exercise - WordPress.com
advertisement

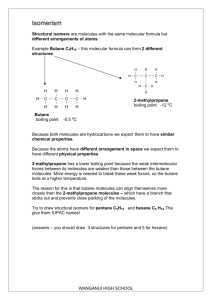
Chemrock DPP No. - SUB. CHEMISTRY TOPIC ISOMERISM : EXERCISE : 1. Isomers of propionic acid are (1) HCOOC2H5 and CH3COOCH3 (3) CH3COOCH3 and C3H7OH (2) (4) HCOOC2H5 and C3H7COOH C3H7OH and CH3COCH3 2. A compound of molecular formula C7H16 shows optical isomerism, compound will be (1) 2, 3-Dimethylpentane (2) 2, 2-Dimethylbutane (3) 2-Methylhexane (4) None of the above 3. 2-butene shows geometrical isomerism due to (1) Restricted rotation about double bond (2) (3) Free rotation about single bond (4) Free rotation about double bond Chiral carbon 4. Stero isomers which are not the mirror images of each other are called (1) Enantiomers (2) Meso isomers (3) tantomers (4) 5. n-Butyl alcohol and isobutyl alcohol exhibit (1) Metamerism (2) Chain isomersism (3) Position isomerism (4) Stereo isomerism 6. An organic compound exhibits optical isomerism when (1) Four groups linked to carbon atom are different (2) Three groups linked to carbon atom are different (3) Two groups linked to carbon atom are different (4) All the groups linked to carbon atom are same 7. C7H9N has how many isomeric forms that contain a benzene ring (1) 4 (2) 5 (3) 6 (4) 7 8. The isomerism exhibited by alkyl cyanide and alkyl isocyanide is (1) Functional (2) Positional (3) Tautomerism (4) Metamerism 9. Which of the following will have geometrical isomers (1) 2-Methylpropene (2) 2-Butene (3) 1-Butene (4) Propene 10. The isomers which can be converted into another forms by rotation of the molecles around single bond are (1) Geometrical isomers (2) Conformers (3) Enatiomers (4) Diastereomers 11. CH3CH2CH = CH2 and CH3 – CH = CH – CH3 show (1) Chain isomerism (2) Position isomerism (3) Functional isomerism (4) Metamerism 12. The total number of isomers formed by C 5H10 is (10 2 (2) 3 (3) 4 (4) 5 13. Total number of isomers of C6H14 are (1) 4 (2) 5 6 (4) 7 14. An isomer of ethanol is (1) Methanol (2) Diethyl ether (4) Ethylene glycol 15. Name the compound, that is not isomer with diethyl ether (1) n-Propylmethyl ether (2) Butane-1-ol (3) 2-Methylpropane-2-ol (4) Butanone 16. Diethyl ether and methyl n-propyl ether are (1) Position isomers (2) Functional isomers (4) Chain isomers 17. The type of isomerism exhibited by maleic and fumaric is (1) Functional isomerism (2) Optical isomerism (3) Cis-trans isomerism (4) Position isomerism 18. A mixture of equimolecular amount of enantiomorphs is known as (1) A atutomeric mixture (2) A racemic mixture (3) An optically inactive mixture (4) Azeotropic mixture 19. The number of possible secondary amine of formula C4H11N (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 (3) Dimethyl ether (3) 1 (3) Metamers (4) Diastereoisomers 4 Chemrock SUB. CHEMISTRY DPP No. 20. 21. TOPIC ISOMERISM Ethanoyl chloride is not an isomer of (1) Chloroethylene oxide (3) 2-Chloroethene-1-ol (2) (4) Which type of isomerism is shown by pentanone (1) Chain isomerism (2) Position isomerism 2-Chloroethanal Ethylene chlorohydrin (3) Functional isomerism (4) All of these 22. The type of isomerism shown by CH3CH(OH)COOH is (1) Position isomerism (2) Stereo isomerism (3) Optical isomerism (4) Cis-trans isomerism 23. Functional isomers of alkadiene is (1) Alkyne (2) Cycloalkene 24. A compound has 3 chiral carbon atoms. The number of possible optical isomers it can have is (1) 3 (2) 2 (3) 8 (4) 4 25. Can homologues be isomers (1) Yes (2) No (3) (3) Alkene (4) Sometimes 1 & 2 both (4) None Staggered form (4) None 26. In butane, which form has the lowest energy (1) Gauche form (2) Eclipsed form (3) 27. The process of separation of racemic