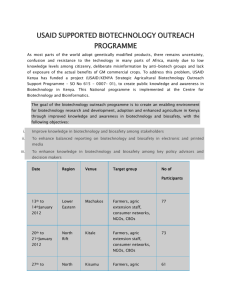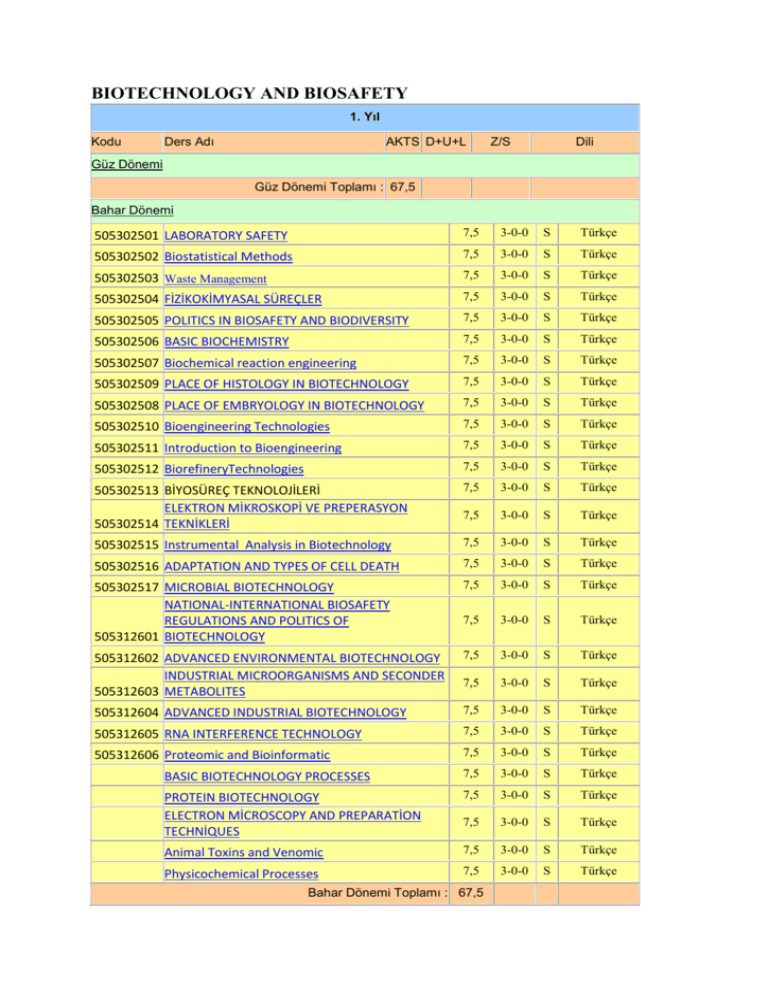
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY
1. Yıl
Kodu
Ders Adı
AKTS D+U+L
Z/S
Dili
Güz Dönemi
Güz Dönemi Toplamı : 67,5
Bahar Dönemi
505302501 LABORATORY SAFETY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302502 Biostatistical Methods
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302503 Waste Management
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302504 FİZİKOKİMYASAL SÜREÇLER
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302505 POLITICS IN BIOSAFETY AND BIODIVERSITY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302506 BASIC BIOCHEMISTRY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302507 Biochemical reaction engineering
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302509 PLACE OF HISTOLOGY IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302508 PLACE OF EMBRYOLOGY IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302510 Bioengineering Technologies
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302511 Introduction to Bioengineering
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302512 BiorefineryTechnologies
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302513 BİYOSÜREÇ TEKNOLOJİLERİ
ELEKTRON MİKROSKOPİ VE PREPERASYON
505302514 TEKNİKLERİ
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302515 Instrumental Analysis in Biotechnology
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302516 ADAPTATION AND TYPES OF CELL DEATH
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505302517 MICROBIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY
NATIONAL-INTERNATIONAL BIOSAFETY
REGULATIONS AND POLITICS OF
505312601 BIOTECHNOLOGY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505312602 ADVANCED ENVIRONMENTAL BIOTECHNOLOGY
INDUSTRIAL MICROORGANISMS AND SECONDER
505312603 METABOLITES
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505312604 ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505312605 RNA INTERFERENCE TECHNOLOGY
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
505312606 Proteomic and Bioinformatic
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
BASIC BIOTECHNOLOGY PROCESSES
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
PROTEIN BIOTECHNOLOGY
ELECTRON MİCROSCOPY AND PREPARATİON
TECHNİQUES
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
Animal Toxins and Venomic
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
Physicochemical Processes
7,5
3-0-0
S
Türkçe
Bahar Dönemi Toplamı : 67,5
YIL TOPLAMI : 67,5
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302503
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
1
Fall
Waste Management
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7.5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( X.)
LANGUAG
E
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and biosafety
Social
Science
X
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
%
1
25
1
30
1
45
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
None
General definitions of waste and waste management, physical,
chemical, biological properties of solid, liquid and gas wastes and
capturing and recycling of these wastes, evaluating the environmental
impacts of wastes.
The result of increasing population of the World and daily growing
technologies, solid, liquid and gas wastes do occur. The aim of this
course is to teach capturing, handling and recycling of these wastes.
Understanding, the management of wastes which causes
enviromental pollutions, the impacts of these wastes and , evaluating
these impacts
1.To learn about water, air and soil pollution
2.To learn physical, chemical and biological cleaning technologies
3.Ability to work effectively in inner or multi-disciplinary teams
4.To learn how to analyse problems with modern experimental
methods and new technologies
1. Karpuzcu M., (1996), Çevre Kirlenmesi ve Kontrolü, Kubbealtı
Yayınları, İstanbul, 1996
2. George T., Frank K., (2002), Handbook of Solid Waste
Management, McGraw-Hill Handbooks, Quebecor/Martinsburg
1. Tchobanoglous G., Theisen H., Vigil, S.S., (1993),Integrated Solid
Waste Management, Singapore, McGraw Hill
2. Mackenzie L D., Susan J M., (2004), Principles of Environmental
Engineering and Science, McGraw-Hill
Computer and Data Show
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
General definitions of waste and waste management
Sources of solid, liquid and gas wastes and varietiesi
Physical, chemical and biological properties of solid wastes
Handling, storing and recycling of solid wastes
Physical, chemical and biological properties of liquid wastes
Mid-Term Examination 1
Handling, storing and recycling of liquid wastes
Physical, chemical and biological properties of gas wastes
Handling, storing and recycling of gas wastes
Handling, storing and recycling of hazardous wastes
Mid-Term Examination 2
Environmental impact assessment (EIA)
Presentation of homeworks
Presentation of homeworks
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Prof. Dr. Sabiha KOCA
Date: 27/11/2012
Signature(s):
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
SEMESTER
Biotechnology and biosafety
COURSE CODE
505101503
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
2012/2013
fall / spring
Biochemical reaction engineering
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7.5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ()
ELECTIVE ( x)
LANGUAG
E
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
x
Biotechnology and Biosafety
[if it containsconsiderabledesign, mark with () ]
( )
SocialScienc
e
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
%
1
30
2
30
1
40
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
Introduction to fermentation technology, fermentation techniques
and processes used in biotechnology, bioreactors, continuous
production, sterilization, automatic control and Bioreactors, aerobic
and anaerobic processes, BOD and COD, biomass production kinetics,
substrate consumption, product formation, biological reactor design,
control systems, product purification method, the advantages and
economy of bioprocesses by other processes.
Investigation the biological production processes, determine the
characteristics of the process.
1. The ability to have knowledge about the biochemical reaction
engineering and bioprocesses
2. To be informed about our problems and to identify enzymes and
enzyme kinetics
3. fermenter design
Processes and products used in the field of biotechnology and food to
be informed about
TEXTBOOK
1.
Türker M., Biyoreaksiyon Mühendisliği, Su vakfı yayınları ,
2005
2.
Kargı F., Çevre Mühendisliğinde biyoprosesler, D.E.Ü. Müh.
Fak. Basım Ünitesi,izmir,1995
3.
Bailey J. E. And Ollis D. F. , Biochemical Engineering
Fundamentals., McGraw-Hill, Edition, New York, 1986
4.
