Critical Drips - SGMC Intranet | Home
advertisement

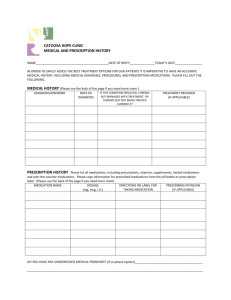
SOUTH GEORGIA MEDICAL CENTER PATIENT CARE POLICY & PROCEDURE TITLE: High Alert-Specialty Medication & Critical Drip Medication Administration: Initiation, Maintenance & Weaning PREPARED/COORD BY: Clinical Practice Council & Critical Care Committee APPROVED BY: NUMBER: IV-A-80 EFFECTIVE: 9/98 REVIEWED: 3/12 REVISED: 3/99, 4/00, 9/01 REVISED: 4/04, 11/05, 8/08 REVISED: 03/09, 12/12 POLICY STATEMENT & PURPOSE This policy serves as a resource for the initiation, maintenance and weaning of specialty medications including calculation for appropriate dosing. Introduction Specialty medications include but are not limited to vasoactive, antiarrhythmic, anticoagulant, and insulin as listed in this policy. The medications included in this policy are considered to be ‘high alert’ medications or medications which may carry a higher risk for adverse outcomes. Patients receiving Nontitrated specialty medications may be located outside the Critical Care units; Patients receiving specialty medications which will be titrated should have an order to admit/transfer to a critical care unit. Definition for High alert medication: Medications that have the highest risk of causing injury when misused. (Cohen, M.R. Medication Errors. 1999. p 5.1). This policy outlines recommendations for administration and monitoring of listed medications. Development of this list was based on information in professional literature from the Institute for Safe Medication Practice (ISMP), Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO), American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (AHSP), etc. and from concepts drawn from humanfactors knowledge of principles of error reduction. These guidelines for administering and monitoring medications known as “high alert medications” (as defined by South Georgia Medical Center’s Medication Safety Team) should be provided for clinical practitioners to use in the care and treatment of the patient. In addition to this policy, resources such as the Electronic Drug Reference and Pharmacists are available and should be consulted when questions arise. Note: The automated dispensing medication cabinet provides special notations in the message field screen (alert/message/ reminder) for some medications. PROCEDURE Refer to Guidelines for Practice Prior to Treatment and Procedures (XVI-D40) I. GENERAL GUIDELINES A. Specialty drip medications should be initiated by a Registered Nurse (RN). B. Specialty drip medications should be maintained on an IV pump at all times including during transport of the patient C. Prior to initiation of a specialty drip, two (2) nurses, one of which must be a RN, (a Pharmacist or physician may substitute for one nurse) should validate concentration, dosages, and infusion pump rates. At each change of shift, transfer from one area to another and/or when a new bag is administered, the off-going and on-coming nurse should verify concentration by visually inspecting the bag, calculate the desired dose rate, and verify the pump is infusing at the calculated rate. Two (2) RNs (one may be a pharmacist/MD) verifying the drip should Co-Sign in the patient’s medical record. Specialty Medication Administration, PCS IV-A-80 D. Highly concentrated drips are to be administered through a central line only. Standard concentrations drips listed in appendix A & B may be administered peripherally if a central line is not available; however a central line is preferred. Changes in recommended drip concentration will require a physician’s order and consultation with Pharmacy. E. Compatible drips may be attached to stopcocks connected to the individual ports of the central venous catheter with compatible IV fluids as the primary line. F. For adult patients, the minimum rate to any IV site is 10 ml per hour. If the specialty drip medication is to run at less than 10 ml per hour, primary IV tubing with ordered fluids should be added to equal a rate of 10 ml per hour. The specialty drip medication should infuse through the first port closest to the IV site of the primary IV fluids. If the specialty drip is more than 10 ml per hour the drip may infuse without primary fluid infusing. G. An additional IV site should be maintained for administration of other IV medications and/or IV fluids by IV route. A peripheral saline lock may be used for this purpose. H. Telemetry should be maintained on patients receiving antiarrhythmic. The Monitor Bank should be notified when patient is receiving IV administration of antiarrhythmic. I. Orders that vary from recommended dosages should be verified with the Physician. If, after clarifying with the Physician and Pharmacy, the