Research Project - Villanova University
advertisement

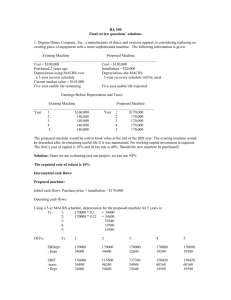
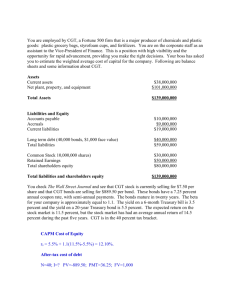
VILLANOVA UNIVERSITY College of Commerce and Finance MASTER OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRTION MBA 8401 CORPORATE FINANCE RESEARCH PROJECT FALL 2003 Dr. A. DeMaskey Introduction. The research project in this course deals with the calculation of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for a U.S. based, publicly traded, business firm. The WACC is important for several reasons. The WACC is that rate which, in general, is used for capital budgeting purposes. The firm’s WACC is also often used as the basis for developing risk adjusted project or divisional discount rates. Additionally, at the optimal or target capital structure, the WACC will be minimized and the value of the firm and the firm’s stock price, in general, will be maximized. Purpose of the Research. There are several distinct goals of this project: To help you understand the application of technology to address a significant research question. To give you the opportunity to work on a technology based project using Internet data and Excel for data analysis. To help you understand both the theory associated with the WACC and the mechanics involved in its calculation. This is important from a practical standpoint, since many firms use the cost of capital in some manner. To help you understand in what contexts financial management concepts can be employed and the limitations of their use. To improve your ability to think creatively, critically, and independently. To enhance your ability to conduct research from model development to data and information gathering to model implementation and analysis. To help sharpen your writing communication skills. Scope of the Project. The scopes of the project, that is, the areas of research, which must be addressed, are The History of the Company The Firm’s Product Lines The Position of the Firm in the Industry Determination of the Firm’s WACC Limitations of the Analysis and Reliability of the Calculations 1 First Step. As a first step in your analysis, please conform to the following: Identify the names of 3 publicly traded, non-financial and non-regulated firms that trade on a major exchange in the U.S. Verify that you can obtain monthly stock price data for these firms for the latest five (5) years (e.g., stocktools.com, yahoo.com, etc.). Verify that you can obtain historical and current information, both general and financial, about the firms (e.g., ceoexpress.com, Compustat, etc.). Your companies must have long-term debt (bonds) that is publicly traded (e.g., Moody's manuals, cnnfn.com, etc.). You may have to obtain some information from printed sources, though most of it should be available on the web. Submit your list of 3 companies in order of priority to me by Wednesday, September 17, 2003. I will let you know (by email) the name of the company you can work on. You will lose points if your submission is delayed. It is your responsibility to ensure that all relevant information is available about your companies, before you submit their names to me. You will be penalized if you are unable to complete your research because of lack of information available about your company. Outline of the Project. The following will comprise the areas of your research: History of the Company 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Founding of the firm State of incorporation Mergers/Acquisitions Growth history Size of the firm, number of shareholders, etc. Potential sources: Company web site, ceoexpress.com, Compustat, the firm’s financial reports, etc. The Firm’s Product Lines 1. Firm’s major product lines 2. Importance of major products in generating the firm’s revenues 3. Success of the firm’s products in the marketplace The Position of the Firm in the Industry 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Size of the firm relative to other firms in the industry (currently and historically) Financial position and profitability of the firm (currently and historically) Leadership position of the firm in the industry (is the firm a leader or a follower?) Include other ratios for your firm that may be relevant to your report. Based on your research this far, assess the riskiness of your company relative to its competitors and its position in the industry (in terms of average risk, high risk, low risk). 2 Potential sources: Firm financial reports, industry reports, Robert Morris Associates, Dun and Bradstreet, Moody’s manuals, yahoo.com, marketguide.com, cbs.marketwatch.com, etc. Determination of the Firm’s WACC. A. Cost of Common Equity (use both models) 1. Calculating the cost of equity using the Gordon Constant Growth Model ks D1 g P0 D1 may be projected as a trend of past dividends g may be estimated as a trend growth rate in dividends or earnings or as a function of ROE P0 is the current market price Note: Please show your calculations and the sources of the data used. If your firm doesn't pay a dividend, you cannot use this model, and will only use the model below. 