Pekin B., Biyokimya Mühendisliği, Ege Üni. İzmir,1983
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TOPICS
Introductiontofermentationtechnology,
Fermentationtechniquesandprocessesused in biotechnology,
Bioreactors,
Continuousproduction,
Sterilization
Mid-Term Examination 1
AutomaticcontrolandBioreactors,
Aerobicandanaerobicprocesses,
Kinetics of biomassproduction, substrateconsumption, productformation,
Biologicalreactordesign, controlsystems,
Mid-Term Examination 2
Product purificationmethod,
Advantagesoverotherprocessesandeconomy of bioprocesses
Homeworkandpresentation
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Ability to obtain necessary knowledge deeply through scientific investigation, ability to
evaluate, conclude and apply this knowledge in chemical engineering.
Having comprehensive knowledge about up-to-date technologies and methods and their
limitations in engineering.
Ability to complete and apply the limited or insufficient data through scientific methods
and ability to use together the knowledge of different disciplines.
Awareness of new and improving applications in chemical engineering and the ability to
learn and study on these applications.
Ability to define and formulate the problems related to chemical engineering, ability to
improve methods to solve these problems and ability to apply innovative methods for
solutions.
Ability to develop new and/or original ideas and methods, ability to design complex
systems and processes and develop innovative/alternative solutions in the designs.
Ability to design and apply the theoretical, experimental and modeling research activities
and ability to discuss and solve the complex problems arisen in these processes.
Ability to study effectively in teams for in-discipline and interdisciplinary activities, ability
to lead these teams, ability to develop useful problem-solving approaches in complex
situations, and ability to have responsibilities and to study independently and individually
in all cases.
Ability of written and oral communication using a foreign language sufficiently.
Ability to present properly, clearly and systematically all processes and results of their
studies oral or in written form in all kinds of national and international media.
3
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
To have the knowledge of social, environmental, health, safety and legal aspects in
engineering applications and the knowledge of project management and engineering
activities, and awareness of all of their limitations in engineering operations.
Having the social, scientific and ethical responsibilities in all stages of collecting,
12 interpreting and presenting the related data and in all professional activities.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3:Completelycontribution.
x
11
Prepared by:Asistant Prof. Dr. MacidNurbaş
Date:
19/11/2012
Signature(s):
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
COURSE CODE
505302506
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
1.
SEMESTER
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
Practice
Laboratory
SPRING
BASIC BIOCHEMISTRY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
3
7.5
TYPE
LANGUAG
E
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
TURKISH
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
MID-TERM
Quantity
1
1
%
20
20
Homework
Project
Report
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
Others (………)
FINAL
1
60
NONE
In this course basic nomenclature, structure and function of
aminoacids, peptides, proteins, enzymes, coenzymes, nucleic acids,
carbohydrates and lipids will be covered.
To gain information about the structure and function of the
biomolecules as well as the chemical mechanism of basic process in
the living organism
At the end of this course students would gain knowledge about the
structure and function of the biomolecules by gaining analytical
thinking ability and they will gain new insight on the importance of
biochemistry in biology.
1. Gaining molecular insight on chemical structure of the living
2. Gaining knowledge about importance water and minerals
3. Describing how structure of bio molecules and functional groups
effect the physical features of the living being
4. Describing structure and function of the amino acids
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
5. Learning how amino acids effect the function of proteins
6. Linking protein structure to its function
7. Learning the kinetics of enzymatic reactions
8. Naming the structure and function of nucleic acids
9. Naming and charecterizing carbohydrates
10. Describing the chemical structure and function of lipids
P.C.Champe, R.A.Harvey Ed. Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews:
“Biochemistry”, Turkish Translation.: E.Ulukaya, Nobel Medical
Book Store, (2007).
1. Keha E.E.,Kührevioğlu I., " Biochemistry", (2004).
2. Nelson, D.L. and Cox, M.M. (2004). Lehninger Principles of
Biochemistry. Chapter 1-13), Worth Publishers, Wisconsin, USA
(in Turkish version: Palme yayıncılık: Ed. Kılıç N.).
3. Gözükara E., Biochemistry, Ankara (1990)
Computer, projection device
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
Biomolecules, chemical compounds, functional groups, configuration and confirmation), aquarious
solutions
Aminoacids in proteins
O in amino acids and nonstandart amino acids not
3D structure of proteins
Characterization of protein structure
I. Midterm Exam / General features of enzymes and their nomenclature
General features of enzymes and their nomenclature, enzymatic reactions, mechanism of catalysis
Monosacharides, polysacharides
Glycolipids, glycoproteins
Covalent structure of nucleic acids
II. Midterm Exam / Covalent structure of nucleic acids, sequance of the nucleic acids, chemical
synthesis of oligonucleotids
Characterizing lipids and their function
Biomembranes, lipoproteins
Classifying vitamins and analyzing their chemical structure and function
FINAL EXAM
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Instructor(s): Asso Prof.Dr. Adnan AYHANCI
Signature:
Date:
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505312602
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
FALL/SPRİNG
ADVANCED ENVIRONMENTAL
BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TÜRKÇE
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
The scope of this course will be included the environmental
biotechnology.
The aim of this course is to provide understanding of the importance
of microorganisms of biodiversity and the ecosystem the by the
students.
This course will contribute to prepare for professional life by
providing knowledge on the importance of microorganisms in
biotechnology and the flow of production processes.
1.
Understanding
the
importance
of
environmental
biotechnology
2.
Sort of environmental biotechnologically relevant
microorganisms
3.
To understand the biotechnological treatment process
4.
Examplify the treatment process of microorganisms
5.
To explain the production of biotechnological treatment
process on a commercial scale
6.
Understanding
the
environmental
biotechnologically
importance of microorganisms.
TEXTBOOK
Atlas, R. M., Bartha, R. (1997) Microbial Ecology Fundamentals and
Applications Wesley Longman Inc
OTHER REFERENCES
Madigan MT and Martinko JM. Brock Mikroorganizmaların
Biyolojisi (2006) (Çeviri Edit: Çökmüş C) Palme Yayıncılık, Ankara.
Prescott, L. M., Harley, J. P., Klein, D. A. (1996) Microbiology Wm.
C. Brown Publishers England Biotechnology Procedures and
Experiments Prescott, L. M., Harley, J. P., Klein, D. A. (1996)
Microbiology Wm. C. Brown Publishers England
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Computer and projection
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TOPICS
Scope to environmental biotechnology
Microbial evolutiın and interactions of microorganisms
Adaptation of microorganisms in environment
Adaptation of microorganisms in environment
Microbial habitats
Mid-Term Examination 1 Cycles of biogeochemistry
Cycles of biogeochemistry
The roles of microorganisms in waste treatment
Microbial interactions with xenobiotics and inorganic pollutants
Biotrasnformation, bioremediation
Mid-Term Examination 2 Biotrasnformation, bioremediation
Roles of microorganisms in recovery of metals, energetics and biomass production
Microbial controls of toxic substant
Toxicity
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
3
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
9
10
11
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
X
X
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Prof. Dr. Semra İLHAN
Date:
Signature(s):
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505312604
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
FALL/SPRİNG
ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL
BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TÜRKÇE
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Engineering Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
The scope of this course will be included the phylogeny and diversity
of Bacteria and its ındustrial application.
The aim of this course is to provide understanding of the importance
of Domain Bacteria as part of biodiversity and the ecosystem the by
the students.
This course will contribute to prepare for professional life by
providing knowledge on the importance of microorganisms in
biotechnology and the flow of production processes.
7.
Understanding the importance of biotechnology
8.
Sort of biotechnologically relevant microorganisms
9.
To understand the biotechnological production process
10.
To create the metabolites of microorganisms
11.
To explain the production of biotechnological products on a
commercial scale
12.
Understanding the biotechnologically importance of
microorganisms and its enzymes.
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Microbial Biotechnology; Fundamentals of Applied Microbiology.
Glazer AN and Nikaido H. 2007. Cambridge University Press.
Madigan MT and Martinko JM. Brock Mikroorganizmaların
Biyolojisi (2006) (Çeviri Edit: Çökmüş C) Palme Yayıncılık, Ankara.
Mikrobial Biotechnology; Fundamentals of Applied Microbiology.
Glazer AN and Nikaido H. 2007. Cambridge University Press.
Biotechnology Procedures and Experiments Handbook. Harisha S.
2007. Infinity Science Press LLC.
Handbook of Fungal Biotechnology. Ed: Arora DK. 2004. Marcel
Dekker, Inc.
Computer and projection
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
TOPICS
Microbial Biotechnology
History of microbial biotechnology, the important microbial processes
Microbial growth and substrates
Fermentation
Strain engineering; Mutation, Recombinant DNA technology, Genetic engineering
Mid-Term Examination 1 Strain engineering; Mutation, Recombinant DNA technology, Genetic
engineering
Bacterial Metabolites and product improvement
Fungal Metabolites and product improvement
Fermentation models for primer and seconder metabolites
Product chracterisation
Mid-Term Examination 2 Product chracterisation
Scale up: pilot scale
Scale up: industrial scale
Selected plant and specifications
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable processes and
environmental consciousness to problems on health, environment, food,
agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the methods of
research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making comments using
scientific developments related to his/her discipline and information technologies
3
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally, in
8
writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
9
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language belonging to
10
European Language Portfolio.
