Practice_1
advertisement

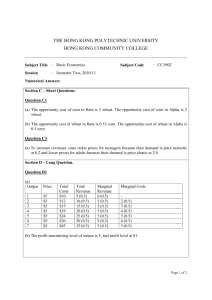
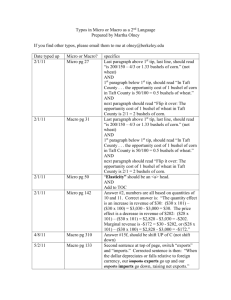
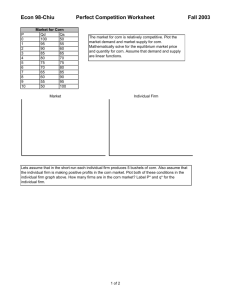
Practice Exam – ECO 2010 1. The word economy comes from the Greek word for a. “environment.” b. “one who manages a household.” c. “one who participates in a market.” d. “conservation.” 2. Which of the following would NOT be true in a world without scarcity? a. There would be no need for the science of economics. b. Everyone would have all the goods and services they wanted. c. There would have to be an infinite supply of every resource. d. There would be opportunity costs. 3. Economists use the phrase “There is no such thing as a free lunch,” to illustrate a. how inflation increases prices. b. that to get one thing, we must give up something else. c. that nothing is free in a market economy. d. that if something looks too good to be true, it probably is. 4. Daniel decides to spend the last two hours of the night before his economics exam studying instead of sleeping. For Daniel, his tradeoff would be a. nothing, since no dollar value can be put on sleep. b. nothing, since studying would be more beneficial than sleep. c. the six hours of sleep he could have had if he had gone to bed before midnight. d. the two hours of rest he would have gotten. 5. The largest single cost of going to college is usually a. books. b. room and board. c. tuition. d. lost wages. 6. Which of the following is the best example of a marginal change? a. The price of housing rose in Seattle by 5% in last year. b. Kim gets a big promotion at work. She also gets a raise from $25,000 per year to $40,000 per year. c. Mark graduates from college and takes a job. His income increases from $10,000 per year to $50,000 per year. d. A drought hits the upper Midwest and the price of wheat increases from $4.00 per bushel to $8.00 per bushel. 7. Which is the most accurate statement about trade? a. Trade can make every nation better off. b. Trade makes some nations better off and others worse off. c. Trading for a good can make a nation better off only if the nation cannot produce that good itself. d. Trade helps rich nations and hurts poor nations. 8. Prices direct economic activity in a market economy by a. influencing the actions of buyers and sellers. b. reducing scarcity of the goods and services produced. c. eliminating the need for government intervention. d. allocating goods and services produced in the most equitable way. 9. The term market failure refers to a. a situation in which the market on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently. b. an unsuccessful advertising campaign which reduces buyer demand. c. a situation in which competition among firms becomes ruthless. d. a firm which is forced out of business because of losses. 10. Economists use models in order to a. learn how the economy works. b. make their profession appear more precise. c. make economics difficult for students. d. make sure that all of the details of the economy are included in their analysis. 11. A circular-flow diagram is a model that a. illustrates cost-benefit analysis. b. explains how the economy is organized. c. shows the flow of traffic in an economic region. d. explains how banks circulate money in the economy. 12. Factors of production are a. used to produce goods and services. b. owned by firms. c. abundant in most economies. d. used by both firms and households. 13. According to the circular-flow diagram, factors of production are owned by a. the government. b. firms. c. households. d. All of the above are correct. 14. If an economy is producing efficiently a. there is no way to produce more of one good without producing less of the other. b. it is possible to produce more of both goods. c. it is possible to produce more of one good without producing less of the other. d. it is not possible to produce more of one good at any cost. 15. In the production possibilities frontier shown, what is the opportunity cost to society of the movement from point A to point C? a. 50 baseballs b. 100 baseballs c. 100 bananas d. 300 bananas 16. According to the graph, if this economy put all available resources into the production of bananas, it could produce a. 200 bananas and also 150 baseballs. b. 300 bananas and also 100 baseballs. c. 400 bananas and no baseballs. d. It is impossible to know unless we know the quantity of resources available. 17. Economists consider normative statements to be a. descriptive, making a claim about how the world is. b. statements about the normal condition of the world. c. prescriptive, making a claim about how the world ought to be. d. statements which establish production goals for the economy. 