Biosafety Definition, History & Regulations in Iran
advertisement

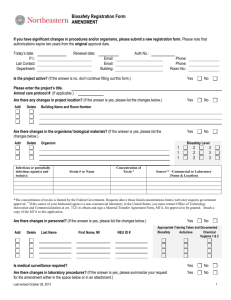
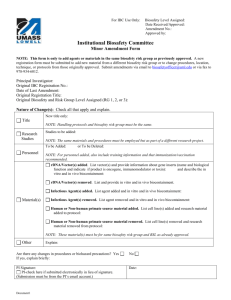
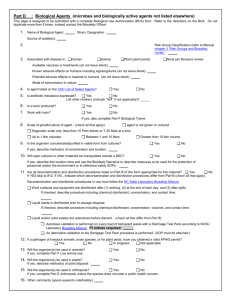
: Definition of biosafety Biosafety is a Set of strategies, policies, regulations and procedures to ensure the use of certain benefits of molecularbiotechnology and prevent the possible adverse effects of this technology on biodiversity and biological reserves, human health and agriculture. The history of biosafety The development of biotechnology and genetic engineering on the development of human society is undeniable, but the potential risks that may arise due to noncompliance with biosafety principles should not be ignored. So the importance of development of biotechnology and genetic engineering activities in all aspects is emphasized, also it is necessary to set rules for the safe conduct of such activities in order to monitor them properly. The main goal of these rules is the application of molecular biotechnology to ensure the biodiversity and human health. Regarding the safety of genetic modified organisms (GMOs), in the 90s many countries prepared regulations in the field of production, consumption, transportation and labeling of these products. In 1995, countries as members of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) started negotiating various legal agreements regarding the risks of GMOs. The most important result of these negotiations was "Cartagena Biosafety Protocol", the legal system to ensure the preservation and transfer of GMOs in the boundaries. "Cartagena Biosafety Protocol" was approved on 29th of January 2000 and up to now 163 countries are its’ members. This protocol is one of the most important agreements of the 21st century, with 40 articles and 3 enclosures. The result from approve of this protocol was a comprehensive legal system to ensure the transmission, storage and the safe use of living modified organisms (LMOs) and their products. Islamic Republic of Iran has signed the mentioned protocol on 25th May of 2001 and this Protocol was approved by the iranian parliament on 20th August of 2003. So, Iranian Biosafety Act including 11 articles and 7 amendments was approved by Iran parliament and confirmed by the guardian council on 12th August of 2003. On the basis of this act, issuing, renewal and revocation of licenses of new biotechnology is done by the bellow following legal authorities considering their regulations and biosafety law. A. Ministry of Agricultural for agricultural productions and natural resources. B. Environmental Protection Agency for wildlife and evaluation of possible environmental risks based on scientific documents presented by the applicants. C. Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOH) is responsible for the issuance, renewal and revocation of any license under Article 2 of the biosafety law on LMOs related to foods, beverages, cosmetics, medical material and human pathogens. Also, in accordance with paragraph (b) of Article 4 of the mentioned law responsibility of assessing and managing the risks of LMOs for human health and food safety on the basis of scientific documents received from applicants and also valid scientific documentations is by MOH. The motto of technical biosafety committee of Ministry of Health and Medical Education To develop the safe use of achievements of molecular biotechnology for preservation and promotion of public health.