11 Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Prof. Dr. Semra İLHAN
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ahmet ÇABUK
Signature(s):
Date:
X
X
X
X
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302505
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
FALL/SPRİNG
POLITICS IN BIOSAFETY AND
BIODIVERSITY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TÜRKÇE
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
50
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
The scope of this course will be included biosafety and biodiversity of
living things.
The aim of this course is to provide understanding of the importance
of biosafety and biodiversity by the students.
This course will contribute to prepare for professional life by
providing knowledge on the importance of biosafety and biodiversty.
13.
Understanding the importance of biosafety
14.
Understanding the importance of together with biosafety and
biodiversity
15.
To understand the biosafety process
16.
Examplify the application of biosafety
17.
To explain the interaction with biosafety and biodiversity
Biyogüvenlik ve Biyoçeşitlilik Ders Notları, ESOGÜ Biyoloji
Bölümü, ESKİŞEHİR
Biosafety and bioethics, Joshi, R., 2006, Delhi.
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Computer and projection
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
Historical aspect of biosafety
Economics of biodiversity
Interactions of sustainable biodiversity and biosafety
Interactions of sustainable biodiversity and biosafety
Component of biosafety
Mid-Term Examination 1 Component of biosafety
Biosafety and transgenic plants
Biosafety and transgenic animals
Biosafety and transgenic microorgansims
Biotechnological process and biosafety
Mid-Term Examination 2 Biotechnological process and biosafety
Future of biosafety
New biotechnological products and biosfety
New biotechnological products and biosfety
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: öğretim elemanı talep edilecektir.
Signature(s):
2
Date:
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
Biotechnology and Biosafety (MSc)
COURSE CODE
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
505302511
Introduction to Bioengineering
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Fall
COURSE OF
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
Credit
ECTS
TYPE
LANGUAGE
3
0
0
3
7,5
COMPULSORY ()
ELECTIVE ( x )
Turkish
1
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety Subjects
[if it contains considerable design mark with
() ]
X
Social
Science
( )
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
Quantity
%
1st Mid-Term
1
30
2nd Mid-Term
1
30
1
40
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
Biomedical engineering, bioengineering and historical overview,
anatomy and physiology, electrical signals in biological systems,
biosensors, bioinstrumentation, principles of biosignal processing,
biomechanics, fundamental biotechnology.
The main aim of the course is to obtain introductory knowledge and
explore fundamental fields of bioengineering, understand and
investigate related concepts.
Obtaining introductory knowledge on bioengineering fields of study
and its interdisciplinary nature.
1. General knowledge on bioengineering related fields and concepts,
2. Ability to apply and associate interdisciplinary knowledge,
3. Ability to understand and solve natural sciences related problems,
4. Ability to work interdisciplinary,
5. Ability to analyze natural sciences related problems by using
modern experimental setups and technology.
Enderle J., Blanchard S., Bronzino J., (2005). Introduction to
Biomedical Engineering. Academic Press.
OTHER REFERENCES
1. Saterbak A., (2007). Bioengineering Fundamentals. Prentice Hall.
2. Webster J.G., (2009). Medical Instrumentation: Application and
Design. Wiley.
3. Boal D. (2002). Mechanics of the Cell. New York: Cambridge Pres.
4. Fung Y.C., (1993). Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living
Tissues. Springer.
5. Alberts B., et.al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland
Science.
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED
OURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
TOPICS
Biomedical engineering, bioengineering and historical overview,
Anatomy and Physiology; Cellular organization, tissues, major organ systems and homeostasis,
Electrical signals in biological systems; Historical perspective, neurons, cell membrane and its
modeling, biophysical approaches,
Biosensors; biopotentials and their measurements,
Biosensors; biopotentials and their measurements,
Mid-Term Examination 1
Bioinstrumentation; Basic instrumentation systems and their principles,
Bioinstrumentation; Basic instrumentation systems and their principles,
Principles of biosignal processing,
Biomechanics; Fundamental mechanical properties of biological systems,
Mid-Term Examination 2
Fundamental biotechnology; basic techniques, medical applications,
Fundamental biotechnology; medical applications,
Fundamental biotechnology; interdisciplinary,
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of specialty.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
3
2
1
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
10
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
11
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Asst.Prof. Sertaç Eroğlu
Date:
12.11.2012
Signature(s):
X
X
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
SEMESTER
Biotechnology and Biosafety (MSc)
COURSE CODE
COURSE NAME
505302510
Bioengineering Technologies
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Spring
COURSE OF
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
Credit
ECTS
TYPE
LANGUAGE
3
0
0
3
7,5
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
Turkish
2
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety Subjects
[if it contains considerable design mark with
() ]
X
Social
Science
( )
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
Quantity
%
1st Mid-Term
1
30
2nd Mid-Term
1
30
1
40
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
Biomaterials, tissue engineering, principles of genetic engineering,
introduction to medical imaging, biomedical optics and lasers.
The main aim of the course is to study introductory knowledge and
explore fundamental bioengineering technologies, understand and
investigate related concepts.
Obtaining introductory knowledge on bioengineering fields of study
and its interdisciplinary nature.
6. General knowledge on bioengineering related fields and
technologies,
7. Ability to apply and associate interdisciplinary knowledge,
8. Ability to understand and solve natural sciences related problems,
9. Ability to work interdisciplinary,
10.
Ability to analyze natural sciences related problems by using
modern experimental setups and technology.
Enderle J., Blanchard S., Bronzino J., (2005). Introduction to
Biomedical Engineering. Academic Press.
6. Saterbak A., (2007). Bioengineering Fundamentals. Prentice Hall.
7. Boal D. (2002). Mechanics of the Cell. New York: Cambridge Pres.
8. Fung Y.C., (1993). Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living
Tissues. Springer.
9. Cho Z.H., et al., (1993). Foundations of Medical Imaging. Wiley.
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
Biomaterials; classification, biological effects and biocompatibility,
Biomaterials; mechanical properties and testing,
Tissue engineering; tissue dynamics, stem cell technology, tissue and environment interaction,
Tissue engineering; tissue dynamics, stem cell technology, tissue and environment interaction,
Principles of genetic engineering,
Mid-Term Examination 1
Introduction to medical imaging; roentgen, computerized tomography,
Introduction to medical imaging; computerized tomography, ultrasound,
Introduction to medical imaging; magnetic resonance and nuclear imaging,
Introduction to medical imaging; magnetic resonance and nuclear imaging,
Mid-Term Examination 2
Biomedical optics and lasers; fundamentals of optics, interaction of light and matter,
Biomedical optics and lasers; light propagation in tissues, photothermal effects of lasers,
Biomedical optics and lasers; light propagation in tissues, photothermal effects of lasers,
Final Exam
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of specialty.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Date:
12.11.2012
Signature(s):
1
X
11
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Asst.Prof. Sertaç Eroğlu
2
X
X
X
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302512
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
2
Spring
Biorefinery Technologies
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( X )
LANGUAG
E
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
1
%
30
1
30
1
40
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
Principles and introduction, petrol refinery and its production, the
lignocellulosic biorefinery, sugar based biorefinery, biological and
thermochemical processes, green biorefineries, biomass, biomass
conversion: processes and technologies, biobased products,
biorefinery economy, political end environmental aspects of
biorefineries.
Examination of biological and chemical processes in order to obtain valueadded chemicals from biomass and wastes instead of oil as a fossil resource is
the main goal of this course.
Definiton of various raw materials biorefinery systems,
Information about biorefinery products,
Learn the biomass and conversion processes,
Definition of economy, politics and environments impacts of biorefineries
Learn the oil refinery and its product,
Define the biorefinery resources,
Learn the conversion processes,
Evaluate the economical, political and environmental impacts of biorefinery
Kamm, B., Gruber, P. R., Kamm M. (Editors), Biorefineries - Industrial
Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions, WILEY-VCH
Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
1.
Demirbaş, A., Biorefineries for Biomass Upgrading Facilities,
Springer, 2010.
2.
Clark J., Deswarte F., (Editors), Introduction to Chemicals from
Biomass, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2008
3.
