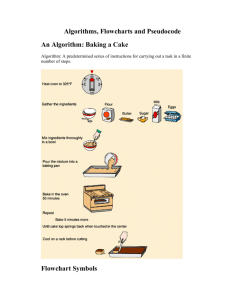
Student Provided Questions Test 1
advertisement

Chapter 1 1. Which of these is not a characteristic that makes information useful? a. b. c. d. Relevance Length Timeliness Verifiability answer: b. Length 2. What entails adding features or services not provided by competitors to a product so you can charge customers a premium price? a. b. c. d. Product differentiation strategy Accounting Information System Low-cost strategy needs-based strategic position answer: a. Product differentiation strategy 3. What are repetitive, routine, and understood well enough that they can be delegated to lower-level employees in the organization. a. b. c. d. Semistructured decisions Unstructured decisions Structured decisions Random decisions answer: c. Structured decisions Chapter 2 1. With what kind of code are blocks of numbers within a numerical sequence reserved for categories, having meaning to the user. a. b. c. d. sequence block group color answer: b. block 2. The set of fields that contain data about various attributes of the same entity forms a: a. b. c. d. attribute data value record file answer: c. record 3. This is a formal expression of goals in financial terms: a. b. c. d. budget performance report charts graphs answer: a. budget Chapter 3 1. This illustrates the flow of documents and information among areas of responsibility within an organization. a. b. c. d. internal control flow chart document flowchart system flow chart program flow chart answer: b. document flow chart 2. In flow chart storage symbols, a file looks like what: a. b. c. d. an inverted triangle with an N in it a circle a pentagon a rhombus answer: a. an inverted triangle with an N in it 3. A rectangle represents this on a flow chart: a. manual operation b. Display c. Computer processing d. On-line storage answer: c. computer processing Chapter 4 1. This represents everything in the database as being stored in the form of tables: a. b. c. d. relational data base tuple TPS reports spread sheet answer: a. relational data base 2. What is used to build the data dictionary and initialize or create the database? a. b. c. d. data manipulation language data query language C++ data definition language answer: data definition language 3. What is a schema? a. b. c. d. How the user of programmer conceptually organizes and understands the data How and where the data are physically stored Describes the logical structural of a database A type of flow chart. answer: c. Describes the logical structural of a database Chapter 1 1) What is it called when the organizations subsystem is not consistent with another subsystem or with the larger system? a. Goal congruence b. Goal conflict c. information overload d. unconformity Answer: b 2) Which characteristic of making information useful reduced uncertainty by helping you predict what will happen or confirm what already has happened? a. reliability b. timeliness c. understandability d. relevance Answer: d 3.) Which is NOT a reason to study accounting information systems? a. the skills are critical to career success b. AIS topics are covered on the new CPA exam c. AIS systems focus on number crunching d. AIS topics impact corporate strategy and culture Answer: c Chapter 2 1) Which is NOT an example of an external party user of Business? a. Customers b. creditors c. governmental agencies d. managers Answer: d 2) Which cycle involves interactions with your suppliers when you buy goods or services and pay cash? a. revenue cycle b. expenditure cycle c. production cycle d. human resources cycle e. financing cycle Answer: b 3.) A file used to store cumulative information about resources and agents is? a. ledger b. Journals c. subsidiary ledger d. general ledger Answer: A Chapter 3 1.) A DFD is a representation of which of the following? a. relationship among modules, data, and programs of an AIS b. flow of data in an organization c. decision rules in a computer program d. computer hardware configuration Answer: b 2.) Which of the following statement is false? a. A flowchart is an analytical technique used to describe some aspect of an information system in a clear, concise, and logical manner b. Flowcharts use a standard set of symbols to describe pictorially the flow of documents and data through a system c. A system flowchart is a narrative representation of an information system d. A program flowchart shows the logic used in computer programs Answer: c 3.) Data sources and destinations are represented in a data flow diagram as? a. a square b. a curved arrow c. a circle d. two parallel lines e. none of the above Answer: a Chapter 4 1.) A data dictionary contains what? a. list of all programs in which a data item is used b. a list of all synonyms for the data elements in a particular file c. a list of all data elements used by a particular user d. list of all output reports in which a data element is used e. all the above Answer: e 2.) Which is used for data maintenance, which includes such operations as updating, inserting, and deleting portions of the database? a. data definition language b. data query language c. data manipulation language d. report writer Answer: c 3.) In each row in a relation, what contains data about a specific occurrence of the tyle of entity represented by that table? a. Foreign Key b. Tuple c. Primary Key d. attribute Answer: b Ch. 1 1. Which is NOT a benefit of information? a. reduction of uncertainty b. Improved decisions c. A better ability to plan and schedule activities d. all are benefits of information 2. Which type of info is for mostly internal use? a. Mandatory Information b. Essential Information c. Discretionary Information d. All of the above 3. Which is NOT a support activity to the value chain? a. Firm infrastructure b. Human Resources c. Technology d. Outbound logistics Ch. 2 1. Which are NOT example of Source Data Automation? a. ATM’s b. Point-or-sale scanners in retail stores c. Bar code scanners d. All are examples or source data automation 2. 1000000-1999999 is and example of what kind of coding? a. Sequence b. Block c. Group d. Random 3. The set of fields that contain data about various attributes of the same entity froms a a. file b. master file c. record d. post it note Ch. 3 1. Data sources and data destinations are represented by what figure usually? a. Triangle b. a Line c. Circle d. Squares 2. Which provides a summary level view of a system? a. Context Diagram b. Data flow c. Data destinations d. Processes 3. Which shows the sequence of logical operations performed by a compter in executing a program? a. system flowchart b. document flowchart c. data store d. program flow chart Chapter 1 1) The Systems Concept _______________ a) discourages integration b) sends information to the user c) are facts collected by an information system d) encourages integration 2) The benefits of information include a) reduction of uncertainty b) improved decisions c) improved ability to plan and schedule events d) All of the above e) None of the above 3) Which of the following is not a characteristic that makes information useful? a) reliability b) completeness c) timeliness d) briefness Chapter 2 1) Businesses engage in many activities including a) acquiring capital b) purchasing inventory c) collecting payment from cutomers d) all of the above 2) An example of a transaction is a) selling goods to customers b) depreciating equipment c) composing an invoice d) all of the above e) both a and b 3) Information output is a step in which cycle? a) revenue cycle b) financing cycle c) data processing cycle d) payroll cycle Chapter 3 1) Documentation includes which of the following tools a) Narratives b) Flowcharts c) Diagrams d) All of the above 2) What do data flow diagrams show? a) where data comes from b) how data flows c) the processes performed on data d) where data goes e) all of the above 3) Which of the following is a type of flowchart? a) Integration flowchart b) Pictoral flowchart c) System flowchart d) Time flowchart Chapter 4 1) Information about attributes of an entity are stored in a) fields b) records c) cases d) lockers 2) The person responsible for the database is the a) database overseer b) database maker c) database administrator d) CEO 3) Database technology provides which of the following benefits to organizations? a) data integration b) data sharing c) reporting flexibility d) all of the above Chapter 1 1. What is the benefit produced by the information minus the cost of producing it? a. value of information b. mandatory information c. discretionary information d. operational control 2. What is a system that collects, records, stores and processes data to produce information for decision makers? a. database b. flowchart c. general ledger d. accounting information system 3. a. b. c. d. Which of the following is not a primary activity of an organization’s value chain? operations marketing and sales outbound logistics technology Chapter 2 1. The _______ cycle is where raw materials are transformed into finished goods. a. revenue b. production c. financing d. expenditure 2. a. b. c. d. Which of the following is not a type of file processing? updating adding deleting producing 3. A ________ is used to record infrequent or not routine transactions. a. specialized journal b. specific journal c. general journal d. detailed journal Chapter 3 1. __________ is a graphical description of the relationship among the input processing and output in an information system. a. system flowchart b. program flowchart c. document flowchart d. data flow diagram 2. A __________ is an analytical technique used to describe some aspect of an information system in a clear, concise, and logical manner. a. Payroll journal b. Context diagram c. Flowchart d. Accounting notebook 3. A ________ represents the flow of data between processes, data stores, and data sources and destinations. a. data flow b. cash disbursements journal c. processing cycle d. general journal Chapter 4 1. A ___________ acts as an interface between the database and the various application programs. a. data warehouse b. database management system c. relational data model d. querie 2. The ________ view refers to how and where the data are physically arranged and stored in the computer system. a. physical b. logical c. detailed d. general 3. a. b. c. A _______ is an attribute in a table that is a primary key in another table. tuple data dictionary foreign key d. function key Chapter 1 1. Information is ___________. a. is data that is meaningless b. is data that must be put in a computer c. is data that has been organized and processed to provide meaning d. is the same as data 2. Which of the following is not a benefit of information? a. reduces uncertainty b. improves decisions c. improves ability to plan and schedule d. reduces time work load 3. Who requires mandatory information? a. IRS b. Managers c. Stock Brokers d. Investors Chapter 2 1. A transaction is a (an) __________. a. transaction between two entities to exchange goods or services b. process that is rarely dealt with in AIS c. other event that can be measured in economic terms d. either a or c 2. Which of the following does not collaborate with AIS systems? a. Vendors b. Children c. Managers d. Government Agencies 3. The Revenue cycle __________. a. involves interaction with customers. b. involves interaction with employees. c. involves selling goods or services and getting cash d. both a and c Chapter 3 1. DFDs show a. Where data comes from b. Where data goes c. How it flows d. all the above 2. This symbol represents a. b. c. d. data source and destinations data flows processes data stores 3. A data dictionary contains a. MIS terms b. explanations of how to use data c. descriptions of all data elements d. none of the above Chapter 4 1. Why did the proliferation of master files develop problems? a. the same information was stored multiple times b. it made it difficult to obtain a wide view of the information c. information was not always constant across the files d. all the above 2. What is a database? a. a spreadsheet b. a set of interrelated, centrally coordinated files c. a financial institution d. a set of unrelated files, ordered alphabetically 3. ________ are the most popular type of data bases for transaction processing. a. Un-relational data bases b. Transaction data bases c. Relational data bases d. None of the above Chapter 1 1. The value of information is _____. A. the benefit produced by the information minus the cost. B. the accuracy of the information. C. the amount at which the information can be sold. D. the level of demand for the information. 