18. In the graph shown, the slope of the curve between points A and B is a. 5/2 b. 2/5 c. –2/5 d. –5/2 19. If Steven chooses to buy more bagels per month at each price his demand curve will a. shift inward. b. shift outward. c. not shift, but he will move along his demand curve from left to right. d. not shift, but he will move along his demand curve from right to left. 20. A rancher can produce only hamburgers, and a farmer can produce only french fries. The rancher and the farmer both like both foods. They a. cannot gain from trade. b. could gain from trade under certain circumstances, but not always. c. could gain from trade because each would enjoy a greater variety of food. d. could gain from trade only if each were indifferent between hamburgers and french fries. 21. According to the graph, if Paul divides his time equally between corn and wheat, he will be able to produce a. 2 bushels of wheat and 2 bushels of corn. b. 3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn. c. 4 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn. d. 4 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn. 22. According to the graph, assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and each were dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product they have a comparative advantage in and trade 3 bushels of wheat for 3 bushels of corn. Cliff would now be able to consume. a. 4 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn. b. 3 bushels of wheat and 4 bushels of corn. c. 3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn. d. 2 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn. Labor Hours Needed to Make One Unit of: Baskets Birdhouses Amount Produced in 24 Hours: Baskets Birdhouses Montana 6 2 4 12 Missouri 3 4 8 6 23. Given the information in the table, the opportunity cost of 1 basket for Montana is a. 1/3 birdhouse. b. 1 birdhouse. c. 3 birdhouses. d. 4 birdhouses. 24. For two people who are planning to trade, it is impossible to a. have a comparative advantage in both goods. b. have an absolute advantage in both goods. c. specialize in the production of one good. d. trade so that both people will be better off. 25. In a free market, who determines how much of a good will be sold and the price at which it is sold? a. suppliers b. demanders c. the government d. suppliers and demanders together 26. A competitive market is one in which a. there is only one seller of the product. b. each seller of the product is free to set the price of his product. c. each seller attempts to compete with other sellers, causing fewer sellers in the market. d. there are so many buyers and many sellers that each has a negligible impact on price. 27. A market with many sellers offering similar but slightly different products is called a. a monopoly. b. oligopolistic. c. monopolistically competitive. d. perfectly competitive. 28. If a good is “normal,” then an increase in income will result in a. no change in the demand for the good. b. an increase in the demand for the good. c. a decrease in the demand for the good. d. a lower market price. 29. The movement from point A to point B on the graph would be caused by a. an increase in price. b. a decrease in price. c. a decrease in the price of a substitute good. d. an increase in income. 30. The market demand is a. the sum of all individual demands. b. the demand for every product in an industry. c. the average quantity demanded at each price. d. difficult to determine and is generally an estimation for most markets. ANSWERS 1 ANSWER: b. “one who manages a household.” 2 ANSWER: c. There would have to be an infinite supply of every resource. 3 ANSWER: b. that to get one thing, we must give up something else. 4 ANSWER: d. the two hours of rest he would have gotten. 5 ANSWER: d. lost wages. 6 ANSWER: a. The price of housing rose in Seattle by 5% in last year. 7 ANSWER: a. Trade can make every nation better off. 8 ANSWER: a. influencing the actions of buyers and sellers. 9 ANSWER: a. a situation in which the market on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently. 10 ANSWER: a. learn how the economy works. 11 ANSWER: b. a model that explains how the economy is organized. 12 ANSWER: a. used to produce goods and services. 13 ANSWER: c. households. 14 ANSWER: a. there is no way to produce more of one good without producing less of the other. 15 ANSWER: b. 100 baseballs 16 ANSWER: c. 400 bananas and no baseballs. 17 ANSWER: c. prescriptive, making a claim about how the world ought to be. 18 ANSWER: d. –5/2 19 ANSWER: b. shift outward. 20 ANSWER: c. could gain from trade because each would enjoy a greater variety of food. 21 ANSWER: c. 4 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn. 22 ANSWER: c. 3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn. 23 ANSWER: c. 3 birdhouses. 24 ANSWER: a. have a comparative advantage in both goods. 25 ANSWER: d. suppliers and demanders together 26 ANSWER: d. there are so many buyers and many sellers so that each has a negligible impact on price. 27 ANSWER: c. monopolistically competitive. 28 ANSWER: b. an increase in the demand for the good. 29 ANSWER: b. a decrease in price. 30 ANSWER: a. the sum of all individual demands.