heat capacity, conductivity, color, and density How a substance reacts with other substances are chemical properties. When atoms and molecules react to form a new chemical there is often a change in physical properties Chemical reactions can be used to change one substance into another In a chemical reaction, reactants are on the left of the arrow and products are on the right Reactants products What you start with what you end up with N2 + H2 NH3 List the products in this reaction: List the reactants in this reaction: Any change in size, shape, mass, or temperature, or phase is a physical change. The change is physical if no new substances are formed. Another clue is the ability to get the original stuff back Chemical changes happen when chemical reactions produce new substances with new physical properties. Once the new substance is made there’s no going back. When you burn a wood splint it’s gone for good. Signs of chemical change are bubbles, formation of a solid, change in temperature or color. Classify the following as either a chemical (CP) or physical property (PP): 1. Color ______ 2. Flammability ______ 4. Odor______ 5. Taste______ 3. Hardness ______ Classify the following as either a chemical (CC) or physical change (PC): 1. Boiling water becomes steam ______ 2. Butter turns rancid ______ 3. Burning of wood ______ 4. Mountain snow melting in spring ______ 5. Decay of leaves in winter ______ Energy Energy is a conserved quantity that, when transferred from one system to another causes a change or the ability to do work. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. The equation for kinetic energy is KE = ½mv2 m = mass and v = velocity Potential energy is energy due to position or stored energy. Examples are a stretched rubber band, a battery, and water behind a dam Energy can be transformed into other forms of energy. Other energy forms besides kinetic and potential energy are mechanical, thermal, and chemical Energy can never be created or lost, it can only be transformed. This is the Law of Conservation of Energy If a reaction or change releases energy it’s called exothermic Examples of Exothermic Reactions Wood burning Fireworks exploding A chemical reaction that causes a beaker to get warm If a reaction or change absorbs energy it’s called endothermic Examples of Endothermic Reactions Water boiling Ice melting A chemical reaction that causes a beaker to get cold