2. The operations activities in the value chain consist of _____. A. distributing products or services to customers. B. transforming inputs into final products or services. C. marketing and selling products or services. D. post-sale support to customers. 3. AIS can add value to an organization by _____. A. improving efficiency B. sharing knowledge. C. improving decision making. D. all of the above. Chapter 2 1. In a typical chart of accounts, accounts receivable would have which of the following account codes? A. 320. B. 410. C. 120. D. 701. 2. Data values are stored in a physical space called a _____. A. record. B. entity. C. file. D. field. 3. The process of selling goods or services in exchange for the promise to pay cash is called the _____ cycle. A. financing B. payroll C. expenditure D. revenue Chapter 3 1. In a data flow diagram, processes are usually represented by a _____. A. square. B. triangle. C. circle. D. arrow. 2. What information should be included on the final copy of a DFD? A. name of the DFD. B. date prepared. C. preparer’s name. D. all of the above. 3. Which of the following statements is false? A. DFD’s and flowcharts are the two most frequently used documentation tools. B. Systems development tools are helpful for internal control purposes. C. Department DFD’s are used by external auditors. D. DFD’s are only used to show ideal methods for documentation routing. Ch. 1 1. __________ occurs when a decision or action of a subsystem is inconsistent with another subsystem or the system as a whole. a. Goal congruence b. Information overload c. Goal conflict d. Systems concept Answer: C 2. Which of the following is not a characteristic of useful information? a. Relevant b. Complete c. Integration d. Timely Answer: C 3. Which of the following is not a primary activity of an organization’s value chain? a. Inbound logistics b. Operations c. Purchasing d. Outbound logistics Answer: C Ch. 2 4. The ________ cycle is where goods and services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash? a. Expenditure b. Production c. Revenue d. Financing Answer: C 5. The ________ contains summary-level data for every asset, liability, equity, revenue, and expense account of the organization. a. Control account b. Sequence code c. General ledger d. Chart of accounts Answer: C 6. A(n) _________ is something about which information is stored. a. File b. Record c. Entity d. Field Answer: C Ch. 3 7. __________ encompasses the narratives, flowcharts, diagrams, and other written materials that explain how a system works. a. Narrative description b. Data sources c. Documentation d. Processes Answer: C 8. __________ symbols represent devices or media that provide input to or record output from processing operations. a. Processing b. Storage c. Input/Output d. Flow and miscellaneous Answer: C 9. This is the symbol for a __________. a. Display b. Terminal c. Document d. Decision Answer: C Ch. 4 10. Companies are developing very large databases called __________. a. Database system b. Database administrator c. Data warehouses d. Database management system Answer: C 11. Which of the following is not a benefit of an organization from database techonology? a. Data integration b. Data sharing c. Logical view d. Reporting flexibility Answer: C 12. __________ describes the logical structure of a database. a. Physical view b. Tuple c. Schema d. Normalization Answer: C Chapter 1 Questions 1). What business strategy entails striving to be the most efficient producer of a product or service? a. product differentiation strategy b. synergy c. low-cost strategy d. semi structured decisions ANSWER: c. low-cost strategy 2). Which of the following is not a primary activity of an organization’s value chain? a. Inbound Logistics b. Operations c. Marketing and Sales d. Sharing Knowledge ANSWER: d. Sharing Knowledge 3). __________________ is a system that collects, records, stores, and processes data to produce information for decision makers. a. Value Chain b. Accounting Information System (AIS) c. Information Technology d. Internal Controls System ANSWER: b. Accounting Information System (AIS) Chapter 2 Questions 1). The process that begins with capturing transaction data and ends with an informational output such as the financial statements is called _____________? a. Transaction Processing b. Give-get Exchange c. Bicycle Processing d. Source Automation ANSWER: a. Transaction Processing 2). The general ledger account corresponding to a subsidiary ledger is called a/an ________________? a. general ledger acquisition b. chart of accounts c. optional account d. control account ANSWER: d. control account 3). Under data processing there are four different types of file processing, which of the following is not one of the types? a. Updating b. Changing c. Listening d. Deleting ANSWER: c. Listening Chapter 3 Questions 1). There are four documentation tools that we discuss they are as follows Data Flow Diagram, Document Flowchart, System Flowchart, and _____________? a. Profit Flowchart b. Program Flowchart c. Destination Flowchart d. Process Flowchart ANSWER: b. Program Flowchart 2). The highest level Data Flow Diagram is referred to as _____________? a. Context Diagram b. Process c. Conceptual Diagram d. Narrative Diagram ANSWER: a. Context Diagram 3). _____________ illustrates the flow of documents and information among areas of responsibility within an organization. a. Internal Control Flowchart b. External Control Flowchart c. Document Flowchart d. Systems Flowchart ANSWER: c. Document Flowchart Chapter 4 Questions 1). Which of the following are not a benefit of database technology? a. Data Integration b. Data Sharing c. Reporting Flexibility d. All of the above are benefits ANSWER: d. All of the above are benefits 2). ______________ is used for data maintenance, which includes such operations as updating, inserting, and deleting portions of the database. a. Data Definition Language (DDL) b. Data Manipulation Language (DML) c. Data Query Language (DQL) d. None of the Above ANSWER: b. Data Manipulation Language (DML) 3). Each row in a relation, called a ____________ , contains data about a specific occurrence of the type of entity represented by that table. a. tuple b. model c. foreign key d. none of the above ANSWER: a. tuple Chapter 1 1. The value of information is: a. the benefit produced by the information minus the cost of producing it b. data that has been organized and processed to provide meaning to a user c. users can make better decisions d. facts about the activities that take place 2. Information should be: a. relevant b. reliable c. timely d. all of the above e. none of the above 3. Structured decisions are: a. characterized by incomplete decision making rules b. are nonrecurring and nonroutine c. repetitive, routine, and understood well enough d. none of the above Chapter 2 1. Source data automation is used to: a. improve the accuracy and efficiency of data input b. improve the accuracy and efficiency of data output c. create turnaround documents d. none of the above 2. An entity is a. characteristics of interest b. something about which information is stored c. a physical space d. all of the above 3. Which is not of the types of file processing: a. updating b. changing c. adding d. formatting Chapter 3 1. The highest level DFD is: a. conceptual diagram b. context diagram c. source diagram d. none of the above 2. A system flowchart: a. illustrates the sequence of logical operations performed by a computer b. depicts the relationship among the input, processing, and output of an AIS c. represents the transformation of data d. none of the above 3. Which of the following is not one of the flowcharting symbol categories: a. Input/output b. Processing c. Storage d. Transformation Chapter 4 1. Which of the following is a level of a schema a. conceptual b. external c. internal d. none of the above e. all of the above . 2. Which of the following is not one of the benefits of Database technology: a. Data integration b. Data sharing c. Reduced labor force d. Data independence 3. A data dictionary is: a. large database b. contains information about the structure of the database c. used to build the DBMS d. used to interrogate the database Chapter 1 1) Information can be provided to both internal and external users, most internal information for a user is? a) Necessary information b) Mandatory information c) Essential information d) Discretionary information 2) How does information flow in the value chain from left to right? a) Inbound Logistics->Operations->Outbound Logistics->Marketing and Sales->Service b) Operations->Inbound Logistics-> Outbound Logistics->Marketing and Sales->Service c) Marketing and Sales-> Operations->Inbound Logistics-> Outbound Logistics-> Service d) Inbound Logistics-> Marketing and Sales-> Operations-> Outbound Logistics-> Service 3) The owner of Company Inc. needs to hire new senior management for the company, what kind of decision is this? a) Structured decision b) Semistructured decision c) Unstructured decision d) Complex decision Chapter 2 4) Going to Wal-Mart and buying a good and giving the cashier cash for the good goes with which type of cycle? a) Production cycle b) Expenditure cycle c) Financing cycle d) Revenue cycle 5) Out of the following which is not useful data for a sales transaction? a) Quantity of each item sold b) Item(s) sold c) Type of item sold d) Total amount of the sale 6) Prenumbered checks, invoices, and purchase orders use what type of coding system, so that there will be no gaps in the sequence? a) Block code b) Group code c) Single code d) Sequence code Chapter 3 7) A data flow diagram (DFD) graphically describes the flow of data within an organization, which one is not one of the four basic elements that DFD is composed of? a) Data flows b) Data sources and destinations c) Data processes d) Data stores 8) This type of flowchart is useful in analyzing the adequacy of control procedures in a system, such as internal checks and segregation of functions. a) System flowchart b) Document flowchart c) Internal control flowchart d) Program flowchart 9) Which one is not a place where data is stored? a) File b) Diskette c) Terminal d) On-line storage Chapter 4 10) A store manager thinks about his information on customers and how it is stored, this is called? a) Physical view b) Imagination view c) Logical view d) Temporary view 11) Every DBMS must provide a means of performing the three basic functions of creating, changing, and querying the database. Which language of DBMS describes the logical views for each individual user or programmer? a) Data manipulation language (DML) b) Data definition language (DDL) c) Data query language (DQL) d) Data internal language (DIL) 12) Several problems can occur when you try to store all the sales invoice data in one table. Which of the follow has to do with changes in vales not being correctly recorded? a) Update anomaly b) Insert anomaly c) Delete anomaly d) Correction anomaly Chapter 1 1. What occurs when the activity of a subsystem is not consistent with another subsystem or with the larger system? a) b) c) d) 2. What word describes dependable and faithfully portraying events and activities? a) b) c) d) 3. information overload goal conflict goal congruence information inconsistency reliability relevance completeness timeliness The AIS design is affected by all the following except: a) b) c) d) Information Technology strategy support activities occupational culture Chapter 2 1. Internal Parties include: a) b) c) d) 2. customers creditors vendors management All of the following are a transaction cycle except: a) information cycle b) expenditure cycle c) production cycle d) payroll cycle 3. In what system is the series of operations performed on data referred to as the data processing cycle? a) b) c) d) manual data AIS computer based Chapter 3 1. What flowchart depicts the relationship among the input, processing, and out put of the AIS? a) b) c) d) 2. What flowchart illustrates the flow of documents and information among areas of responsibility within an organization? a) b) c) d) 3. program system process document program system process document Data sources are represented in a data flow diagram as a: a) b) c) d) square circle triangle two parallel lines Chapter 4 1. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of database technology? a) b) c) d) Data integration data sharing more data inconsistencies cross-functional analysis 2. All of the following are a DBMS language except: a) b) c) d) 3. data definition language query information language data manipulation language data query language An attribute, or combination of attributes, that uniquely identifies a specific row in a table is called a/an_______? a) b) c) d) primary key foreign key anomaly tuple Chapter 1 1. Data that have been organized and processed to provide meaning to a user are? a. b. c. d. Answer: a Information Goal Conflict AIS Value Chain 2. Which one of the following is NOT one of the characteristics that make information useful? a. b. c. d. Answer: d Relevance Reliability Completeness None of the above 3. A system that collects, records, stores, and processes data to produce information to decision makers is a(n)? a. b. c. d. Answer: a AIS MIT AAA WVU Chapter 2 1. The interaction between external and internal parties is usually? a. b. c. d. Answer: b one way two way three way no way 2. The 5 major transaction cycles include all of the following except? a. b. c. d. Answer: d Revenue Expenditure Production Management 3. The give-get of the Financing Cycle is? a. b. c. d. Answer: a give cash-get cash give goods-get goods give cash-get goods give cash-get labor Chapter 3 1. Which one of the following is NOT one of the 4 basic DFD elements? a. b. c. d. Answer: d Data Sources and Destinations Data Flows Data Stores Flowcharts 2. Data sources and Destinations appear in a DFD as? a. arrows b. triangles c. squares d. diamonds Answer: c 3. Data Flow Diagrams place heavy emphasis on _________ of a system whereas Flowcharts place more emphasis on _________ of a system. a. b. c. d. Answer: a logical aspects / physical characteristics physical characteristics / logical aspects the same emphasis is on both none of the above Chapter 4 1. All the fields containing data about one entity for a(n)? a. b. c. d. Answer: a record table attribute database 2. A(n) ______ describes the logical structure of a database. a. b. c. d. Answer: d entity file class schema 3. A(n) _______ is an abstract representation of the contents of a database. a. b. c. d. Answer: a data model data storage data item none of the above Chapter 1 1.) ___________ occurs when a decision or action of a subsystem is inconsistent with another subsystem or the system as a whole. A: Goal Congruence B: Goal Conflict C: Information Overload D: Integration Answer: B 2.) An organization’s value chain consists of all of the primary activities that directly provide value to its customers except A: Inbound Logistics B: Operations C: Technology D: Marketing and Sales Answer: C 3.) __________________ relates to the effective and efficient performance of specific tasks. A: Operational Control B: Management Control C: Strategic Planning D: Low Cost Strategy Answer: A Chapter 2 1.) The __________________ cycle is where raw materials are transformed into finished goods. A: Revenue B: Financing C: Expenditure D: Production Answer: D 2.) __________________ is a list of all general ledger accounts an organization uses. A: Sequence Codes B: Chart of Accounts C: Subsidiary Ledger D: General Journal Answer: B 3.) __________________ is a characteristic of interest, which needs to be stored. A: Record B: Entity C: Attribute D: File Answer: C Chapter 3 1.) __________________is/are the data flow diagram symbol for transformation processes. A: A square B: Two horizontal lines C: Straight or curved lines with arrows D: A circle Answer: D 2.) __________________depict the relationship among the input, processing, and output of an Accounting Information System. A: System Flowcharts B: Program Flowcharts C: Document Flowcharts D: Internal Control Flowcharts Answer: A 3.) __________________are written step-by-step explanations of system components and interactions. A: Documentations B: Data Sources C: Narrative Descriptions D: Transformation Processes Chapter 4 1.) __________________is used to interrogate the database. It is also responsible for retrieving, storing, ordering, and presenting subsets of the database in response to user queries. A: Data Definition Language (DDL) B: Data Query Language (DQL) C: Data Manipulation Language (DML) D: All of the above Answer: B 2.) All of the following are advantages of database systems except: A: Data integration B: Reporting flexibility C: Data redundancy D: Data sharing Answer: C 3.) The rule, __________________, explains that the primary key cannot be null. A: Attribute integrity rule B: Referential integrity rule C: Entity integrity rule D: None of the above Answer: D Chapter 1 1. What is the characteristic of making information useful? a. Relevance b. Reliability c. Completeness d. All the above Answer: d 2. ____________ is the accounting, finance, legal and general administration activities that allow an organization to function. a. Human resources b. Technology c. Firm infrastructure d. Purchasing Answer: C 3. _________ information is required to conduct business with external parties. a. mandatory b. Internal c. External d. Essential Answer: d Chapter 2 1. Major activity of revenue is a. Receive customer payments b. Update payroll records c. Handle purchase returns d. Store goods Answer: a 2. The cycle where raw materials are transformed into finished goods is called a. Revenue b. Production c. Expenditure d. Financing Answer: b 3. Which cycle is involving interactions with customers? a. Production b. Expenditure c. Revenue d. Business Answer: c Chapter 3 1. Which symbols represent the device used to store data that the system is not using right now? a. processing b. Input c. Flow d. Storage Answer: d 2. Which flowcharts describe the flow of documents and information of an organization? a. Internal control b. External control c. General d. Document Answer: d 3. What percentages of professionals use DFDs? a. 68.2% b. 97.6% c. 62.5% d. 76.2% Answer: c Chapter 4 1. Which data language used to build the data dictionary and create database? a. The data query language b. The data manipulation language c. The data definition language d. None of the above Answer: c 2. A _________ illustrate the logical structure of a database. a. data b. tuple c. files d. schema Answer: d 3. Which level of schema provides a low level view of database? a. External level b. Internal level c. Conceptual level d. Relational level Answer: b Chapter 1 1. _____ occurs when the activity of a subsystem is not consistent with another subsystem or with the larger system. A. Goal congruence B. Goal conflict C. Goal resolution D. Goal acceptance 2. Organizations collect data about: A. events B. resources C. agents D. all of the above 3. A. B. C. D. Benefits of information – cost of information = ________. value of information information overload. Information costs. All of the above. Chapter 2 1. A. B. C. D. Giving goods and getting cash is the _______ cycle. expenditure production revenue financing 2. A ________ file is a file that stores cumulative information about an organization’s entities. A. transaction B. master C. entity D. attribute 3. A. B. C. D. Which is not a type of output? documents reports queries processing Chapter 3 1. A. B. C. D. Which is not a type of flowcharting symbol? input/output processing storage attribute 2. A. B. C. D. A rectangle is a ______ symbol. Computer processing Manual operation Online storage document 3. A. B. C. D. A decision is represented by a ____. circle rectangle diamond arrow Chapter 4 1. A. B. C. D. Which are benefits of database technology? data integration data sharing reporting flexibility all of the above 2. A. B. C. D. A ______ describes the logistical structure of a database. schema attribute file none of the above 3. A. B. C. D. The entity integrity rule states that _______. the primary key has to be 1. the primary key cannot be null. the primary key has to be a number none of the above. Chapter 1 1. ___________ occurs when the subsystem’s goals are in line with the organizations goals. a. b. c. d. goal conflict goal congruence goal orientated none of the above Answer: B 2. Facts that are collected, recorded, stored and processed by an information system is/are called ____________. a. Information b. System concepts c. Data d. A and C Answer: C 3. Benefits of Information may include a. b. c. d. reduction of uncertainty improved decisions improved ability to plan and schedule activities All of the above Answer: D Chapter 2 1. Which one of the five major business transaction cycles involves interaction with employees? a. b. c. d. revenue cycle expenditure cycle production cycle human resource/payroll cycle Answer: D 2. Which one of the five major business transaction cycles involves interactions with investors and creditors a. b. c. d. Revenue Cycle Expenditure cycle Financing cycle Production cycle Answer: C 3. Which step is not a step in the data processing cycle a. b. c. d. data input data storage data processing These are all steps. Answer: D Chapter3 1. ____________ show graphical descriptions of the sources and destinations of data. a. b. c. d. Data Flow diagrams Document Flowcharts System Flowcharts Program Flowcharts Answer: A 2. Which of the following is considered to be a basic element in a data flow diagram? a. b. c. d. data sources and destinations data stores a and b none of the above Answer: C 3. In a data flow diagram processes appear as a _____ and represent ________. a. arrows; the flow of data between sources and destinations, processes, and data stores b. Squares; organizations or individuals that send or receive data used or produced by the system. c. Circles; the transformation of data d. None of the above Answer: C Chapter 4 1. A ______ is anything about which the organization wishes to store data. a. b. c. d. attributes entity field record Answer: B 2. Database technology provides which of the following benefits to organizations a. Data Integration b. Data sharing c. Data independence d. All of the above Answer: D 3. Which of the following is not one of the three levels of a schema? a. b. c. d. internal level external level first level conceptual level Chapter 1 1) ______________ decisions are characterized by incomplete decision making rules and the need for subjective assessments and judgments to supplement formal data analysis. a. Structured b. Semistructured c. Unstructured d. Constructed 2) a. b. c. d. Which of the following is not an example of a Support Activity? Human Resources Technology Firm Infrastructure Marketing and Sales 3) A _______________ strategy entails adding features or services not provided by competitors to a product so you can charge customers a premium price. a. Low-cost b. Product Differentiation c. Access-based d. Planning Chapter 2 1) The ________________ is the transaction cycle in which goods and services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash. a) Revenue Cycle b) Expenditure Cycle c) Production Cycle d) Financing Cycle 2) a) b) c) d) An employee’s pay rate is an example of a(n): record entity attribute