2009
Pandey, A. (Editor), Handbook of Plant-Based Biofuels, CRC Press,
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
Principles and introduction, petrol refinery and its production,
the lignocellulosic biorefinery,
sugar based biorefinery,
biological processes,
thermochemical processes,
Mid-Term Examination 1
green biorefineries,
biomass, biomass conversion: processes and technologies,
biobased products.
biorefinery economy,.
Mid-Term Examination 2
political end environmental aspects of biorefineries
Student presentations
Student presentations
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
3
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Assist. Prof. Dr. H. Levent HOŞGÜN
Signature(s):
Date :
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302516
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Labratory
3
0
0
Spring
SPRING
ADAPTATION AND TYPES OF CELL
DEATH
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
LANGUAG
E
COMPULSORY ( ) ELECTIVE
Turkish
(x )
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety Profession
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
1
%
30
1
30
1
40
2nd Mid-Term
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
Homework
PREREQUIEITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Plants as nutrients are consumed for their changes due to
environmental conditions and the effects of these altered foods will be
examined in the cells.
We consume nutrients to the cells of the molecular-level learning will
be affected.
ADDITIVE OF COURSE TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
Air pollution and industrial solid, liquid and gas waste that occur in
plants by examining the effects will be evaluated in terms of molecular
biology. These effects may bring about changes in the cell and will be
defined in terms of damage. In addition to these changes in cell
adaptation responses will be evaluated. In addition to these changes,
cell death mechanisms will be examined. These are; programmed cell
death which is known apoptosis; Autophagy which is known cell
death by using lysosomes and yhe last one is necrosis which is known
physical and chemical changes affecting in environmental factors.
Today, mechanisms of cell death are grouped under three main
headings. In this course, the mechanisms of adaptation to other types
of cell death mechanisms and the information will be given about the
damage they create.
TEXTBOOK
1.
Alberts, B., Bray, J., D., Lewis, Raff, M., Roberts, K.,
Wartson, J., D. : Molecular Biology of The Cell, Third
Edition, Gurland Puplishing, Inc. New York London 1994.
2.
Basaran A.: Tıbbi Biyoloji Ders Kitabı., Güneş&Nobel
Kitabevleri, Genişletilmiş 7. Baskı, 2005.
3.
Bray, A., Raff L., Watson, R.: Molecular Biyology of the
Cell., Newyork, London, 2002.
4.
Cooper, G.M.: The Cell, Dara-Farber Cancer Instıtute
School. North America, 1997.
5.
Güneş H.V.: Moleküler Hücre Biyolojisi, Güneş Kitabevi,
Genişletilmiş 2. Baskı, 2007.
6.
Pollard, T.D., Earnshaw, W.C.: Cell Biology, London, NewYork, St-Louis, Sydney,Toronto, 2002.
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Computer, Projector
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
What are natural plant nutrients?
Types of Cell Death Mechanisms
Effect of domestic and industrial waste water on morphological deformations in plants.
Effects of air pollution and industrial pollution types like solid, liquid and gas on plants
Effects of accumulation heavy metal on changes in ruderal and culture plants.
Mid-Term Examination 1
Consequential damages resulting when cell death have seen
Cell damage caused and mechanisms.
Tissue damage caused and mechanisms.
Chemical damage, kinds of chemical damage.
Mid-Term Examination 2
Reversible damage.
Cellular adaptation for damage
Heterophagy. Autophagy. Natural plant nutrients and autophagy.
Final Exam
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Instructor(s):
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Didem TURGUT COŞAN
Signature:
Date:
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
SEMESTER
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND AND BIOSAFETY (PhD)
COURSE CODE
BASIC BIOTECHNOLOGY PROCESSES
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
COURSE OF
Theory
Practice
Labratory
Credit
ECTS
TYPE
2
0
0
2
7,5
COMPULSORY ( ) ELECTIVE ( x )
Spring
Spring
LANGUAGE
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety Profession
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
Homework
Quantity
1
%
30
1
30
1
40
1
PREREQUIEITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
For the researchers working on various biological systems, a full
knowledge of molecular biology techniques and applications is a must
for the accomplishment of observations at the molecular level. This
theoretical course includes concept of The History, Description,
Purpose and Usage of Biotechnology, Biotechnologic Products,
Procedures, Basic Biotechnology and Biomolecule Design,
Biotechnology and Biomarkers, Biotechnological Transformation and
Transfection, Clinic Approaches and Ethic Principles of Medical
Biotechnology, Basic Biotechnology Laboratories and Safety and
Status of Medical Biology in Turkey.
To transpose what is need to know about medical biotechnology,
which shows a wide spread from industry to medicine and has an
importance of growing day by day and to have knowledge about this
actual subject.
ADDITIVE OF COURSE TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
We aim to give information about Medical Biotechnology which is the
most popular subject in our present day. Biotechnologic procedures
which is used various study of biology will help us treating various
diseases in future and there are too many studies. Knowledge about the
usage and function of medical biotechnology, many researches
continues in this area, is important for medicine.
TEXTBOOK
Understanding Biotechnology by A. Borém, F.R. Santos, D. E. Bowen
(2003)
Synthetic Polymers for Biotechnology and Medicine by R.
Freitag (2002)
2.
Bionanotechnology: Lessons from Nature by D. S. Goodsell
(2004)
3.
Cell and Tissue Culture: Laboratory Procedures by A. Doyle, J. B.
Griffiths, A. Griffiths, J.B. Doyle, D.G. Newell (1998)
1.
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Computer, Projector
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
TOPICS
The History and Description of Biotechnology
The Purpose, Compherension and Usage of Biotechnology
Biotechnological Products and Procedures
Basic Biotechnology, Biyomarkers and Biyomolecules
Biopolymeric Materials in Biotechnology and their Transfection
Mid-Term Examination 1
Cell and Tissue Engineering in Biotechnology
Biotechnological In vitro and In vivo Gene Transfer
Treatment with Inhibition of Biotechnology and Gene Expression
Priciples of Treatment with non-coding RNA Technology and its Application
Mid-Term Examination 2
Regenerative Treatment for Stem Cell Usage with Biotechnology
The Medical Importance of In Vivo Screening System in Biotechnology
Necessary Equipments for Basic Biotechnology Laboratory and Laboratory Spesifity
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Gains skill to analyze problems that require expertise in the field of
Biotechnology and Biosafety using scientific research methods.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
As individuals with capacity of researcher, producers and entrepreneurs,
gains skills of using high-level mental processes such as creative and
critical thinking, initiative and decision-making.
Gains skill of making leadership by taking responsibility for working with
interdisciplinary teams and solving problems.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
3
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
10
11
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning
x
x
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Instructor(s): Assoc. Prof. Dr. Didem TURGUT COŞAN
Signature:
Date:
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Labratory
2
2
0
Autumn
AUTUMN
PROTEIN BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
TYPE
LANGUAG
E
COMPULSORY ( ) ELECTIVE (x
Turkish
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
)
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety Profession
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
1
%
30
1
30
1
40
2nd Mid-Term
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
Homework
PREREQUIEITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Basically overview of the course is the discussion of the structure and
function of protein, the basic methods of purity of different classes of
proteins, the proteins isolated by physical and chemical analysis
methods and significance of characterization of proteins. Although
protein biotechnology fields of study, proteins are used for the purpose
of diagnosis and treatment are described in detail. Medical aspects of
the proteins are discussed. Description and history of proteom,
identification of protein and peptides, protein databases, methods used
in the identification of proteomes
To give basic and current informations related with protein and
proteomics which are thought to be an important guiding in the
investigation of new methods of diagnosis and treatment
ADDITIVE OF COURSE TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
To give information about description of proteom, which resarch areas
it is used in and about the methods used in the identification of
proteom.
1.
Brown T.A.: Essential Molecular Biology Volume I A
Practical Approach. IRL Press, Oxford University
Press,Oxford, New York, Tokyo, 1990.
2.
M. Schena, (Editor) DNA Microarray. Publisher: Scion
Publishing Ltd. Publication date: October 2007
3.
Richard J. Simpson Basic Methods in Protein Purification
and analysis: A Laboratory Manual Joint ProteomicS
Laboratory (JPSL) of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer
Research and the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical
Research, Melbourne, Australia; Peter D. Adams, Fox Chase
Cancer Center, Philadelphia; Erica A. Golemis, Fox Chase
Cancer Center, Philadelphia 2009
4.
Richard Simpson: Proteomics: A Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory
Course
Manual
Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, Melbourne 2009.
5.
Sambrook J, Fritsch E.F., Maniatis, T.: Molecular Cloning, A
Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press,
1989.