dosage still exceeds the recommendation below, the nurse should notify the Administrative Coordinator. J. Non-titrated specialty drip medications may be administered in Non-Intensive Care areas when patient monitoring is ordered as no greater than every 4 to 8 hours. K. Heparin may be titrated in non-intensive care areas. L. For vesicant infiltration/extravasation refer to PC policy IV-C-100, Treatment of Vesicant Extravasation. M. For Weight-Based drips, use the weight obtained when the drip was started. If a subsequent drip is started, use the weight obtained for the first drip. All drips should be based on the same weight. The admission weight appears as the default weight in IV Manage. The default weight should be manually changed in IV Manage when the drip is started N. Documentation verification Stock Bottles of IV fluids and medicated drips are documented on the IV Manage screen in HED and the name of RN verifying the information. Verifying nurse utilizes the Co-Sign feature in HED or document in the patient’s medical record. O. Vital signs should be monitored prior to initiation and during administration of specialty medications. For Vital Signs monitoring, see specific drug guidelines: Non-titration specialty medication Infusion guidelines (appendix A) Titrating specialty medication Infusion guidelines – Critical Care (appendix B) . II. HIGH ALERT SPECIALTY MEDICATIONS High alert specialty drip medications and selected monitoring parameters include but are not limited to: 1. Immune Globulin Intravenous (IVIG)- See Pediatric policy “Administration of Intravenous Immune Globulin to Pediatric/Adolescent Patient” 2. Immune Globulin Intravenous (IVIG) - See PC policy IV-E-25 (Adult) 2 Specialty Medication Administration, PCS IV-A-80 3. Antidysrhythmics – IV Push NOTE: For the purpose of this policy, IV antidysrhythimic is defined as a medication listed below that is administered for the emergent/urgent rhythm management and NOT routine administration for health maintenance. A. Antidysrhythmics IV push should be administered by a RN. B. Licensed Practical Nurses and Paramedics in the Emergency Department setting may administer IV push antidysrhythmics under the direct supervision of the physician/LIP. C. The patient should be monitored on telemetry during administration of IV antidysrhythmic agents. D. The Monitor Bank should be notified prior to administration of the antidysrhythmic agent. E. The patient’s vital signs should be monitored as indicated by the patient’s condition until dysrhythmia is stabilized. F. Refer to the Electronic Drug Reference or pharmacist for rates of infusion. G. Examples of antidysrhythmic agents include but are not limited to the following: 1. Adenosine (Adenocard) 2. Diltiazem (Cardizem) 3. Metoprolol tartrate (Lopressor) 4. Xylocaine (Lidocaine) 5. Procainamide (Pronestyl) 6. Verapamil (Isoptin, Calan) 7. Amiodarone (Cordarone) 4. Non-Titrating Specialty Medication Infusion Guidelines – See Appendix A 5. Titrating Specialty Medication Infusion Guidelines Critical Care – See Appendix B 6. Neuromuscular Blocking Agents For use in the presence of a physician with airway management equipment, oxygen and reversal agents immediately available. Follow physicians order for dose parameters. Indications include the following: A. Adjunct to general anesthesia B. Facilitate endotracheal intubation C. Skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation 7. Fibrinolytics A. Activase (Alteplase) 1. Follow Activase order Set 8. Argatroban For use to decrease the clotting ability of the blood and to help prevent harmful clots from forming in the blood vessels. This medicine is used to treat or prevent blood clots in patients with bleeding problems caused by another medicine called heparin. It may also be used in patients who are having certain heart and blood vessel procedures, such as coronary angioplasty. 1. Follow Argatroban order set or physician order 3 Specialty Medication Administration, PCS IV-A-80 III. SUBCUTANEOUS MEDICATIONS A. IV. ORAL MEDICATIONS A. V. Refer to Administration of Chemotherapy Agents policy IV-F- 5 PATIENT CONTROL ANALGESIA (PCA) A. VII. Coumadin (warfarin) 1. Verify PT and/or INR level prior to administration. CHEMOTHERAPY A. VI. Insulin (See Policy, IV-A-20) 1. Orders containing the use of ‘u’ rather than ‘units’ should be clarified. 2. Dose should be verified with second independent check of physician order, medication container and syringe containing the insulin prior to administration. The second check should be by another licensed person (nurse, physician or Pharmacist). Refer to PCA Administration and Documentation, policy IV-B-5 PEDIATRIC MEDICATIONS A. B. Weight based dosing 1. Refer to HPP 99, Physician Order, Section M. Chloral Hydrate (for procedures) 1. Prior to administration, inquire as to whether child has had previous sedation and if yes, determine time the sedation was given. Notify the physician if patient received any sedation within past 8 hours. 