field 3) A general journal is used to record: a. cash receipts b. loan payments c. purchases on account d. cash disbursements Chapter 3 1) a. b. c. d. Processing symbols are used to show what type of device is used to process data indicate when processing is performed manually a. & b. none of the above 2) a. b. c. d. Data sources and data destinations are represented by squares circles triangles rectangles 3) Which of the following is not one of the four basic elements of a data flow diagram? a. data sources and destinations b. data flows c. data charts d. data stores Chapter 4 1) The _________________ contains information about the structure of the database. a. schema b. data dictionary c. data warehouse d. data chart 2) Which of the following is used for updating, inserting, and deleting portions of the database? a. data query language b. data definition language c. data delivery language d. data manipulation language 3) a. b. c. d. An attribute in a table that is a primary key in another table is a foreign key standard key comparable key cross key Chapter 1 1. What type of decisions can often be fully automated? a. unstructured decisions b. semistructured decisions c. structured d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: C. 2. A variety-based strategic position offers a. a wide range of products and services b. a subset of the industry’s products or services c. products or services to serve most of the needs of particular group of customers d. products or services to customers in a specific geographic location Answer: B. 3. What decision scope relates to establishing organizational objectives and policies for accomplishing those objectives? a. Management control b. Operational control c. Strategic planning d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: C. Chapter 2 4. Retail stores do not utilize which on of these major transaction cycles in its AIS? a. revenue cycle b. financing cycle c. production cycle d. all of the above e. none of the above Answer: C. 5. Which type of data processing method is more accurate? a. batch processing b. real-time processing c. both a and b have the same accuracy d. none of the above Answer: B. 6. A group of interrelated, centrally coordinated computer files are a. transaction files b. database files c. master files d. none of the above Answer: B. Chapter 3 7. In addition to data sources and destinations, a context diagram includes a. a data store b. a transformation process c. all of the above d. none of the above Answer: B. 8. Which is the highest level data flow diagram? a. Level 0 DFD b. Level 1 DFD c. Level 2 DFD d. A context DFD Answer: D. 9. Which would be an example of a designated Level 2 process on a DFD? a. 0.2 b. 1.2 c. 2.0 d. 2.2.2 Answer: D. Chapter 4 10. Semantic data modeling has which of the following advantages over normalization? a. Produce tables in third normal form, which are free to delete anomalies b. Make use of a system designer’s knowledge about business processes and practices c. Resulting graphical model explicitly represents information about the organization’s business processes and policies d. a and b e. b and c Answer: E. 11. Creating smaller tables with primary and foreign keys solves which of the following anomalies? a. insert anomaly b. delete anomaly c. update anomaly d. all of the above Answer: D. 12. The relational data model of DBMS’s represents data in the form of a. graphs b. charts c. tables d. none of the above Answer: C. Ch. 1 1. ________ are sets of interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal. a. Data b. Information c. Systems d. None of the above 2. ________ occurs when the subsystem’s goals are in line with the organization’s goals. a. Goal conflict b. Goal congruence c. System alignment d. Matching 3. Which of these actions would be considered to “add value?” a. Make a product faster b. Make a product more reliable c. Make a product with enhanced features d. All of the above Ch. 2 1. In which cycle would you sell a good or service in order to get cash? a. Revenue cycle b. Production cycle c. Financing cycle d. Expenditure cycle 2. A _________ is a set of interrelated, centrally-coordinated files. a. File b. Database c. Record d. Field 3. In which cycle would you raise capital through stock or debt? a. Revenue cycle b. Production cycle c. Financing cycle d. Expenditure cycle Ch. 3 1. A ________ is a graphical description of the sources and destinations of data. a. System flowchart b. Document flowchart c. Program flowchart d. Data flow diagram 2. What should be included on each page of a data flow diagram? a. Name of the DFD b. Date prepared c. Preparer’s name d. All of the above 3. This symbol - represents what in a flowchart? a. Decision b. On-page connector c. Document d. File Ch. 4 1. Very large databases are called what a. DBMS b. Data warehouses c. Records d. All of the above 2. Which one of the following is not a level of schema in a database? a. Internal level b. External level c. Interrelated level d. Conceptual level 4. Every DBMS must provide a means of performing the three basic functions of: a. Creating a database b. Querying a database c. Changing a database d. All of the above Chapter 1 1. __________ occurs when the activity of a subsystem is not consistent with another subsystem or with the larger system. a. goal conflict b. goal congruence c. information overload d. systems concept 2. __________ are facts that are collected, recorded, stored, and processed by an information system. a. information b. data c. events d. agents 3. All of these are characteristics that make information useful except: a. relevance b. reliability c. timeliness d. organization Chapter 2 1. All of these are major transaction cycles for basic exchanges except: a. revenue cycle b. production cycle c. expenditure cycle d. tax cycle 2. A _________ is an agreement between two entities to exchange goods or services. a. data b. sales order c. transaction d. invoice 3. Employees are hired, trained, paid, evaluated, promoted, and terminated in what cycle. a. revenue b. HR/payroll c. finance d. expenditure Chapter 3 1. ___________ promulgated by the PCAOB requires that the external auditor express an opinion on the client’s system of internal controls. a. SAS-94 b. SOX (2002) c. Auditing Standard No. 2 d. none of the above 2. A data flow diagram consists all these basic elements except: a. Data sources and destinations b. Data flows c. Transformation processes d. Data stores e. all of the above 3. The highest level of DFD is called a __________. a. context diagram b. flowchart c. department d. destination Chapter 4 1. A(n) _______ is anything about which the organization wishes to store data. a. entitiy b. field c. attribute d. record 2. As technology improves, many large companies are developing very large databases called ____________. a. data administrator b. data warehouse c. data system d. data shed 3. A _______ describes the logical structure of a database. a. field b. file c. schema d. attribute Chapter 1 1) If information is available to users when they need it and in a format they can use, then it is described as: a) timely b) accessible c) verifiable d) relevant answer: b 2) Account Information Systems are important to learn about because we will learn how to: a) use information to make decisions b) collect data and turn the data into useful information c) create financial reports d) steal large amounts of money answer: b 3) Shipping is considered part of what primary activity: a) service b) operations c) marketing and sales d) outbound logistics answer: d Chapter 2 1) The file that stores the cumulative information about an organization, including their resources and the agents they interact with is called a(n): a) master file b) transaction file c) data file d) entity file answer: a 2) Reports are primarily prepared for: a) internal users to make decisions and design strategies b) external users to evaluate the company c) both a & b d) neither a or b answer: c 3) What is not a type of file processing: a) updating b) changing c) recording d) deleting answer: c Chapter 3: 1) In flowcharting, a means: a) the operation is processed manually b) a document needs prepared c) the document has been filed d) a decision needs made answer: d 2) System flowcharts: a) depict the relationship among the input, processing, and output of and accounting information system b) illustrate the sequence of logical operations performed by a computer in executing a program c) illustrate the flow of documents and information among areas of responsibility in an organization d) graphically describe the flow of data within an organization answer: a 3) Which is not a category of flowcharting symbols? a) storage b) data flow c) input/output d) processing answer: b Chapter 4 1) Data query language (DQL) is used to: a) interrogate the database b) build the data dictionary c) maintain the data d) create the database answer: a 2) The attribute that uniquely identifies a specific row in a table is called the: a) foreign key b) entity key c) data key d) primary key answer: d 3) What does a schema describe? a) the logical structure of database b) how the data is physically arranged and stored in a system c) the ability of a database to share data d) how the data is managed answer: a Ch1. 1. Which of the following choices is not one of the components of an Accounting Information System(AIS)? a) The software used to process the organization’s data b) The people that operate the system c) The location at which the organization operates d) The data about the organization Answer: c 2. Which type of primary activity distributes finished products or services to customers? a) Marketing and sales activities b) Inbound logistics activities c) Operations activities d) Outbound logistics activities Answer: d 3. Structured decisions that are repetitive and routine are performed by what level of employees in an organization? a) Mid-level managers b) Lower-level employees c) Owners d) Executive level Answer: b Ch2. 1. The _________ cycle, is where goods and services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash. a) Production b) Financing c) Revenue d) Expenditure Answer: c 2. An ATM is an example of what type of device? a) Source data automation device b) Source document c) Banking transaction device d) A turnaround document Answer: a 3. A _______ is a set of fields that contains data about various attributes of the same entity. a) File b) Record c) Database d) General Ledger Answer: b Ch3. 1. _________ depicts the relationship between the input, processing, and output of an AIS. a) Program Flowchart b) System Flowchart c) Input/Output Symbols d) Processing Symbols Answer: b 2. A ____________ graphically describes a flow of data within an organization a) System Flowchart b) Program Flowchart c) Data Flow Diagram (DFD) d) Data Destination Answer: c 3. A data store is described as what? a) The highest level DFD b) The Transformation of data c) Repository of Data d) Storage Medium Answer: c Ch4. 