OTHER REFERENCES
Computer, Projector
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
Description of proteom the history
General strategy used in proteom analysis
Protein and/or peptides definition (Identification)
Three-dimensional structure and Protein Databases
Gel electrophoresis, polyacrilamide gel and Gel stain techniques
Mid-Term Examination 1
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
ELISA
Elektrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
Mass Spectrometer
Mid-Term Examination 2
Kinds of chromatography column chromatography
Protein microarray
Immunoassay, Bioinformatic
Final Exam
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Instructor(s):
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Didem TURGUT COŞAN
Signature:
Date:
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
COURSE CODE
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (PhD)
505312605
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Labratory
3
0
0
Autumn
AUTUMN
RNA INTERFERENCE TECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
LANGUAG
E
COMPULSORY ( ) ELECTIVE (
Turkish
x)
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety Profession
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
1
%
30
1
30
1
40
2nd Mid-Term
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
Homework
1
PREREQUIEITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide basic information about gene silencing, RNA interference
and non-coding RNAs.
To flash on the world of non-coding RNA which has got an important
role in gene silencing that is an important area of research in the
development of new treatment methods.
ADDITIVE OF COURSE TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
With emerging technologies in molecular biology in the field of
development and many new ones are added to our knowledge. RNA
that is not code issue is one of the issues going on in the last period.
Up to date, we have also known that there are 34 different RNA
mechanisms, there are 340 of RNA known. Recently, RNAi has been
discovered, and then we know interferens miRNA forms of RNA,
siRNA, and dsRNA were added as concepts. Continuing research on
this subject and information is increasing every day. Therefore, this
matter is very contemporary, the course will be the subject matter is
broad. Another issue arising with the discovery of RNA interferensin
in the treatment of the disease can be targeted based on gene silent
about the so-called upgrading. This revolutionary innovation in
science subjects for the examination will be enlightening.
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Understanding Biotechnology by A. Borém, F.R. Santos, D. E. Bowen
(2003)
1.
Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello The Nobel Prize in
Physiology or Medicine The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska
Institutet October 2006.
2.
Krishnarao Appasani RNA Interference Technology - From
Basic Science to Drug Development Edited by, Andrew Fire,
Marshall Nirenberg CUP GeneExpression Systems, Inc.,
Massachusetts March 2005.
Computer, Projector
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
TOPICS
Discovery of RNA interferense
Interferens RNA (RNAi).
Non coding small RNAs
MicroRNA
siRNA
Mid-Term Examination 1
Transkripsiyonal genes
Transposon and Transgenes
Post-transcriptional gene silent
dsRNA, Dicer
Mid-Term Examination 2
RNAi-like mechanisms.
RNAi treatment and in the future.
Non coding RNAs in molecular biology and medicine in the place.
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Gains skill to analyze problems that require expertise in the field of
Biotechnology and Biosafety using scientific research methods.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
As individuals with capacity of researcher, producers and entrepreneurs,
gains skills of using high-level mental processes such as creative and
critical thinking, initiative and decision-making.
Gains skill of making leadership by taking responsibility for working with
interdisciplinary teams and solving problems.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
3
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
8
9
10
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning
11
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Instructor(s): Assoc. Prof. Dr. Didem TURGUT COŞAN
Signature:
Date:
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (YL)
COURSE CODE
SEMESTER
Electron Microscopy and Preparation
Techniques
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTE
R
Theory
Practice
2
1
2012-2013
Spring
COURSE OF
Laboratory
Credit ECTS
3
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE (x )
7,5
LANGUAG
E
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Social
Science
Biotechnology and Biosecurity Department
x
( )
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
Quantity
%
1st Mid-Term
1
30
2nd Mid-Term
1
30
1
40
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
The description of electron microscope, operating principles, types,
techniques used in the ultrastructure studies, sample protocols, using
chemicals and techniques developed in recent years. In addition,
equipment of electron microscope laboratory, laboratory safety
COURSE DESCRIPTION
procedures and rules, sample preparation techniques for transmission
(TEM) and scanning (SEM) electron microscope, the difficulties that
occur during sample preparation,
observation and evaluation of
samples in TEM and SEM.
Electron microscopes are very powerful tools for visualising different
samples such as cells, microorganisms, biopsy sample, metals, crystals
COURSE OBJECTIVES
and large molecules. This course is intended to train students in the
understanding and application of transmission electron microscopy
(TEM) and scanning (SEM) electron microscope in the different
science areas. The students are trained in methods of sample
preparation, the principles and operation of the electron microscopes
and latest developments in this area. In addition, students will acquire
the skills to analyse and present data, and be aware of the role,
importance and relevance of electron microscope in scientific
researchs.
Sufficient knowledge of science and engineering subjects; an ability to
use and apply theoretical and practical knowledge on this areas.
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
Ability to work effectively in inner or multi-disciplinary teams;
proficiency of interdependence
Use of theoretical and practical knowledge within the electron
COURSE OUTCOMES
microscopy at a proficiency level.
Kuo J. (2007) Electron Microscopy: Methods and protocols (Methods
TEXTBOOK
in Molecular Biology) Humana Pres, USA.
John J. Bozzola,Lonnie Dee Russell. Electron microscopy: principles
OTHER REFERENCES
and techniques for biologists 1992
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
The history and description of the electron microscope, types and application areas
Basic properties and operating principles of scanning (SEM) and transmission (TEM) electron
microscopes
Electron microscope laboratories: preparation and laboratory safety procedures
Sample preparation for scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Sample drying techniques, mounting samples to stub, coating process and observation
Mid-Term Examination 1
Sample preparation for transmission electron microscope (TEM), tissue process
Ultramicrotomes, study principles, glass knife makimg and using techniques
Preparation of blocks for semihtin sections, sectioning, staining and investigation
Ultrathin sections, common problems associated with ultrathin sectioning
Mid-Term Examination 2
Staining of ultrahtin sections, staining techniques
Drying of grids and observation in TEM
The evaluation of electron microscopic images for research and diagnosis, Final exam
Cryo electron microscopy, Final Exam
NO
1
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Sufficient knowledge of science and engineering subjects; an ability to use and apply
3
x
theoretical and practical knowledge on this areas.
2
Ability to solve of problem and apply on the subjects in related area
3
To gain ability on research and learn scientific method
x
4
Ability to apply the content of this course on current subject
x
x
Ability to work effectively in inner or multi-disciplinary teams; proficiency of
5
foreign language.
Awareness of life-long learning; ability to reach information; follow developments in
7
x
interdependence.
Ability to communicate in written and oral forms in Turkish; proficiency at least one
6
science and technology and continuous self-improvement.
2
x
x
8
Understanding of professional and ethical issues and taking responsibility
x
9
Ability to design and conduct experiments as well as to analyze and interpret data
x
10
Usage of modern technique and devices required for related applications
x
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Yrd. Doç. Dr. ilknur Dağ
Date:
19.12.2012
Signature(s):
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
1
1
Animal Toxins and Venomic
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE (x)
LANGUAG
E
Turrkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Basic Engineering
x
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
%
1
1
30
1
60
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
30
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
Study strategies and biothecnological benefit of venom producing
animals (scorpions, snakes, spiders, bees, ants, conus, sea anemones).
The purpose of this course; venom studies which is a new area of
toxicology to facilitate the flow of information to the students, give to
information about using of venoms in biotechnological research.
Moreover, to gain knowledge on using of bioinformatics based on
“natural library” which is generated by animal venom proteome
(venomic).
Animal toxins (zootoxin) are bioactive components of complex
mixtures.
In this context, students will gain ability to use of venom for
development of new pharmacological molecule due to their high
selectivity of the target in biotechnological research.
1. To gain an overview of venom producing animals and their
secretions
2. To know purpose and benefits of the use of venom and apply in
industrial environments
3. To gain ability of apply and assciate interdisciplinary of
information obtained from the results of biochemical and molecular
experiments of venom studies
4. To gain a new perspective on their professional activities using the
sources of the natural wealth of our country,
5. To use the sources of the current experimental methods and
bioinformatics capability for developing of biotechnological
innovations
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Harve Rochat and Marie-France Martin-Eauclaire (eds)(2000).
Animal Toxins: Facts and Protocols. Birkhauser Verlag AG, P. O.
Box 133, CH-4010 Basel, Switzerland. 384pp.
Andrea Giuliani and Andrea C.Rinaldi (2010). Antimicrobial
Peptides: Methods and Protocols (Methods in Molecular Biology),
Humana Press. 412 pp.
Steven Foster, Roger Caras, (1998) Ed. By Roger Tory Peterson.