2. Consult with Pharmacy to calculate dose 3. Dose should be verified with second independent check of order, medication container and syringe. 4. Monitor patient pre and post administration and document. DOCUMENTATION: PC IV-A-20: Medication-Insulin Administration PC IV-C-55: Medication Administration Documentation REFERENCES: Pediatric Standard of Care & Practice policy, Administration of Intravenous Immune Globulin to Pediatric/Adolescent Patient PC policy IV-C-100: Treatment of Vesicant Extravasation. PC policy IV-F-5: Administration of Chemotherapy Agents PC policy IV-B-5 PCA Administration and Documentation PC policy IV-A-20: Insulin Administration HPP 94 Procedural Sedation 9/98-Policies that were consolidated into this policy: Dopamine, Dobutamine, Lidocaine, Recommended Guidelines for the Administration of IV Potassium Chloride, and IV Pharmacological Intervention for The Non-ICU/Non-ER Patient Experiencing An Unstable Dysrhythmia. 9/12 Critical Drip Initiation, Maintenance & Weaning consolidated into this policy 4 Specialty Medication Administration, PCS IV-A-80 Non-Titrating Specialty Medication Infusion Guidelines – Appendix A Medication Brand/Generic Name Drip Concentration Dosage Monitoring 1mg/ml 2-5 mcg/kg/min Intropin Dopamine 1.6mg/ml 2-5 mcg/kg/min Lidocaine 4mg/ml 1-4 mg/min Vital signs are taken when infusion is initiated, dosage is changed PRN using following schedule: VS every 15 minutes X 1 hr THEN Every 1 hour X 4 THEN Every 4 hours thereafter Monitor IV site closely for signs or symptoms of infiltration/extravasation Vital signs are taken when infusion is initiated, dosage is changed PRN using following schedule: VS every 15 minutes X 1 hr THEN Every 1 hour X 4 THEN Every 4 hours thereafter Monitor IV site closely for signs or symptoms of infiltration/extravasation Vital signs every 4 hours or as ordered Peripheral Max conc: 0.2mEq/ml Per Physician order/protocol Dobutrex Dobutamine Potassium Replacement Therapy via IV PB Central Line Max conc: 0.4mEq/ml Calcium Gluconate Infusion Refer to Physician order and/or Refer to Electronic Drug Reference Refer to Physician order and/or Refer to Electronic Drug Reference Natrecor Nesititide 6 mcg/ml Bolus: 2 mcg/kg over 1 minute Infusion: 0.01 mcg/kg/min MAXIMUM infusion rate outside ICU/ER should not exceed 20 mEq/hr Potassium infused as a PRIMARY line Pt should be monitored on telemetry Recommend K+ serum level monitoring Monitor IV site closely for S/S infiltration & extravasation May be administered by a LPN after verification by RN Vital signs every 15 minutes while drug infusing Watch for hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias Use caution in patients receiving digoxin Monitor serum calcium as ordered Pharmacy should provide as a piggyback BP prior to and after bolus; every 15 minutes X 4; then every hour X 4; then every 2 hours thereafter Special Considerations: 1. Natrecor is not usually titrated 2. Major side effect is hypotension. Notify physician if systolic BP is less than 90 mmHg 3. Do not give IV push medications through the line infusing Natrecor Reference: Electronic Drug Reference; American Heart Association 5 Specialty Medication Administration, PCS IV-A-80 Titrating Specialty Medication Infusion Guidelines: Critical Care – Appendix B Medication Drip Brand/Generic Concentration Name Dosage Titration Weaning Ativan Lorazepam 0.24 mg/ml Very agitated: 1 mg/hr. Less agitated: 0.25-0.5 mg/hr. Once adequate sedation achieved, titrate to lowest effective dose Wean according to MD order Breviblock Esmolol 10 mg/ml Bolus: 500 mcg/kg over 1 minute; then 50mcg/kg/min Over 4 minutes then maintenance 50-200 mcg/kg/min Varies, but usually if no satisfactory response. refer to MD orders Cardene Nicardipine 0.1 mg/ml 5-15 mg/hr Increase by 2.5 mg/hr. every 15 minutes After clinical control of heart rate & patient stabilization, should be changed to alternate antiarrhythmic; decrease rate by 50% 30 minutes after first dose of other drug. D/C one hour after second dose of other drug if rate control Decrease by 2.5mg/hr every 15 minutes Cardizem Diltiazem 1 mg/ml Bolus 0.25 mg/kg Over 2 minutes; then start @ 10 mg/hr. Decrease as ordered Cordarone Amiodarone Bolus: 1.5 mg/ml Diprivan Propofol 10 mg/ml Bolus: 150 mg over 10 minutes then 1mg/min over 6 hrs. then 0.5 mg/min for 18 hrs. 10-70 mcg/kg/min Increase by 5 mg/hr. up to max of 15 mg/hr. or until desired response Not usually titrated Dose adjustments as noted in