1. A _________ describes the logical structure of a database. a) Schema b) Data Dictionary c) Logical View d) Physical View Answer: a 2. Data definition languages (DDL) in Database Systems are used to: a) Build the data dictionary b) Describe logical views for each individual user c) Initialize/Create the database d) All of the above Answer: d 3. What is the process of following the guidelines for properly designing a relational database that is free from delete, insert, and update anomalies? a) Using a primary key b) Using a foreign key c) Normalization d) Using a data model Answer: c Chapter 1 1. Organizations collect data about: A. events that occur B. resources that are affected by events C. agents who participate in the events D. all of the above Answer: D 2. is receiving, storing, and distributing the materials that are inputs to the organization’s product or service. A. operations B. inbound logistics C. outbound logistics D. marketing and sales Answer: B 3. primarily uses discretionary information. A. internal users B. external users C. management D. stockholders Answer: A Chapter 2 1. A is an agreement between two entities to exchange goods. A. input B. cycle C. transaction D. output Answer: C 2. In systems, data is entered into paper journals and ledgers. A. manual B. computer-based C. scan D. automatic Answer: A 3. When non-routine transactions occur, they are recorded in the ___________. A. cash receipts journal B. special journal C. other journal D. general journal Answer: D Chapter 3 1. The highest level of DFD is called a __________. A. top level B. context diagram C. maximum level D. flowchart Answer: B 2. On each page of a DFD _____________ should be included. A. the name of the DFD B. the date prepared C. the preparer’s name D. all of the above Answer: D 3. ___________ place more emphasis on the physical characteristics of the system. A. DFD’s B. general ledgers C. flowcharts D. computer program Answer: C Chapter 4 1. A set of all related records forms a ________. A. file B. entity C. attribute D. field Answer: A 2. ___________ is achieved by combining master files into larger pools of data accessible by many programs. A. data sharing B. data integration C. data redundancy D. data independence Answer: B 3. The three levels of schema are: A. conceptual level B. external level C. internal level D. all of the above Answer: D Chapter 1 1. Data is different from information. Data is… a. Facts that are collected, recorded, and stored b. A collection of facts that has been organized and processed c. Surveys, maps, statistics, etc d. Things you read in a book Answer: A 2. Value of Information is a combination of what things? a. Benefits and costs b. Benefits and relevance c. Reliability and relevance d. Costs and completeness Answer: A 3. AIS’ role in the value chain is… a. Inbound logistics/outbound logistics b. Operations/marketing c. Service d. All of the above Answer: D Chapter 2 1. A computer based storage concept is a. Data storage b. Attribute c. Data input d. Field Answer: B 2. A group of related records is a a. Attribute b. Entity c. File d. Data dictionary Answer: C 3. The final step in information processing is… a. Data input b. Data processing c. Information output d. None of the above Answer: C Chapter 3 1. In documentation, other written materials include all of the following except: a. Information output b. Memos c. Software d. Manuals Answer: A 2. DFD’s must include the name of the DFD, the date prepared, and___________. a. Preparer’s name b. Financial institutions name c. Name of vendor d. Name of CEO Answer: A 3. In data flow diagrams, squares indicate ________ and circles indicate ___________. a. Inputs, outputs b. Nouns, verbs c. Verbs, nouns d. Outputs, inputs Answer: B Chapter 4 1. Where is database systems found? a. AIS b. Mainframe computer sites c. PC’s d. All of the above Answer: D 2. When you combine master files into larger pools of data accessible by many programs you are performing data __________? a. Integration b. Sharing c. Redundancy d. Independence Answer: A 3. In database systems, there are 2 views. What is one? a. DBMS view b. Operating systems view c. Logical view d. Database view Answer: C Chapter 1 1. Information is ________. a) different than data b) data that has been processed c) useful for decision making d) all of the above Answer: d 2. Which of the following does not make information useful? a) Relevance b) Reliability c) Completeness d) Length Answer: d 3. A function of an AIS is to: a) Sell products b) Meet potential employers c) Collect and store data about events, recourses, and agents. d) Organize effective solutions to common business related problems. Answer: c 4. Goal conflict occurs when? a) The activity of a subsystem is not consistent with another subsystem or with the larger system.The subsystem’s goals are in line with the organization’s goals c) Employees recognize the importance of AIS. d) The activity of a subsystem is consistent with another subsystem and with the larger system. Answer: a Chapter 2 1. Any event that can be measured in economic terms by an organization is a ________. a) Transaction b) Purchase c) Sale d) Liability Answer: a 2. Which of the following is not a major transaction cycle? a) Revenue b) Expenditure c) Purchasing d) Production Answer: c 3. Which of the following is not one of the four steps of the data processing cycle? a) Data Input b) Data Storage c) Data Processing d) Data Production Answer: d Chapter 3 1. Which of the following is not one of the four basic elements of a data flow diagram? a) Data sources and destinations b) Data inputs c) Transformation processes d) Data stores Answer: b 2. In a data flow diagram Processes represent _______. a) The transformation of data b) The input of data c) The sale of goods d) All of the above Answer: a 3. Which of the following is not a type of flow chart symbol? a) Input/output b) Processing c) Storage d) Accounting Answer: d Chapter 4 1. A _________ describes the logical structure of a database. a) Relationship b) Query c) Schema d) File organization Answer: c 2. A ________ represents everything in the database as being store in the forms of tables. a) Relational data model b) Query c) Master file d) Primary key Answer: a 3. The Data Dictionary is ________. a) Not necessarily useful in a database b) Contains information about the structure of the database c) Contains a record for some corresponding data elements in a database d) None of the above. Answer: b Chapter 1 1. ______ ______ occurs when the human mind cannot effectively absorb or process more information. a. Information value b. Information overload c. Goal conflict d. Goal congruence Answer: b. Information overload 2. _____ _____ are repetitive, routine, and understood decisions on actions to take. a. b. c. d. Structured decisions Semi-structured decisions Unstructured decisions Strategic planning Answer: b. Structured decisions 3. How do AIS accounting information systems add value to organizations? a. b. c. d. Improve efficiency Improve decision making Improve knowledge All of the above Answer: d. All of the above Chapter 2 1. What transaction cycle is the cycle where raw materials are transformed into finished goods? a. b. c. d. Revenue cycle Expenditure cycle Human resources cycle Production cycle Answer: d. Production cycle 2. Many financial reports are prepared for and used by: a. b. c. d. e. f. Internal users External users Those individuals who have nothing vested in the company None of the above Both A & B All of the above Answer: e. Both A & B 3. _____ request specific information from a computer. a. b. c. d. Questions Auditors Queries Checks Answer: c. Queries Chapter 3 1. _____ _____ are written step-by-step explanations of system components and interactions a. b. c. d. Document reports Adjusting entries Narrative descriptions Data diagrams Answer: c. Narrative descriptions 2. _____ _____ represent the movement between processes a. b. c. d. Data destinations Data sources Data flows None of the above Answer: c. Data flows 3. What do circles represent in data flow diagrams DFD’s? a. b. c. d. Nouns (destinations) Documents Verbs (actions) Taxes Answer c. Verbs (actions) Chapter 4 1. _____ describes the logical structure of a database: a. b. c. d. Reports Schemas Integrations Independences Answer: b. Schemas 2. _____ _____ _____ is the organization-wide view of the entire database: a. b. c. d. External-level schema Conceptual-level schema Internal-level schema None of the above Answer: b. Conceptual-level schema 3. In relational database queries, what Query number answers the question of what the invoice number of all sales made, and who made those sales? a. b. c. d. e. Query 1 Query 2 Query 3 Query 4 Query 5 Answer: a. Query 1 Chapter #1 1. What happens when you pass the amount of information the human mind can effectively absorb and process? a. goal overload b. data overload c. goal conflict d. information overload 2. What is a system that collects, records, stores, and processes data to produce information for decision makers? a. goal information system b. financing information system c. accounting information system d. information technology infrastructure 3. Which of these is not a factor that influences the design of the accounting information system? a. economy b. strategy c. developments in information technology d. organizational culture Chapter #2 1. Which of these is not one of the five major transaction cycles? a. revenue cycle b. financing cycle c. asset cycle d. production cycle 2. What is the systematic assignment of numbers or letters to items to classify and organize them? a. coding b. number cycle c. input d. output 3. Checks, receipts, and invoices are all examples of what? a. files b. attributes c. reports d. documents Chapter #3 1. What is a temporary or permanent repository of data? a. process b. data store c. diagram d. data flow 2. Which flowchart depicts the relationship among the input, processing, and output of the Accounting Information System? a. program flowchart b. system flowchart c. data flowchart d. internal control flowchart 3. What provides the reader with a summary level view of a system and is the highest level DFD? a. processes b. flowchart c. context diagram d. templates Chapter #4 1. Who is responsible for the database? a. accountant b. manager c. database secretary d. database administrator 2. What is used for data maintenance, which includes such operations as updating, inserting and deleting portions of the database? a. data query language b. data updating language c. data manipulation language d. data definition language 3. What starts with the assumption that everything is initially stored in one large table? a. normalization b. digitizing c. entity integrity rule d. schemas Name: Daniel Rogers Chapter 1: 1. Data that have been organized and processed to provide meaning to a user is referred to as: a. Integration b. System c. Information d. Synergy 2. Which of the following is not a primary activity of the value chain? a. Operations b. Service c. Marketing d. Technology 3. A company that strives to be the most efficient producer of a product or service would best be described is pursuing what kind of strategic position? a. Needs-based b. Low-cost c. Variety-based d. Product Differentiation Chapter 2: 1. The transition cycle in which goods and services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash is known as the: a. Revenue cycle b. Production cycle c. Financing cycle d. Expenditure cycle 2. What item contains summary-level data for every asset, liability, equity, revenue, and expense account of an organization? a. Source document b. Subsidiary ledger c. Cash budget d. General ledger 3. Which step of the data processing cycle captures the data for each transaction and enters that transaction into the system? a. Data Storage b. Data Input c. Information Output d. Data Processing Chapter 3: 1. In a data flow diagram, what does a process represent? a. The transformation of data b. The source of data c. The flow of data d. The storage of data 2. Which of the following is a basic element of a Data Flow Diagram (DFD)? a. Data sources and destinations b. Data flows c. Data stores d. All of the above 3. In a DFD, what would a square represent? a. Data flow b. Data Source c. Processes d. Data storage Chapter 4: 1. An individual user’s view of a subset of the organization’s database is known as a(n): a. Internal-level schema b. Conceptual-level schema c. External-level schema d. Logical-level schema 2. What key component of a DBMS contains information about the structure of the database? a. Data model b. Relation c. Data dictionary d. Schema 3. Which of the following would managers use to update portions of the database? a. DDL b. DSL c. DQL d. DML Chapter 1 1. Decisions that are repetitive, routine, and understood well are: a. Semistructured Decisions b. Structured Decisions c. Unstructured Decisions d. Operational Decisions 2. A strategy that entails being