Peterson Field Guide to Venomous Animals & Poisonous Plants,
Houghton-mifflin
Actual publications and review articles from international
journals
Computer,projector and internet access
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
Introduction to venom producing animals (scorpions, snakes, spiders, bees, ants, conus, sea
anemones), collecting strategy from nature and housing in laboratory
Source of venom peptides, purification, characterzation by biochemical and molecular methods
Venoms and its enzymatic activities (lipolytic, proteolytic (caseinolytic, gelatinolytic),
phospholipases and fibrinolytic
Arthropoda venoms and its anti-tumoral activities
Venoms and its antimicrobial effects
Mid-Term Examination 1 Examinaion of current international manuscripts related venom studies
from databases
Venoms and their uses as pesticide
Anti-malarial and multiple sclerosis properties of venoms
Scorpion toxins and acting on ion channels (Sodium and potassium)
Scorpion toxins and acting on ion channels (cloride and calcium)
Mid-Term Examination 2 Examinaion of current international manuscripts related venom studies
from databases
Immunological properties of venom toxins
Venom peptidlerin aminoasit ve nükleotid dizilerinin ApE programı uygulamaları ve
Biyoinformatik veri tabanlarında dizi karşılaştırma ve benzerlik analizi;
Application of plazmid editor program (ApE) and BLAST with venomic sequences (protein and
DNA)
Application of MEGA5 software and building phylogenetic tree with venom peptides
Final Exam
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Dr.Figen CALISKAN
Date:20.11.2012
Signature(s):
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302515
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
1
2
Instrumental Analysis in Biotechnology
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
LANGUAG
E
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE (x)
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Basic Engineering
x
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
%
1
25
1
1
25
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
50
This course is includes using devices in biotechnology laboratories
and current applications of the instrumental analysis, methods and
principles.
The aim of the course is to provide students with information about
the basic techniques which is used in biotechnology laboratories,
furthermore learn analytical separation techniques required for
biotechnological studies and provide the ability for evaluating the
outcomes of planning, operation
At the end of this course, students will learn concepts of current
analytical and instrumental techniques, steps of isolation and
characterization of biological materials from the sources. In addition,
they will learn according to the sample choose of bio-analytical
methods which are uses of determine of the amount of component,
gain skills to solve encountered problems using of the principles of the
analytical chemistry.
1.To gain knowledge of the basic concepts of modern analytical and
instrumental techniques in the field of biothecnology
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
2. Learning strategy and the stages of purification and characterization
of
instrumentel analysis
3. To gain selection skills of bio-analytical chemistry methods for
determination of sample component
4. To learn the basic principles and mechanisms of instrumental
techniques
5. To learn application areas of instrumental techniques on industrial
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch, " Principles of
instrumental analysis", Philadelphia : Saunders College Pub., 2007.
ISBN 0-03-002078-6.
1. Keith Wilson and John Walker, " Principles and techniques of
biochemistry and molecular biology", Cambridge : Cambridge
University Press, 2005. ISBN 0-521-53581-6.
2.Edmond de Hoffmann, Vincent Stroobant, " Mass spectrometry :
principles and applications", Hoboken, N.J. : J. Wiley, 2007. ISBN
978-0-470-03310-4.
Computer and projector
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
Basic equipments of biotechnology laboratories; utilities of instrumental techniques in clinical and
industrial areas
Chemical preparations before analysis (buffers,reactives,spesific dyes for identification) and
preparation of the strategic plan of analysis
standardization, instrument calibration, validation methods and applications of the ISO 17025
standard on Biotechnology laboratories,
Mass Spectrometry Principles and its biotechnological applications
Optical spectroscopy and analysis methods of biomaterials
Mid-Term Examination 1 Surface analysis methods
Chromatographic techniques in biotechnology: principles, clinical & industrial examples
Chromatographic techniques in biotechnology: principles, clinical & industrial examples
Electrophoretic techniques, principles and applications on biotechnology
Electrophysiological techniques, principles and applications on biotechnology
Mid-Term Examination 2
Biyoteknoloji laboratuarları güncel kombine teknikler
Micro-array analysis of; proteins N-terminal and C-terminal sequencing, cDNA preparation and
Gene Sequencing
Immunological identification techniques
Final Exam
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Dr.Figen Caliskan
Date:20.11.2012
Signature(s):
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (PhD)
COURSE CODE
505312606
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
1
1
Proteomic and Bioinformatic
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7.5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE (x)
LANGUAG
E
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
x
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
Quantity
%
Project
1
25
Report
Others (Seminar
presentation)
1
25
1
50
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
Homework
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
The content of this course includes how to obtain proteomic
information by classical instrumental analysis and development of this
information by the means of information technologies.
To gain finding proteomic data from bioinformatic databases, using
the knowledge, analyzing and storing, the sequence comparison and
alignment, using similarity searching applications.
For development and automation of biotechnology and information
technology they will learn advantage of proteomics and
bioinformatics resources
1.Ability to achieving proteomic knowledge
2. To understand the working methods of protein in biotechnology
3.Scanning of bioinformatic databases
4.To understand organization of databases and in proteomic studies
finding and using different datas
5. Using computer and information technologies for effective
utilization of genomic and proteomic data
6. Prepare a strategic plan for protein studies
7. Using proteomic and bioinformatics information for built
phylogenetic relationships.
N. Gautham, "Bioinformatics", Oxford University, Alpha Science
2006. ISBN 1-8426-5300-8
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
3. Ignacimuthu, S. "Basic bioinformatics", Harrow : Alpha Science
Int., 2005. ISBN 1-8426-5231-1
4. Jean-Michel Claverie, Cedric Notredame "Bioinformatics for
dummies"2nd Ed. Wiley Publishing,Inc., 2007. ISBN 978-0470-08985-9.
5. D.Voet, G.Voet, "Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Wiley Int. Ed., (Chapter
7-4.) 2004. ISBN 0-471-19350-X.
6. S.Hubbart, A. Jones“Proteom Bioinformatics” Humana press,
2010.ISBN 978-1-60761-443-2
7. www.expasy.org
8. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast
9. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/
10.
http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/
11.
http://www.genome.jp/kegg/
11.http://www.brenda-enzymes.org/
12.Actual publications and review articles from international journals
Computer,projector and internet access
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
Proteomics: Introduction, sample taking,preparation,and problems
2D Gel Electrophoresis
Mass Spectroscopy of Peptides and Proteins, finger print analysis
Protein chips
Microsequencing and purification strategy
Mid-Term Examination 1 How and where is to find biological data?
Introduction to proteome bioinformatics
Bioinformatic tools and its uses
Use of proteomic databases; PDB, UniProtKB, PIR, PRF,
Use of Nucleotide sequence databases; GenBank, EMBL, DDBJ ve EBI.
Mid-Term Examination 2 application and uses of databases
Sequence scanning and analysis
Similarity comparison
Determination of the phylogenetic proximity
Final Exam
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Gains skill to analyze problems that require expertise in the field of
Biotechnology and Biosafety using scientific research methods.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
As individuals with capacity of researcher, producers and entrepreneurs,
gains skills of using high-level mental processes such as creative and
critical thinking, initiative and decision-making.
Gains skill of making leadership by taking responsibility for working with
interdisciplinary teams and solving problems.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
Prepared by: Dr.Figen CALISKAN
Date:
Signature(s):
1
x
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
20.11.2012
2
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505312603
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
FALL/SPRİNG
INDUSTRIAL MICROORGANISMS AND
SECONDER METABOLITES
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TÜRKÇE
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
The scope of this course will be included the seconder metabolites
and its ındustrial application.
The aim of this course is to provide understanding of the importance
of seconder metabolites by the students.
This course will contribute to prepare for professional life by
providing knowledge on the importance of microorganisms in
biotechnology and the flow of production processes.
18.
Understanding the importance of seconder metabolites
19.
Sort of seconder metabolites
20.
To understand the microbiological production process
21.
To create the metabolites of microorganisms
22.
To explain the production of seconder metabolites on a
commercial scale
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Biotechnology Procedures and Experiments Handbook. Harisha S.
2007. Infinity Science Press LLC.
Madigan MT and Martinko JM. Brock Mikroorganizmaların
Biyolojisi (2006) (Çeviri Edit: Çökmüş C) Palme Yayıncılık, Ankara.
Handbook of Fungal Biotechnology. Ed: Arora DK. 2004. Marcel
Dekker, Inc.