dosage column 10-20 mcg/kg/min every 10-15 minutes until desired effect Dobutrex Dobutamine 1 mg/ml 2-20 mcg/kg/min Titrate to desired parameter Avoid abrupt discontinuation. Decrease by 10-20mcg/kg/min increments every 10-15 minutes until patient reaches a light sedation level Decrease by 0.5mcg/kg/min every 15 minutes as long as desired parameter maintained Epinephrine 4 mcg/ml 2-10 mcg/min Start @ 2 mcg/min; Increase by 0.5 mcg/min to maintain desired parameter Decrease by 0.5mcg/min to maintain desired parameter Heparin 50 units/ml See Specific Heparin Protocol Intropin Dopamine 1.6 mg/ml 2-20 mcg/kg/min Increase by 0.5-1 mcg/kg/min until desired parameter reached Decrease by 0.5mcg/kg/min every 15 minutes as long as desired parameter maintained Insulin 1 unit/1 ml Per MD order or protocol/order set Per MD order or protocol/order set As ordered Infusion: 1.8 mg/ml See Diprivan order for Intubated & ventilated patients See Weight Based Heparin Order See Policy IV-A-20 As ordered by MD; usually stops with completion of final 18 hour dose Monitoring Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour. Wake daily to assess CNS status Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Recommend VS every 4 hours or as ordered Recommend PTT monitoring as ordered: PTT 6 hours after any dosage change Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour See Policy IV-A-10 Blood glucose monitoring per MD order or protocol Reference: Electronic Drug Reference; American Heart Association 6 Specialty Medication Administration, PCS IV-A-80 Titrating Specialty Medication Infusion Guidelines: Critical Care – Appendix B Medication Brand/Generic Name Drip Dosage Non weight base: 0.5-30 mcg/min Weight based: 0.04-1 mcg/kg/min Bolus: 1-1.5 mg/kg IVP Then 1-4 mg/min Decrease slowly to avoid abrupt hypotension Start @ 2 mg/min, increase by 0.5-1 mg/min to control PVCs Not usually titrated Decrease by 0.5 mg/min every hour as long as PVCs suppressed Decrease by 10-20 mcg/hr. as long as desired parameter is maintained 0.5-5 mg/min DO NOT EXCEED 180MG/HR. Start @ 100 mcg/min and increase by 10 mcg/min to maintain desired parameter Start @ 0.5 mcg/kg/min. Increase by 0.5 mcg/kg/min q 5 minutes to reach desired parameter Increase 0.5 mg/min every 30 minutes until desired response GI bleed: 0.2-0.8 units/min GI bleed: 0.2 units/hr 16 mcg/ml Lidocaine 4 mg/ml Natrecor Nesititide 6 mcg/ml Bolus: 2 mcg/kg over 1 minute Infusion: 0.01 mcg/kg/min Neosynephrine Phenylephrine 0.04 mg/ml 100-180 mcg/min Nipride 0.2 mg/ml 0.3-10 mcg/kg/min 1 mg/ml 0.4 units/ml Nitroprusside Sodium Trandate Labetalol Pitressin Vasopressin Weaning None Levophed Norepinephrine Normodyne Titration Monitoring Concentration Precedex Dexmedetomidine 4 mcg/ml Primacor Milrinone 0.2 mg/ml Pronestyl Procainamide 4 mg/ml Tridil Nitroglycerine 0.2 mg/ml Septic shock: 0.01-0.04 units/min Loading dose: 1mcg/kg over 10 Minutes then 0.1-0.7 mcg/kg/hr. Loading dose: 50 mcg/kg over 10 Minutes then 0.5 mcg/kg/min Loading dose 20 mg/min up to 1 Gram then 2-4 mg/min Start @ 5-10 mcg/min Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Vital signs every 4 hours or as ordered BP - prior to and after bolus; then q 15 minutes X4; then q hour X4; then q 2 hours thereafter Considerations Major side effect is hypotension. Notify MD if systolic BP is less than 90 mmHg Do not give IV push medications through the line infusing Natrecor Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Decrease by 0.5 mcg/kg/min q15 minutes as long as desired parameter maintained Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Decrease by 0.5 mg/min every 30 minutes Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour GI bleed: If bleeding controlled for 12 hours, may decreased drip by 50% then stop in 12-24 hours Not usually weaned. Patients may be extubated while on Precedex Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour May be titrated as ordered Often not titrated Decrease as ordered Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Start @ 2 mg/min. Increase by 0.5-1 mg/min as to control PVC’s. Do not exceed 4mg/min Increase 5-10 mcg/min q 3-5 minutes until chest Decrease by 0.5 mg/min every hour as long as PVCs suppressed Vital signs every 4 hours or as ordered Decrease by 5-10 mcg/min every 15 minutes as long as desired parameters maintained Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Septic shock: DO NOT TITRATE None discomfort relieved, highest ordered dose achieved, hypotension develops Vital signs every 5-15 minutes for first hour and at least every 15 minutes and PRN for drip rate changes. If not titrating and vital sign stable document every hour Reference: Electronic Drug Reference; American Heart Association 7