the most efficient producer of a product or service is: a. Product differentiation strategy b. Needs-based strategy c. Variety-based strategy d. Low-cost strategy 3. Most internal information is: a. Mandatory information b. Essential information c. Incorrect information d. Discretionary information Chapter 2 1. In which cycle are goods and services sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash? a. Revenue cycle b. Expenditure cycle c. Production cycle d. Financing cycle 2. A system where items are numbered consecutively to ensure that there will be no gaps is a: a. Sequence code b. Block code c. Group code d. Block and group combination 3. The journal used to record infrequent or nonroutine transactions is the: a. Specialized journal b. Sales journal c. Receipts journal d. General journal Chapter 3 1. A graphical description of the input, processing, and output relationships is a: a. Data flow diagram b. Document flowchart c. System flowchart d. Program flowchart 2. Which of the following is the usual symbol for a magnetic disk? a. b. c. d. Correct Answer 3. A graphical description of the logical sequences found in computer software is a: a. Data flow diagram b. Document flowchart c. System flowchart d. Program flowchart Chapter 4 1. Which type of language is responsible for data maintenance within in database? a. Data definition language b. Data manipulation language c. Data creation language d. Data query language 2. A unique attribute or combination of attributes that identifies a specific row of a table is a: a. Primary key b. Secondary key c. Foreign key d. Uniform key 3. Which of the following is not a necessity of a relational database? a. Every column in a row must be single valued b. Primary keys must be null c. Foreign keys, if not null, must correspond to primary keys in a different table d. All nonkey attributes should describe a characteristic about the object identified by the primary key Chap 1 1 Which of these is not 1 of the 5 primary activities in an organizations value chain? A inbound logistic B Marketing & Sales C Operations D Human resources 2 How can AIS add value to an organization? A improve efficiency B improve decision making C aid in employee theft D improve internal control 3 What is not a component of AIS A the consumer B the people C information technology D software Chap 2 1 what is part of the human resource cycle A Borrow money from lenders B Discharge employees C Approve credit sales D Design products 2 Which is not a code technique A block B Sequence C Group D Individual 3 which is one of the four basic transaction cycle A Revenue B R&D C Promotions D merging Chap 3 1 This symbol represents devices or media that provide input to or record output from processing operations. A storage B processing C relational D input/output 2 A graphical of the relationship among input processing and output in an information system is. A data flow diagram B system flowchart C program flowchart D processing diagram 3 this is an entry from or an exit to another page. A off page connector B terminal C communication link D data flow Chap 4 1 which is not a benefit of database technology A data sharing B reporting flexibility C data theft D cross functional analysis 2 data definition language is used to A interrogate database B build data dictionary C initialize of create database D describe logical views for each user 3 what is not a requirement for a relational database A every column in a row must be single valued B primary keys can’t be null C must be easy for everyone to understand D foreign keys must have values that correspond to the value of a primary key in another table. Chapter 1 1. The primary activities that directly provide value to its customers include all of the following except for: A. Operations B. Purchasing C. Service D. Marketing and Sales 2. Information is timely if: A. it is available to users when they need it and in a format they can use B. it reduces uncertainty and improves decision makers’ ability to make predictions C. it is provided in time for decision makers to make decisions D. Both A and C 3. Which of the following is a benefit with respect to the value of information? A. Better ability to plan and schedule activities B. Reduces the difficulty in quantifying the costs and benefits of information C. Both A and B D. None of the above Chapter 2 1. Data values are stored in a physical space called a: A. Master File B. Record C. Database D. Field 2. Which cycle encompasses all transactions involving the purchase of and payment for merchandise? A. Expenditure B. Production C. Revenue D. Purchasing 3. A specialized journal is most likely to contain: A. adjusting and closing entries B. repetitive cash disbursement transactions C. summary-level data for every account D. loan payments Chapter 3 1. Which of the following shapes represents data sources and destinations? A. Circle B. Square C. Triangle D. Oval 2. A ____________ is a graphical description of the relationship among the input, processing, and output in an information system. A. Program flowchart B. Document flowchart C. System flowchart D. Data flow diagram 3. Guidelines for drawing a data flow diagram include: A. Understand the system B. Pay close attention to all aspects of the system C. Identify all data sources and destinations D. A and C E. Only A Chapter 4 1. What type of key is an attribute, or combination of attributes, that uniquely identifies a specific row in a table? A. Foreign key B. Domestic key C. Primary key D. International key 2. Which language is used for data maintenance? A. DML B. DDL C. DTL D. DQL 3. What is a benefit of database technology? A. Multi-functional analysis B. Decentralized management of data C. Reporting flexibility D. All of the above Stefanie Snyder 1. Which of the following is an outbound logistic? a. Receiving materials b. Manufacturing c. Distribution d. Advertising 2. A list of account numbers used in general journals for organizations can be found in the a. Source documents b. Chart of accounts c. Vendor invoice d. Transaction file 3. A flowchart symbol that commonly indicates an on-page connector is a. A circle b. A square c. An arrow d. A triangle 4. This is used to find information about the structure of a database a. Report writer b. Data dictionary c. Primary key d. Foreign key 5. Unauthorized copying of company data is known as a. Data leakage b. Data diddling c. Rationalization d. Kiting 6. The amount of risk a company is willing to accept to achieve their goals and objectives is known as a. Risk factor b. Risk ratio c. Risk appetite d. Risky business 7. Which of the following is not a factor for determining the strength of any encryption system a. Key length b. Firewall c. Key management policies d. Nature of the encryption algorithm 8. Data backup can be performed in several ways; this back up should be stored a. On-sight only b. Off-sight only c. On-sight and off-sight d. Data backup is only used by large corporations Chapter 1 1. Goal conflict occurs when: a. the activity of a subsystem is not consistent with another subsystem or with the larger system. b. the subsystems goals are in line with the organizations goals. c. one system is composed of subsystems. d. When two goals have no effect on each other. 2. Organizations collect data about all of the following except: a. Events that occur. b. Resources that are affected by those events. c. Agents who participate in the events. d. Events in the personal lives of the employees. 3. All of these characteristics make information useful except: a. Relevance b. Reliability c. Size d. Understandability Chapter 2 1. The five major transaction cycles of a business include all of the following except: a. Revenue Cycle b. Expenditure Cycle c. Production Cycle d. Sales Discount Cycle 2. Data is entered into paper journals and ledgers in the: a. Manual System b. Computer- based system c. Data- Retrieval System d. Auditing System 3. A __________ is a file used to store cumulative information about resources and agents. a. Chart of Accounts b. Ledger c. Journal d. Audit Trail Chapter 3 1. A ___________ is a graphical description of the sources and the destination of data. a. Data Flow Diagram b. Data Dictionary c. General Ledger d. Subsystem 2. All of these are the basic elements of a Data Flow Diagram except: a. Data Sources and Destinations b. Data Flows c. Information Processing Systems (IPS) d. Data Stores 3. This type of symbol indicates the type of device or media that provides input to or records output from a process. a. input/output symbols b. processing symbols c. storage symbols d. flow symbols Chapter 4 1. Information about the attributes of an entity are stored in __________. a. fields b. charts c. cells d. records 2. A set of interrelated, centrally coordinated files forms a ____________. a. file b. chart c. database d. system 3. The 3 levels of a schema include all of the following except: a. Conceptual b. External c. Cross-functional d. Internal Chapter 1 Characteristics of useful information include all of the following except: a. timely b. verifiable c. relevant d. helpful Facts that are collected, recorded, stored, and processed by an information system is called a. AIS b. data c. information d. essential information __________ __________ relates to the effective and efficient use of resources for accomplishing organizational objectives. a. management control b. strategic planning c. structured decisions d. decision scope Chapter 2 The __________ cycle is where goods and services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash. a. financing b. revenue c. production d. transaction A major activity in the Human Resource/Payroll cycle is a. receive vendor invoices b. approve credit sales c. recruit, hire, and train employees d. forecast cash needs The __________ __________ provides a means to check the accuracy and validity of ledger postings. a. audit trail b. data value c. master file d. general ledger Chapter 3 The highest-level Data Flow Diagram is referred to as a. narrative description b. system flowchart c. data destination d. context diagram In what year was the Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) passed? a. 1905 b. 1994 c. 2002 d. 2000 Which of the following flowcharts illustrates the flow of information among areas of responsibility in an organization? a. system flowchart b. document flowchart c. internal control flowchart d. flowcharting template Chapter 4 A relational data model portrays data as being stored in a. tables b. physical view c. files d. hierarchies A __________ is a key component of a DBMS which contains information about the structure of the database. a. subschema b. data query language c. data dictionary d. tuple What acts as an interface between the database and various application programs? a. data warehouse b. data definition language c. database management system d. insert anomaly Ch. 1. 1. A system is _________ ? A. a set of two or more interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal. B. of facts that are collected, recorded and processed C. required by a governmental entity D. something that makes activities harder to do 2. Data are (is) _________? A. a system that collects, records, stores, and processes data to produce information for decision makers. B. facts that are collected, recorded, store, and processed by an information system C. a decision or action of a subsystem is inconsistent with another subsystem or the system as a whole. D. eliminating duplicate recording, storage, reporting, and other processing activities in an organization. 