Computer and projection
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TOPICS
Specific function of seconder metabolites
Function of seconder metabolites
Bioactive seconder metabolites
Bioactive seconder metabolites
Diversity of biyosynthetics
Mid-Term Examination 1 Diversity of biyosynthetics
Bacterial seconder metabolites and product improvement
Fungal seconder metabolites and product improvement
Production strategies of seconder metabolites
Production strategies of seconder metabolites
Mid-Term Examination 2 Production strategies of seconder metabolites
Characterisation of seconder metabolites
How many microbial metabolites may be discovered in the future?
Selected plant and specifications
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
3
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
11
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Prof. Dr. Semra İLHAN
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ahmet ÇABUK
Date:
Signature(s):
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302501
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
2
0
0
Fall
LABORATORY SAFETY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
2
7,5
TYPE
LANGUAG
E
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE (x )
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
2( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
Quantity
%
1
40
1
30
1
30
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
The importance of laboratory safety; general rules in the lab, risk
factors in the lab; safety work with chemical substances; the disposal
of waste chemicals; laboratory accidents and precautions; first aid,
occupational diseases; the personal safety and hygiene in the
laboratory; fire safety; biosafety in the laboratory; laboratory
biosafety levels; legal regulations in the country.
To teach basic principles of work safely in the laboratory, providing
knowledge to students about risks and dangers in the lab, safety
working rules, personal protective equipment etc.
Students learn chemical, physical and biological risks in the lab
environment, learn how to take precautions against those risks, work
safely in the lab.
1. Obtain basic information about lab safety.
2. Recognize the risks that may occur in the lab.
3. Explain the importance of safety in the lab.
4. Gain knowledge about waste disposal.
5. Explain the importance of biosafety in the lab.
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
1.
Yeni Mevzuat Işığında İş Sağlığı ve Güvenliği Temel
Bilgileri, RİSK MED Akademi Yayınları, 2012/1.
2.
Dizdar E.N., (2008). İş Güvenliği, Murathan Yayınevi.
3.
Merck Laboratuvar El Kitabı, 2007.
4.
Laboratory biosafety manual, Third Edition, World Health
Organization, Geneva, 1994.
Computer and projector.
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
The importance of lab safety, the definition of occupational health and safety, general
rules in the laboratory, rules that must be followed in the use of laboratory
instruments/equipment
The lab of risk factors; physical, chemical and biological risks
Safe operation of chemical substances; chemical material safety data sheet (MSDS),
chemical material safety information card, label hazard symbols
The safe storage of chemicals; general rules of the hazardous substances deposition; waste
disposal.
Laboratory accidents and measures, first aid measures
Mid-Term Examination 1
Occupational diseases
Personal hygiene and safety in the laboratory; personal protective equipment
Fire safety; fire extinguishers, fire extinguisher types, proper use of fire extinguisher
Laboratory safety measures; ventilation, gas and fire detectors, eyes shower, emergency
shower etc.
Mid-Term Examination 2
Biosafety in the laboratory; risk groups, risks and safety of microorganisms.
Laboratory biosafety levels, disinfection, sterilization, contaminations , biological waste
management
Lab safety and biosafety-related institutions, legal regulations in our country
Final Exam
NO
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
1
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable processes and
2
environmental consciousness to problems on health, environment, food,
agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the methods of
3
research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
4
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
5
Has the professional and social ethics.
6
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making comments using
7
scientific developments related to his/her discipline and information technologies
at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally, in
8
writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
9
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language belonging to
10
European Language Portfolio.
11 Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Belgin Karabacakoğlu
Date: 21.11.2012
Signature(s):
3
2
1
x
x
x
x
x
x
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505312601
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
FALL/SPRİNG
NATIONAL-INTERNATIONAL BIOSAFETY
REGULATIONS AND POLITICS OF
BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( )
LANGUAG
E
TÜRKÇE
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
The scope of this course will be included biosafety and regulatıons.
The aim of this course is to provide understanding of the importance
of biosafety regulatıons by the students.
This course will contribute to prepare for professional life by
providing knowledge on the importance of biosafety and biodiversty.
23.
Understanding the importance of biosafety
24.
Understanding the importance of laws and regulatıons of
biosafety
25.
To understand the biosafety process
26.
Examplify the laws and regulations of biosafety
27.
To comparison of the national and international laws of
biosafety
Biyogüvenlik ve Biyoçeşitlilik Ders Notları, ESOGÜ Biyoloji
Bölümü, ESKİŞEHİR
Biosafety and bioethics, Joshi, R., 2006, Delhi.
Biyoteknoloji; Uluslar arası eğilimler ve görüşler. Bull. A. Geoffrey.
H. B. (1987). İstanbul. İstanbul Üniversitesi.
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Computer and projection
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
Importance of laws and biosafety
Biodiversity convention nd biosafty protocol
Internatıonal regulations
Turkey become party to an agreement in international conventions and protocols
Turkey become party to an agreement in international conventions and protocols
Mid-Term Examination 1 Turkey become party to an agreement in international conventions and
protocols
Historical aspects of local regulations and development stage of biosafety in Turkey
Law regulations in Turkey.
Local regulations and laws in Turkey
Local regulations and laws in Turkey
Mid-Term Examination 2 Local regulations and laws in Turkey
Future of biosafety laws
New biotechnological products and biosfety, law regulations
New biotechnological products and biosfety, law regulations
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
3
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: öğretim elemanı talep edilecektir.
Signature(s):
Date:
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302508
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
2
0
0
AUTUMN
AUTUMN
PLACE OF EMBRYOLOGY IN
BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TURKISH
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
1
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
CONTRIBUTION OF EMBRYOOLOGY IN THE
BIOTECHNOLOGY FIELD
PRESENTATION OF CONTRIBUTIONS OF EMBRYOLOGY IN
THE BIOTECHNOLOGY FIELD
KNOWING BASIC EVENTS AND MECHANISMS OF HUMAN
EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT
LEARNING BASIC EVENTS AND MECHANISMS OF HUMAN
EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT
EMBRİYOLOJİ VE DOĞUM DEFEKTLERİNİN TEMELLERİBEFORE WE ARE BORN 7. BASKI, ÇEVİRİ EDİTÖRÜ SEVDA
MÜFTÜOĞLU, GÜNEŞ TIP KİTABEVLERİ, ANKARA, 2009.
İNSANIN ÜREMESİ VE GELİŞMESİ, MERAL TEKELİOĞLU,
ANKARA, 1995.
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
Introduce to human embryology
Development of male germ cells
Development of female germ cells
Fertilization and the factors influencing fertilization
Development of zygote, blastula, morula and blastocyst
Mid-Term Examination 1
Implantation
Development of bilaminar and trilaminar embryonic discs
Basic events and mechanisms of embryology
Formation mechanisms of congenital defects
Mid-Term Examination 2
Embryonic stem cells
Contributions of embryology to assisted reproductive technology therapies
Future of embryology
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: PROF. DR. VAROL ŞAHİNTÜRK
Signature(s):
Date: 28.11.2012
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
2
Spring
Physicochemical Processes
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7.5
TYPE
Compulsory ( ) Elective ( X)
LANGUAG
E
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Social
Science
X
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
MID-TERM
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
Quantity
%
1
25
1
30
1
45
None
General definitions of physicochemical processes, the aim of particle
size enlargment and methods, solid-liquid seperation methods, general
principles of froth floatation and methods, adsorbtion ve ion exchange
processes
To teach cleaning of fine wastes by physicochemical processes, such
as coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, floatation and
industrial applications of these processes.
Understanding applications of physicochemical processes to fine
wastes
1. To learn general knowledge about fine wastes
2. To learn physicochemical processes which are applying to fine
wastes
3. Ability to work effectively in inner or multi-disciplinary teams
4. To learn how to analyse problems with modern experimental
methods and new technologies
Wills B. A., Mineral Processing Technology, 6th Edition, 1997,
Camborne School of Mines, Cornwall, England
Somasundaran P., Fine Particles Processing, 1980, Las Vegas
Computer and Data Show
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
TOPICS
Properties of minerals and ores
General definitions of physicochemical processes
Particle size englargement methods
Coagulation, flocculation and agglomeration processes
Industrial applications of particle size englargement
Mid-Term Examination 1
Dewatering methods
Sedimentation, thickeners
Filtration
Froth floatation
Mid-Term Examination 2
Adsorption and ion exchange
Presentation of homeworks
Presentation of homeworks
Final Exam
NO
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at related
1
disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable processes and
2
environmental consciousness to problems on health, environment, food, agriculture,
industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the methods of
3
research.
4
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
5
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
6
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making comments using
7
scientific developments related to his/her discipline and information technologies at the
level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally, in writing,
8
visually to field and outside field groups.