2. Calculating the cost of equity using the Capital Asset Pricing Model k s = kRF + bs(kM - kRF ) kRF may be proxied using the latest yield on a 10-year T-bond. kM is the rate of return on the market portfolio (e.g., S&P 500 as a proxy). You can calculate the S&P return for the last 10 years. The beta index (bs) of systematic risk may be calculated using simple linear regression on Microsoft Excel (regress Y (firm’s returns) vs. X (market returns)). Use monthly returns for the past 5 years and assume that each return has an equal probability of occurrence. You must calculate the beta of the firm and not use a published beta. You can however compare your calculated beta to a published source for accuracy. Potential sources: yahoo.com, stocktools.com, Tradeline through Dow Jones New Retrieval, etc. B. Cost of Long-Term Debt. The cost of debt should be calculated using the YTM approach (solve for the discount rate that equates the bond cash flows to the bond’s price). Your firm must have at least one issue of long-term debt outstanding. Note: Your firm may have several issues of long-term debt outstanding, and they may all have different costs. You would then find the weighted average cost of debt, by using the market value of various debt issues as weights. For this project, however, we will consider just one issue of long-term debt. For any one issue of long-term debt for your company, determine the following: 3 The number of periods, N, until the bond matures Determine the coupon payment on the bond Note if the bond pays annual or semi-annual interest and calculate the cost of debt accordingly Potential sources: Wall Street Journal, Moody's manuals, cnnfn.com, yahoo.com, etc. C. Cost of Preferred Stock. The cost of preferred stock is to be calculated as a perpetuity. Calculate the cost of any one issue of preferred stock, even if more than one issue is outstanding. (If there are multiple issues, they may have different costs, and you would find a weighted average of the cost using market value of the preferred stock as weights). k PS DPS P0 D. Calculation of the Capital Structure Weights. The capital structure weights are to be calculated as follows Common Equity Weight wcommon equity = Market Value of Common Equity/Sum of the Market Values Long-Term Debt Weight wlong-term debt = Market Value of L-T Debt/Sum of the Market Values Preferred Equity Weight wpreferred stock = Market Value of Preferred Equity/Sum of the Market Values The Sum of the Market Values is the Sum of the Market Values of Common, Preferred, and L-T Debt. If you are unable to find the market value of all these components (long-term debt may be difficult because of multiple issues outstanding) use book value weights. Please specify what weights you have used. E. Calculation of the WACC. The WACC is the weighted average of the component costs of common equity, long-term debt, and preferred equity WACC = wcommon equityks + wlong-term debtk long-term debt(1-T)+ wpreferred stockk ps The above calculation will be performed twice, using the two different specifications for ks given above in part A. Compare the computed WACC to your earlier assessment of your company’s risk. Evaluate the consistency or inconsistency of your findings. 4 Discussion of the Limitations of the Analysis and Reliability of the Calculations Organization and Form of the Written Report. Your written report should conform to the following: The report must have a cover page, which will include the title of your study and your name Include a table of contents, indicating the major topics and sub-topics addressed. Corresponding page numbers should be given in the right-hand column. If tables, charts, figures, exhibits etc. are used, they should also be indicated in the table of contents. The table of contents should be followed by the report’s introduction, the main body of the paper, and then a conclusion or summary. Include references throughout the paper by noting the name(s) of the author(s) followed by the publication year enclosed in parentheses without punctuation: e.g., Smith (1990). When a specific page, section, or quote is referenced, the reference should also be placed in parentheses: (Newsweek (1990), p. 56). You can also use footnotes to cite your sources. Remember that information obtained from the Internet must also be cited with the complete Internet address; e.g., http://www.kelley.iu.edu/cholden/smcf/Part1.htm. Include a bibliographic reference section at the end of your report. Your report should be no longer than 20 pages (a shorter report is fine, as long as it is complete). Just make sure all information and calculations that are required are included. The report should be typed and double-spaced, checked for correct spelling and grammar, and include page numbers. The report should be clearly written, well organized, well researched, and adhere to an appropriate form of presentation. Include copies of all data you have used to do your analysis in an appendix at the end of the report as supporting documents as well as a disk with the electronic version of your paper. Note: This report should reflect your own work. Please refer to Villanova's Academic Integrity Policy (a summary of which is included in the syllabus) before you start work on the project. Due Date: This report is due in class on December 10, 2003. Your grade will be dropped by 10% for each day that your report is late. In addition, failure to adhere to this format will result in a lower grade. 5