3. An accounting information system (AIS) is __________? A. required by a governmental entity B. a decision or action of a subsystem is inconsistent with another subsystem or the system as a whole. C. a system that collects, records, stores, and processes data to produce information for decision makers. D. something that makes activities harder to do Ch. 2 1. Source data automation __________? A. is yet another means to improve the accuracy and efficiency of data input B. something that makes activities harder to do C. a decision or action of a subsystem is inconsistent with another subsystem or the system as a whole. D. is a list of all general ledger accounts an organization uses 2. Coding is __________? A. the systematic assignment of numbers or letters to items to classify and organize them. B. used to simplify the record infrequent or nonroutine transactions C. something that makes activities harder to do D. a set of interrelated, centrally coordinated files 3. Documents ________? A. store cumulative information about an organization’s resources and the agents with whom it interacts. B. a set of interrelated, centrally coordinated files C. are records of transactions or other company data D. required by a governmental entity Ch. 3 1. Documentation encompasses _______? A. Narratives B. Flow charts and diagrams C. other written materials that explain how a system works D. All of the above 2. A data flow diagram (DFD) A. Graphically describes the flow of data within an organization B. something that makes activities harder to do C. required by a governmental entity D. a written step-by-step explanation of system components and interactions 3. Data Flow ______________? A. represents the flow of the data between processes, data stores, and data sources and destinations B. is found at the water cooler C. represented in squares D. is a list of all general ledger accounts an organization uses Ch. 4 1. A data warehouse A. very large data base to provide customer service, marketing analysis, and managerial information. B. a large warehouse in Nevada where companies keep their records C. describes the logical structure of a database D. None of the above 2. The relational data model A. represents everything in the database as being stored in the form of tables B. is the attribute, or combination of attributes, that uniquely identifies a specific row in a table C. a written step-by-step explanation of system components and interactions D. All of the Above 3. A primary key A. is the attribute, or combination of attributes, that uniquely identifies a specific row in a table B. is the CEO’s master key to all the companies’ facilities C. each row in a relation D. represents everything in the database as being stored in the form of tables Chapter 1 1. Data differ from information in which way? a. Data are output and information is input b. Information is output and data are input c. Data are meaningful bits of information. d. There is no difference. B is correct answer 2. Which of the following is not a characteristic that makes information useful? a. It is reliable. b. It is timely. c. It is inexpensive d. It is relevant C is correct answer 3. Which of the following is a primary activity in the value chain? a. Purchasing b. Accounting c. Post-sales service d. Human resource management C is correct answer Chapter 2 4. Which cycle includes interactions between an organization and its suppliers? a. Revenue cycle b. Expenditure cycle c. Human resources cycle d. General ledger and reporting system B is correct answer 5. All of the information (name, gpa, major, etc.) about a particular student is stored in which of the following? a. file b. record c. attribute d. field B is correct answer 6. Which of the following would contain the total value of all inventory owned by an organization? a. Source document b. General ledger c. Cash budget d. Subsidiary ledger B is correct answer Chapter 3 7. A DFD is a representation of which of the following? a. Relationship among modules, data, and programs of an AIS b. Flow of data in an organization c. Decision rules in a computer program d. Computer hardware configuration B is correct answer 8. Documentation methods such as DFDs and flowcharts save both time and money, adding value to an organization. a. True b. False c. Not a choice d. Not a choice A is correct answer 9. Which of the following statements is false? a. Flowcharts make use of many symbols. b. A document flowchart emphasizes the flow of documents or records containing data. c. DFDs help convey the timing of events d. Both a and b are false. C is correct answer Chapter 4 10. The relational data model portrays data as being stored in a. Hierarchies b. Tables c. Objects d. Files B is correct answer 11. How a user conceptually organizes and understands data is referred to as the a. Physical view b. Logical view c. Data model view d. Data organization view B is correct answer 12. What is each row in a relational database table called? a. Relation b. Attribute c. Anomaly d. Tuple D is correct answer Chapter 1 1. The value of information is ….. a) Data that have been organized and processed to provide meaning to a user. b) The benefit produced by the information minus the cost of producing it. c) Achieved when a subsystem meets its goal while contributing to the organizations overall goal. d) A set of two or more interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal. 2. The study of accounting information systems focuses on_____________ and ___________. a) b) c) d) e) Information, decision making Design and use Accountability, control Understandability and reliability All of the above 3. What is an access-based strategic position? a) It involves serving a subset of customers who differ from other custom3rs in terms of factors such as geographic location or size, which creat4s different requirements for serving customers. b) It involves trying to serve all most or all of the needs of a particular group of customers in a target market. c) It involves producing or providing a subset of the industry’s products or services. d) It involves the entire system of organizational activities that are greater than the sum of each individual part. Chapter 2 1. What is source data automation? a) It means to collect data about business activities. b) It means to exchanger data with customers and suppliers via the internet. c) To collect data about business activates and then transfer the data into the computer. d) It means to improve the accuracy and efficiency of data input. 2. _________ contains summary level data for every account in an organization. a) b) c) d) General ledger Control account Accounts payable Subsidiary ledger 3. Enterprise resource planning systems are designed to…. a) Control the allocation or resources amongst various departments in the organization. b) Encompass all transactions involving sales to customers and the collection of cash receipts in payment for those sales. c) Encompass all the transactions involving the investment of capital in the company. d) Overcome these problems as they integrate all aspects of a company’s operations with its traditional AIS. Chapter 3 1. Data sources and data destinations are represented by… a) b) c) d) Squares Circles Triangle Rectangle 2. ________ _________illustrates the sequence of logical operations performed by a computer in executing a program. a) b) c) d) System flowcharts Document flowcharts Internal control flowcharts Program Flowchart 3. Guidelines for drawing a Data Flow Diagram include… a) b) c) d) e) f) Identify data flows Identify transformation processes Give each process a sequential number Repeat the processes A, B and C All of the above Chapter 4 1. ________ acts as an interface between the database and the various application programs. a) b) c) d) Data warehouses Database management system Database system Database administrator 2. The logical view refers to….. a) How the user or programmer conceptualize all information about customers as being stored in the form of a table. b) How and where the data are physically arranged and stored in the computer system. c) How combining master files into larger pools of data that many application programs can access. d) How reports can be revised easily and generated as needed and the database can be easily browsed to research a problem or obtain detailed information. 3. The entity integrity rule ensures…. a) Consistency of the database b) Consistency of the information being inputted into the database. c) That every row in every relation must represent data about some specific object in the real world. d) That the tables depicted in a database represent a well-structured relational database. Erica Wolford Chapter 1 1. Which is not a primary activity a. Inbound Logistics b. Operations c. Human Resources d. Services 2. What is a set of interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal? a. Data b. System c. Information d. Completeness 3. Which characteristic makes information presented in a manner that you can comprehend and use? a. Reliability b. Timeliness c. Verifiability d. Understandability Chapter 2 1. Which is an internal party? a. Customers b. Management c. Creditors d. Vendors 2. Which cycle involves interaction with suppliers? a. Expenditure Cycle b. Revenue Cycle c. Production Cycle d. Financing Cycle 3. In which step of the data processing cycle does the data need to be organized for easy and efficient access? a. Information Output b. Data Storage c. Data Input d. Data Processing Chapter 3 1. Data sources and destinations a. Represent the flow of data between sources and destinations, processes and the data stores. b. Represent the transformation of data. c. Represent organizations or individuals that send or receive data used or produced by the system. d. Represent a temporary or permanent repository of data. 2. __________________ indicate the type of device used to process the data or whether the data was processed manually. a. Input symbols b. Storage symbols c. Flow symbols d. Processing symbols 3. Which symbol is represents computer processing? a. b. c. d. Chapter 4 1. The set of commands used to change the database is known as a. Data Manipulation Language (DML) b. Data Definition Language (DDL) c. Data Query Language (DQL) d. None of the above 2. Which of the following is a benefit to an organization that uses database technology a. Reporting flexibility b. Data Sharing c. Data Integration d. Data Independence e. None of the above f. All of the above 3. Which of the following is not a level of schema? a. Conceptual Level b. Internal Level c. Actual Level d. External Level Chapter 1 1. An organization’s value chain can be connected with the value chains of its________. A. B. C. D. Customers Suppliers Distributors All of the above Answer: D 2. Michael Porter suggests that there are two basic business strategies that companies can follow. A. Product Differentiation B. Low-cost strategy C. High-cost strategy D. A and B E. None of the above Answer: D 3. Internal users primarily use which of the following kinds of information? A. Incomplete Information B. Discretionary Information C. Mandatory Information D. Essential Information Answer: B Chapter 2 4. In the Revenue Cycle what is taken and what is received? A. give goods, get goods B. give cash, get goods C. give goods, get cash D. None of the above Answer: C 5. Examples of external parties that interact with AIS include which of the following? A. Customers B. Vendors C. Creditors D. Governmental Agencies E. All of the Above Answer: E 6. A _______ is a set of interrelated, centrally-coordinated files. A. Chart B. Table C. Database D. Spreadsheet Answer: C Chapter 3 7. Data processes appear as which of the following? A. circles B. squares C. lines D. trapezoids Answer: A 8. Data stores appear as which of the following? A. Wavy lines B. Horizontal Lines C. Arcs D. Diamonds Answer: B 9. The highest level of a DFD is which of the following? A. context diagram B. executive spreadsheet C. relational diagram D. None of the above Answer: A Chapter 4 10. Very large databases are called which of the following? A. Data Storage Units B. Data Holding Units C. Data Traps D. Data Warehouses Answer: D 11. Database technology provides which of the following benefit(s) A. Cross Functional Analysis B. Minimal Data Redundancy C. Reporting Flexibility D. Data Sharing E. All of the Above Answer: E 12. The primary key