9
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language belonging to
10
European Language Portfolio.
11
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
3
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
Date:
Signature(s):
1
x
Prepared by: Yrd.Doç.Dr. Derya ÖZ AKSOY
27/11/2012
2
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302509
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
2
0
0
SUMMER
SUMMER
PLACE OF HISTOLOGY IN
BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TURKISH
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
1
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
CONTRIBUTION OF HISTOLOGY IN THE BIOTECHNOLOGY
FIELD
PRESENTATION OF CONTRIBUTIONS OF HISTOLGY IN THE
BIOTECHNOLOGY FIELD
KNOWING THE CELLS AND TISSUES OF HUMAN BODY
LEARNING THE CELLS AND TISSUES OF HUMAN BODY
HISTOLOGY, Mıchael Ross and Wojciech Pawlina, Sixth edition
2011, Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia,
USA.
Histoloji ve Hücre Biyolojisi, Çeviri editörü: Ramazan Demir, Palme
Yayıncılık, Ankara 2006.
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TOPICS
Basic cytology
Cells of human body
Introduce to histology
Cover epithelium
Secretion and glands
Mid-Term Examination 1
Connective tissue
Blood and bone marrow
Cartilage and bone
Muscular and nervous tissues
Mid-Term Examination 2
Cell cultures
In vitro tissue production
Selected actual literatures
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
3
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: PROF. DR. VAROL ŞAHİNTÜRK
Signature(s):
Date: 28.11.2012
1
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND BIOSAFETY (MSc)
COURSE CODE
505302517
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
Practice
Laboratory
3
0
0
FALL/SPRİNG
MICROBIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
COMPULSORY ( )
ELECTIVE ( x )
LANGUAG
E
TÜRKÇE
COURSE CATAGORY
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
Engineering Subjects
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social
Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term
2nd Mid-Term
Quantity
1
1
%
25
25
Quiz
MID-TERM
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
FINAL EXAM
50
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
The scope of this course will be included the phylogeny and diversity
of Bacteria
The aim of this course is to provide understanding of the importance
of Domain Bacteria as part of biodiversity and the ecosystem the by
the students.
This course will contribute to prepare for professional life by
providing knowledge on the importance of microorganisms in
biotechnology and the flow of production processes.
28.
Understanding the importance of biotechnology
29.
Sort of biotechnologically relevant microorganisms
30.
To understand the biotechnological production process
31.
Examplify the metabolites of microorganisms
32.
To explain the production of biotechnological products on a
commercial scale
33.
Understanding the biotechnologically importance of
microorganisms.
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
İLHAN S (2012) Mikrobiyal Biyoteknoloji Ders Notları, ESOGÜ
Biyoloji Bölümü, ESKİŞEHİR
Madigan MT, Martinko JM, Parker J, and Clark DP, (2009). Brock
Biology of Microorganisms. Pearson Prentice Hall.
Willey M, Sherwood LM., Woolverton CJ, (2007). Prescott, Harley,
and Klein’s microbiology. 1088 p. McGraw- Hill College.
http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/
Computer and projection
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TOPICS
Scope to Microbial Biotechnology
History of microbial biotechnology, the important microbial groups and processes
Growth substrates
Fermentation equipment
Strain improvement; Mutation, Recombinant DNA technology, Genetic engineering
Mid-Term Examination 1
Primery Metabolites
Secondery Metabolites
Lactic acid fermentations
Fungal products
Mid-Term Examination 2
Microbial Polysaccharides and Polyesters
Other Biotechnological Products
Immobilize Enzyms and Cells
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at
related disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable
processes and environmental consciousness to problems on health,
environment, food, agriculture, industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the
methods of research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making
comments using scientific developments related to his/her discipline and
information technologies at the level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally,
in writing, visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information
technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language
belonging to European Language Portfolio.
3
2
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
11
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
X
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
Prepared by: Prof. Dr. Semra İLHAN
Date:
Signature(s):
T.R.
ESKISEHIR OSMANGAZI UNIVERSITY
GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
COURSE INFORMATION FORM
DEPARTMENT
Biotechnology and Biosafety
COURSE CODE
505302502
SEMESTER
COURSE NAME
WEEKLY COURSE PERIOD
SEMESTER
Theory
FALL
Practice
Laboratory
3
Fall / Spring
Biostatistical Methods
COURSE OF
Credit ECTS
3
7,5
TYPE
LANGUAGE
COMPULSORY ()
ELECTIVE ( X )
Turkish
COURSE CATAGORY
Biotechnology and Biosafety
Basic Science
Basic Engineering
X
[if it contains considerable design, mark with ()
]
( )
Social Science
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
MID-TERM
FINAL EXAM
PREREQUISITE(S)
COURSE DESCRIPTION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
COURSE ADDITION TO APPLY
PROFESSIONAL EDUATION
COURSE OUTCOMES
Evaluation Type
1st Mid-Term (Written)
2nd Mid-Term
(Written)
Quiz
Homework
Project
Report
Others (………)
(Written)
Quantity
%
1
20
1
30
1
15
1
35
None
Definition of probability and basic terms, Random variables and
probability functions, some discrete and continuous distributions,
definitions of statistics and basic terms, descriptive statistics, data
analysis,sampling and sampling distributions, confidence intervals, tests
of hypotheses, one way analysis of variance,linear regression and
correlation analysis.
The basic aim of the course is to introduce the basics of probability and
statistics, probability distributions, statistical methods and their
applications, especially in biology, chemistry and medicine.
The student will be able to use probability and statistical knowledge and
methods in the professional studies. In this context, the student will ;
1. Learn the basics of probability,
2. Learn and be able to apply some important discrete and continuous
probability distributions
3. Learn basics of statistics,
4. Be able to gather data and analyze them,
5. Infer about the population from where the data were gathered,
6. Learn and apply the testing of hypotheses procedure,
7. Learn Analysis of Variance and multiple comparisons,
8. Learn and apply Linear Regression and Correlation Analysis
Knowledge related to the basics of probablity and statistics, able to
apply important probability distributions and statistical methods.
TEXTBOOK
OTHER REFERENCES
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTS
REQUIRED
ÖZDAMAR, K. (2011) : PASW ile Biyoistatistik; Kaan Kitabevi,
Eskişehir.
DEVORE, J. L. (2004): Probability and Statistics for
Engineering and the Sciences, Thomson;
BELLE, Gerald van [et al.] (2004): Biostatistics : a
methodology for the health sciences; / 2.Basım, J. Wiley, NJ
ER, F., PEKER, K. Ö., (H. Sönmez, ed.) (2009) Biyoistatistik /
, Anadolu Üniversitesi Yayınları No: 1932, Eskşişehir
VITTINGHOFF, E. [et al.] (2005) :.Regression methods in
biostatistics : linear, logistic, survival and repeated measures
models , Springer, NY
HERITIER, S. [et. al] (2009) : Robust Methods in Biostatistics;
J. Wiley, Chichester, UK
Standard Normal, F, Binomial probability tables;
MS Office programs
COURSE SYLLABUS
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15,16
NO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TOPICS
Basics of probability
Random variables, probability and probability density functions and
Distribution functions
Some important discrete distributions
Some important continuous distributions
Basics of statistisc
Mid-Term Examination 1
Descriptive statistics
Sampling Distributions and Confidence intervals
Basics of tests of hypothesis
Single sample hypothesis tests
Mid-Term Examination 2
Double sample hypothesis tests
Linear Regresion and Correlation
Anaylsis of Variance
Final Exam
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
Based on qualifications of Bachelor's Degree, improves knowledge of one at related
disciplines at the level of speciality.
Gains the ability of produce alternative solutions within sustainable processes and
environmental consciousness to problems on health, environment, food, agriculture,
industry, etc. sectors.
Produces alternative solutions to problems related to the field using the methods of
research.
Gains ability to work in interdisciplinary teams.
Gains consciousness of topics of work safety and quality management.
Has the professional and social ethics.
Gains the skills of monitoring, reading, understanding and making comments using
scientific developments related to his/her discipline and information technologies at the
level of advanced.
Gains skill of transfer his/her knowledge and experience in the field orally, in writing,
3
2
X
X
1
visually to field and outside field groups.
Gains skill of examining of the information obtained using information technologies.
Able to communicate verbally and in writing using a foreign language belonging to
10
European Language Portfolio.
11
Displays a positive attitude to lifelong learning.
1:None. 2:Partially contribution. 3: Completely contribution.
9
Prepared by: Prof. Dr. Nimetullah BURNAK
Signature(s):
X
Date: 28.11.2012