modification into d- and l-enantiomers is called (1) Resolution (2) Dehydration (3) Revolution (4) Dehydrohalogenation 28. Find the non-staggered form(s) of ethane - H H H H (1) (2) H 29. H H H H H H (3) H H H (4) H H H None H Methylpropyl thioether and isopropyl methyl thioether are (1) Metamers (2) Position isomers (3) Chain isomers (4) Chain and position both 30. The (1) (2) (3) (4) enolic form of acetaldehyde contains 6 Sigma bonds, 1 pi bond and 2 lone pairs 8 sigma bonds, 2 pi bonds and 2 lone pairs 10 sigma bonds, 1 pi bonds and 1 lone pair 9 sigma bonds, 2 pi bond and 1 lone pair 31. Possible number of disubstituted benzene isomers is – (a) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 32. Which type of isomerism is mutually shown by the following structures (4) 4 Cl CH3 — CH — CH2 — CH2 — CH3 (1) (3) CH3 — CH2 — C — CH3 Cl Only functional group isomerism Positional and chain isomerism (2) (4) CH3 Only chain isomerism Only positional isomerism 33. What should be the minimum number of carbon atoms present in an ether to exhibit chain isomerism (1) 2 (2) 3 (3) 4 (4) 5 34. Which of the following is not a functional group isomer of ethyl acetate (1) Isobutyric acid (2) 2, 3-Butanediol (3) 3-Hydroxybutanal (4) 4-Hydroxybutanone 35. Which of the following can be regarded as an enolic form of acetone (1) Propanal (2) 2-Propene-1-ol (3) 1-Propen-1-ol (4) 36. How many carbon atoms are present in lowest possible alkane which can exhibit enantiomerism (1) 5 (2) 6 (3) 8 (4) 7 2 Isopropenyl alcohol Chemrock SUB. CHEMISTRY DPP No. - TOPIC ISOMERISM 37. A compound whose molecule is superimposable on its mirror image inspite of the presence of chiral centres is called (a) Diastereomer (2) Meso compound (3) An enantiomer (4) A threo enantiomer 38. Among the following structure which one is called erythro isomer B (A) (1) 39. The (1) (2) (3) (4) B A X A X (B) Y (A) and (B) (2) B A X X A Y Only (B) (C) (3) pair of structure given below represent Enantiomers Conformers H Position isomers Homologues Br (1) H3C C 41. 42. 43. H H H H H H Me Cl CH2CH5 CC CH3 C HO H CHCl2 (4) CC Cl H Only (C) and CH CH2 (3) Y (4) H CH2CH3 H3C A H (2) CC X Me Which of the following represent E isomer : Cl B Only (A) H 40. A CHCl2 CH3 The instrument used for measuring specific rotation is (1) Spectrometer (2) Polarimeter (3) Lactometer (4) Ammeter Ethyl acetoacetate exhibits which of the following isomerism (1) Optical (2) Geometrical (3) Tautomerism (4) Enantiomerism Examine following three pairs of possible isomers Cℓ CH3 Cℓ Cℓ CH3 (ia) Now (1) (2) (3) (4) (ib) Cℓ (iia) CH3 COOH CH3 (iib) COOH COOH (iiia) (iiib) COOH state whether the pairs represent identical compounds or different isomers All threee pairs represent different compounds (ia) and (ib) are identical; (iia) and (iib) are identical; and (iiia) and (iiib) are identical (ia) and (ib) are isomers; (iia) and (iib) are identical; (iiia) and (iiib) are isomers (ia) and (ib) are identical; (iia) and (iib) are identical; and (iiia) and (iiib) are isomers 44. & (1) Position isomers 45. asdf (1) are called as (2) Chain isomers & Chain (3) Funcitonal isomers (4) Ring chain isomers Show isomerism (2) Position (3) 3 Functional (4) None of these Chemrock SUB. CHEMISTRY DPP No. - TOPIC ISOMERISM ANSWER KEY : QUE. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ANS. 1 1 1 4 2 1 2 1 2 2 QUE. 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ANS. 2 4 2 2 4 3 3 2 3 4 QUE. 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 ANS. 4 3 4 3 2 3 1 2 2 1 QUE. 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 ANS. 3 2 4 2 4 4 2 3 2 2 QUE. 41 42 43 44 45 ANS. 2 3 4 1 3 4