must have which of the characteristics? A. It must be null B. It must be a foreign key in another table C. It can not be null D. None of the Above Answer: C Chapter 1 Questions 1. What is a system? a) a fact that is collected recorded, stored and processed b) data that has been organized and processed to provide meaning to a user c) a set of interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal d) it consists of receiving, storing and distributing the materials an org. uses to create the serveices/products that it sells Answer: C 2. Primary Value Chain activities include the following except: a) inbound logistics b) production c) marketing/sales d) operations Answer: B 3. Data is ______. a) facts collected, recorded, stored and processed by an information system b) set of two or more interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal c) operations that a company does to keep in business d) a type of supply chain Answer: A Chapter 2 Questions 1. Goods & services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash in the _____ cycle. a) financing cycle b) production cycle c) revenue cycle d) expenditure cycle Answer: C 2. In the production cycle, _______ is transformed into _______. a) information; data b) raw materials; finished goods c) inventory; cash (or promise to pay cash) d) services; cash (or promise to pay cash) Answer: B 3. All of these are steps in the data processing cycle, except: a) data processing b) information output c) data storage d) revenues Answer: D Chapter 3 Questions 1. Which is a common documentation tool? a) data flow diagrams b) ledger c) flowchart d) both A & C 2. A flowchart is: a) piece of hard, flexible plastic on which the shapes of symbols have been die cut b) an analytical technique used to describe some aspect of an information systems in a clear, concise, and logical manner c) device that provides input to or records output from processing operations d) none of the above Answer: B 3. What percent of information systems professionals use flowcharts? a) 5.0 % b) 47.2 % c) 97.6 % d) 99.9% Answer: C Chapter 4 Questions 1. Which of the following acts as an interface between the database and the various application programs?: a) database system b) data warehouse c) database management system d) all of the above Answer: C 2. Which of these are the three levels of schemas?: I. conceptual II. external III. tutorial IV. internal a) I, II, III b) I, II, IV c) I, III, IV d) II, III, IV Answer: B 3. Data definition language is used: a) to build a data dictionary b) for data maintenance c) to interrogate the database d) all of the above Answer: A Test 1 Review Questions Which of the following is not a characteristic that makes information useful? A. Reliable B. Accessible C. Inexpensive D. Understandable Answer: C Information can be classified as? A. Mandatory Information B. Essential Information C. Discretionary Information D. All of the above Answer: D Which of these is not one of an organizations five primary activities that directly provide value to its customers? A. Operations B. Firm Infrastructure C. Logistics D. Marketing and Sales Answer: B In which cycle does a company turn raw materials into finished goods? A. Revenue cycle B. Production cycle C. Expenditure cycle D. Financing cycle Answer: B In which cycle does a company pay dividends to its stockholders? A. Expenditure cycle B. Revenue cycle C. Payroll cycle D. Financing cycle Answer: D A field is…..? A. Related records grouped together B. The part of a data record that contains the data value for a particular attribute C. Set of fields that contain data about various attributes of the same entity D. The item about which information is stored in a record Answer: B In a DFD, transformation processes are represented by? A. Squares B. Straight Lines C. Triangles D. Circles Answer: D DFD should include? A. The name of the DFD B. The date prepared C. The prepares name D. All of the above E. None of the above Answer D Which law required public companies to include a report in internal controls in its annual reports? A. Free Information Act B. Sarbanes Oxley Act C. FASB opinion 122 D. None of the above Answer: B Which of the following attributes would most likely be a primary key? A. Supplier Name B. Supplier Address C. Supplier Number D. Supplier Phone Number Answer: C Which of the following is used for data maintenance? A. Data Manipulation Language (DML) B. Data Query Language (DQL) C. Data Definition Language (DDL) Answer: A Which of the following refers to how and where data are arranged and stored on the computer? A. Physical view B. Logical view C. Data Model View D. Data Organization View Answer A Chapter 1 1. The text defines information as: a. facts that are collected, recorded, stored, and processed by an information system b. data that have been organized and processed to provide meaning to a user c. the sum or range of what has been perceived, discovered, or inferred d. NONE OF THE ABOVE 2. Which of the following is NOT one the five primary activities in the value chain? a. purchasing b. inbound logistics c. operations d. outbound logistics e. marketing and sales 3. A variety-based strategic position _________________. a. involves trying to serve most or all of the needs of a particular group of customers in a target market b. involves serving a subset of customers who differ from other customers in terms of factors such as geographic location or size c. involves producing or providing a subset of the industry’s products or services d. ALL OF THE ABOVE Chapter 2 1. The transaction cycle where raw materials are transformed into finished goods is called the _____________________. a. revenue cycle b. expenditure cycle c. human resources/payroll cycle d. financing cycle e. NONE OF THE ABOVE 2. Related records are grouped to form a __________________. a. field b. entity c. file d. attribute e. NONE OF THE ABOVE 3. A ____________________ is used to simplify the process of recording large numbers of repetitive transactions. a. general journal b. specialized journal c. general ledger d. operational documents e. ALL OF THE ABOVE Chapter 3 1. The circle symbol in a data flow diagram indicates: a. Data sources and destinations b. Data flows c. Transformation processes d. Data stores e. NONE OF THE ABOVE 2. A ______________ is an analytical technique used to describe some aspect of an information system in a clear, concise, and logical manner. a. flowchart b. data flow diagram c. context diagram d. transformation process e. NONE OF THE ABOVE 3. Which of the following symbols are NOT found in a flowchart? a. input/output symbols b. processing symbols c. storage symbols d. flow and miscellaneous symbols e. NONE OF THE ABOVE Chapter 4 1. The set of commands used to interrogate the database is known as: a. data definition language b. data manipulation language c. standard query language d. report writer e. NONE OF THE ABOVE 2. A ___________________ is the attribute, or combination of attributes, that uniquely identifies a specific row in a table. a. foreign key b. primary key c. entity d. tuple e. NONE OF THE ABOVE 3. A schema ___________________. a. is how the user or programmer conceptually organizes and understands data b. refers to how and where data are physically arranged and stored in the computer system c. describes the logical structure of the database d. ALL OF THE ABOVE Test 1 Chapter 4 questions 1) Which of the following is DDL not used for? a) help with data implementation b) build the data dictionary c) create a data base d) describe the logical views for each individual user or programmer 2) Which kind of schema is the organization- wide vew of the entire data- base a) internal- level schema b) subschema c) conceptual level schema d) external- level schema 3) DML stands for _______ a) data maintenance language b) data manipulation language c) data monitoring language d) data miscellaneous language Test 1 Questions Chapter 1 1) A _________ is a set of two or more interrelated components that interact to achieve a goal. a) intergration b) system c) information d) accounting information system 2) Which of the following is not a part of an organizations value chains’ primary activites a) marketing and sales b) operations c) inbound logistics d) human resources 3) Which of the following is not one of the concepts that the FASB suggested to be provided to students in order for them to have a solid understanding. a) Financial information reporting b) The use of information in decision making c) Provide them with enough information for them to gain a better understanding of accounting systems and to help guide them through the CPA exam d) The nature, design, use, and implementation of an AIS Chapter 2 4) Which of the following cycles is the one which is where raw materials are transformed into finished goods? a) financial cycle b) production cycle c) expenditure cycle d revenue cycle 5) The second basic type of file is called a ________? a) transaction file b) secondary file c) master file d) database file 6) Which of the following is not one of the types of file processing? a) Deleting b) Updating c) Recording d) Adding Chapter 3 7) A _______ encompasses the narratives, flow charts, diagrams and other written materials that explain how a system works. a) Narrative description b) Data flow diagram c) Program flow chart d) Documentation 8) A ______ is a piece of hard, flexible plastic on which the shapes of symbols have been die cut. a) Flowcharting template b) Documentation template c) Context diagram template d) Data flow diagram template 9) _______ symbols either show what type of device is used to process data or indicate when processing is performed manually. a) flow and miscellaneous symbols b) input/output symbols c) processing symbols d) storage symbols Chapter 1 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary activities in the value chain that directly provide value to its customers? A) Inbound Logistics B) Service C) Marketing and Sales D) Human Resources 2) Serving a subset of customers who differ from the other customers in terms of such factors as geographic location or size is the definition of _____. A) Access-Based Strategic Position B) Needs-Based Strategic Position C) Low-Cost Strategy D) Variety –Based Strategic Position 3) Which of the following is a primary activity in the value chain? A) Technology B) Operations C) Purchasing D) Accounting Chapter 2 1) The __________ is where goods and services are sold for cash or a future promise to pay cash. A) Financing Cycle B) Revenue Cycle C) Production Cycle D) Expenditure Cycle 2) A __________ is used to record infrequent or nonroutine transactions, such as loan payments and end-of-period adjusting and closing entries. A) Specialized Journal B) General Journal C) Subsidiary Ledger D) General Ledger 3) The set of fields that contain data about various attributes of the same entity forms a ______. A) File B) Record C) Value D) Column Chapter 3 1) ________ represents devices or media that provide input to or record output from processing operations. A) Processing Symbols B) Input/Output Symbols C) Storage Symbols D) Flow and Miscellaneous Symbols 2) Transformation processes are represented in a data flow diagram as _______. A) Square B) Circle C) Curved Arrow D) Two Parallel Lines 3) Data Flows are represented in a data flow diagram as _______. A) Square B) Circle C) Curved Arrow D) Two Parallel Lines Chapter 4 1) Which of the following is not a benefit of database technology? A) Data Sharing B) Data Independence C) Data Integration D) All the above are benefits of database technology 2) The key component of a Database Management System is ________? A) The Data Dictionary B) Conceptual-level Schema C) Data Query Language D) Data Warehouse 3) __________ is used for data maintenance, which includes such operations as updating, inserting, and deleting portions or the database. A) Data Definition Language B) Data Manipulation Language C) Data Query Language D) Report Writer