78. Force of Muscle Contraction
advertisement

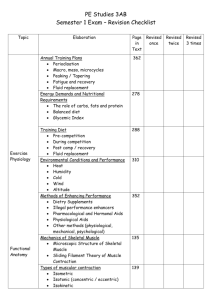
1. Muscle Physiology 2 - 4. Muscle Tissue Review – ______________________________________________ http://www.siumed.edu/~dking2/ssb/NM017b.htm ______________________________________________ http://www.siumed.edu/~dking2/ssb/NM018b.htm ______________________________________________ http://www.siumed.edu/~dking2/ssb/NM016b.htm ______________________________________________ 5. Muscle Tissue Characteristics Excitability or Irritability - ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Contractility - ______________________________________________ Extensibility - ______________________________________________ Elasticity 6. Muscle Key Words Muscle Type Associated Terms General Myo-, Mys-, Sarco-, Fibers Skeletal Striated, Voluntary Cardiac Striated, Involuntary Smooth Visceral, Nonstriated, Involuntary ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 7. Muscle Functions Production of Movement Locomotion, manipulation Movement of fluids through hollow organs Maintenance of Posture Skeletal muscle Stabilization of Joints Skeletal muscle Generation of Heat Skeletal muscle, body temperature homeostasis ______________________________________________ 8. Skeletal Muscle – The Organ Skeletal muscle fibers Nerve fibers Nerve fiber for each muscle fiber Blood vessels Highly metabolic Connective tissue ______________________________________________ 9. Muscle Anatomy Epimysium Dense irregular CT Continuous with other sheaths and with tendons ______________________________________________ http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Illu_muscl e_structure.jpg_ 10.Muscle Anatomy Fascicle - Bundle of muscle fibers Perimysium -Fibrous CT covering of fascicle http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Illu_muscl e_structure.jpg 11.Muscle Fiber Elongated, striated, multinucleate Endomysium Fine sheath CT with reticular fibers http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Illu_muscl e_structure.jpg ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 12. Series Elastic Components Continuous with each other and with tendon Transmit forces to bone Entry/exit routes Elasticity ______________________________________________ http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Illu_muscl e_structure.jpg ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 13. Skeletal Muscle Fiber Sarcolemma Plasma membrane Sarcoplasm Cytoplasm Glycosomes Myoglobin Myofibrils Sarcoplasmic reticulum ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/images/Image286.gif ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 14. Myofibrils Parallel rods Bulk of cell volume Striations Features Z disc H zone I band A band M line ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/images/Image286.gif ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 15. Sarcomere Segment of myofibril Between adjacent Z discs Functional unit of contractility ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/images/Image286.gif ______________________________________________ 16. Anatomy of a Muscle Sarcomeres end-to-end Myofibrils Fibers (endomysium) Fascicles (perimysium) (epimysium) ______________________________________________ Myofibril Fiber Fascicle Muscle 17. Filaments of Sarcomere Thick filaments A band Thin filaments I band A band except H zone ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/images/Image286.gif ______________________________________________ 18. Thick Filaments – [Fig. 8-4b, p. 206] Myosin Two polypetide chains forming tail and 2 heads form cross bridges with thin filaments 19. Thick Filaments Central area Tails of myosin Surface ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Studded with heads Actin binding sites ATP binding sites and enzymes for splitting ATP http://www.ivy-rose.co.uk/Topics/Muscles/Filament.jpg 20. Thin Filaments Actin 22. Filaments ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ http://www.snv.jussieu.fr/vie/dossiers/muscles/muscles.htm ______________________________________________ 23. Contraction H zone disappears I bands get smaller Z discs get closer together A band does not change in length ______________________________________________ 26. http://pharyngula.org/images/myosin_contractcycle.jpg 27. Role of Calcium Low intracellular Ca2+ Relaxation High intracellular Ca2+ Contraction Calcium-troponin binding Tropomyosin unblocks active sites on actin Myosin heads attach to active sites, pulling thin filaments toward center of sarcomere 29. http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/movies/actin_myosin_gif.html ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 30. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Smooth ER Surrounds myofibril Longitudinal Lateral sacs (terminal cisternae) Calcium regulation Storage Release ______________________________________________ http://www.etsu.edu/cpah/hsci/forsman/Histology%20of%20mu sclefor%20web_files/image009.jpg ______________________________________________ 32. T Tubules/Transverse Tubules Sarcolemma Continuous w/extracellular space Form triad Terminal cisterna T tubule Terminal cisterna Electrical impulse conduction http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/musclecell.jpg 33. Triad Electrical impulses conducted via T tubules Triggers calcium release from terminal cisternae ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 34. Innervation Every muscle has a nerve that innervates it Every muscle fiber has nerve fiber that innervates it ______________________________________________ http://academic.wsc.edu/faculty/jatodd1/351/motor_unit.jpg ______________________________________________ 35. Neuromuscular Junction Nerve impulse end of axon at synapse ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Ca2+ channels open Synaptic vesicles release acetylcholine ACh binds to receptors on muscle fiber 36. Neuromuscular Junction ACh receptors have ion channels that open when ACh binds Diffusion of Na+ into muscle fiber, K+ out Depolarization ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 37. Depolarization of the Sarcolemma Influx of Na+ change in membrane potential Depolarization adjacent areas of sarcolemma Propagation of action potential ______________________________________________ 38. Propagation and Repolarization After depolarization, Na+ channels close, K+ channels open Initial polarized state is restored Refractory period ______________________________________________ 41.http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/nmj.html ______________________________________________ http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/myosin.html 42. Sarcomere – Unit of Contraction Filaments Z disc A band I band H zone M line ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/images/Image286.gif ______________________________________________ 43. Sliding Filament Theory Contraction of the sarcomere occurs when the actin filaments slide past the myosin filaments ______________________________________________ http://physioweb.med.uvm.edu/muscle_physio/muscle_contrac tion/mscl_cntrct_filaments.htm ______________________________________________ 44 –45. Muscle Contraction http://www.cannock.ac.uk/sports/sport_zip/muskel5.html ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Tension - ______________________________________________ Load – ______________________________________________ http://www.sciencebase.com/images/muscle_contraction.jpg 46. Isotonic Contraction Tension overcomes load Muscle shortens Object moves Measure amount of shortening 47. Isometric Contraction Muscle tension develops Load is not moved Muscle does not shorten Measure muscle tension 48. http://img.tfd.com/dorland/thumbs/contraction_isometric.jpg ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 49. Muscle Contraction ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 50. Motor Unit Motor neuron Nerve cell that carries information re: movement Axon branches; Its terminals form multiple neuromuscular junctions with individual muscle fibers Muscle fibers served by that neuron ______________________________________________ http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/neuro/c49x38motorunit.jpg ______________________________________________ 51 - 53. Muscle Twitch Response of a motor unit to an action potential of its motor neuron Phases Latent Contraction Relaxation 54. Latent Phase 55. Contraction Phase 56. Relaxation Phase 57. Graded Muscle Responses Variations in strength of muscle contractions Grading Frequency of stimulation Changing strength of stimulation 58. Treppe Staircase effect Initial contractions not as strong as those that follow ? - Increasing Ca2+ Active sites on actin Heat leading to pliability and enzyme efficiency http://media.wiley.com/Lux/05/21805.nfg002.jpg 59. Changes in Stimulation - Frequency Wave (or Temporal) Summation If 2 stimuli of same intensity in rapid succession, second twitch stronger that first http://www.abcbodybuilding.com/magazine03/tetanus2.jpg 60. Incomplete Tetanus Increased rate of stimulation leads to sustained but not smooth contract Relaxation time becoming shorter http://www.abcbodybuilding.com/magazine03/tetanus2.jpg 61. Tetanus No relaxation Smooth, sustained contraction http://www.abcbodybuilding.com/magazine03/tetanus2.jpg ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 62. http://www.unm.edu/~jimmy/wave_summation.jpg ______________________________________________ 63. http://media.wiley.com/Lux/05/21805.nfg002.jpg ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 64. Fatigue Muscle cannot perform at required level;physiologic inability to contract Relative deficit of ATP Gradual reduction in performance 65. Fatigue Muscle is no longer able to sustain its level of tension and begins to elongate Buildup of acidic compounds which affect function of proteins, relative lack of ATP, ionic imbalances resulting from membrane activities Able to respond to stimulation after rest and adequate blood supply 66. Fatigue 67. Changes in Stimulation - Strength Threshold stimulus First observable contraction occurs Maximal stimulus Strongest stimulus that produces an increase in tension 69. Multiple Motor Unit Summation Recruitment Increasing stimulus increases the number of motor units stimulated Laboratory Increase voltage In Vivo Stimulate more motor neurons 70. Multiple Motor Unit Summation Motor units Usually asynchronous Delay fatigue Synchronous Strong contraction 71. Summary Multiple Motor Unit Summation Strength of stimulation Increases force of contraction by stimulation of the appropriate number of motor units Wave or Temporal Summation Frequency of stimulation Smoothes contraction via rapid stimulation of muscle cells 72. Muscle Tone Continual slight contraction Spinal reflexes Stabilize joints Maintain posture 73. Isotonic Contractions Muscle length changes Load moves http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/Notes/API%20Notes% 20J%20Complete%20Muscle%20Contraction.htm 74. Isotonic Contractions ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Tension increases until sufficient to move load Tension then remains constant through rest of contraction 75. Isometric Contractions Muscles neither shortens or lengthens Load is greater than force generated by muscle 76. Isometric Contractions Cross bridges generate force, thin filaments not sliding Isotonic Sliding of thin filaments Peak tension developed and maintained but no change in resting length Stabilization of joints Maintenance of posture 86. Velocity and Duration 87. Adaptation Improved ATP-synthesizing activity Oxidative fibers Increased mitochondria Hypertrophy Increased diameter of glycolytic ifbers Increased mysoin/actin Testosterone Atrophy Disuse Denervation ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 77. Comparison ______________________________________________ 78. Force of Muscle Contraction Number of fibers stimulated Multiple Motor Unit Summation Frequency of stimulation Wave or Temporal summation Size of fibers Large fibers produce more powerful movements Degree of muscle stretch Optimal resting length ______________________________________________ 79. Length Optimal length 80-120% of normal resting length Length-tension relationship 80. Velocity and Duration of Contraction Load / Recruitment / Muscle Fiber Type 81. ATP Requirements myosin energized break cross bridges pump calcium back into sarcoplasmic reticulum Sources Creatine phosphate/Oxidative phosphorylation/ Glycolysis Oxygen debt or deficit 82- 84. Muscle Fiber Type Slow Fibers (oxidative) Contract slowly Fatigue resistant Thin – allowing rapid diffusion of nutrients Limited power – fewer myofibrils Red – abundant myoglobin Fast Fibers (glycolytic) Contract rapidly Tire quickly Larger White Powerful – larger diameter and more myofibrils Fast Fibers (Oxidative) Type IIa Contract rapidly Somewhat fatigue resistant Red http://www.octc.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/Notes/API%20Not es%20J%20Complete%20Muscle%20Contraction.htm ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ _____ _______________________________________