Exam 1 Study Questions
advertisement

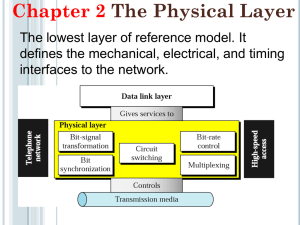
CENG 3331 Introduction to Telecommunications and Networks Ch. 1-5 Study Questions (9th Edition of Stallings) Ch. 1 Introduction 1. Draw a diagram illustrating a simplified communication model and describe each key element. Include a general block diagram and an example in your figure. (See page 16.) 2. Briefly contrast WANs and LANs (page 22-24). Ch. 2 Protocol Architecture 1. Draw and briefly describe Stalling’s model for TCP/IP Layers and Example Protocols (Fig.2.3) 2. Be able to identify the functions of the 5 TCP layers in Figure 2.3. 3. What is a protocol data unit? 4. Which version of IP is the most prevalent today? Ch.3. Data Transmission 1. What is meant by guided media and unguided media? 2. Contrast a direct link, point-to-point and multipoint link. 3. Contrast simplex, half duplex and full-duplex transmission. 4. What is the formal (mathematical) definition of a continuous signal? What is a discrete signal? 5. What is a periodic signal? 6. What are the 3 basic parameters of a periodic signal? 7. What is the relationship between the wavelength and the frequency? 8. What is the spectrum of a signal? 9. Contrast the absolute bandwidth and the effective bandwidth of a signal. 10. Give an example of devices that communicate: (see Fig. 3.14) a. analog data using analog signaling. b. digital data using analog signaling. c. analog data using digital signaling. d. digital data using digital signaling. 11. Briefly contrast analog vs. digital transmission . 12. What is meant by: a. attenuation? b. delay distortion? 13. Express the thermal noise (in watts) present in a bandwidth of B Hz. 14. What causes intermodulation noise? 15. What is meant by crosstalk? 16. If the transmission rate is 56k bps, how much data is lost if a sharp spike (impulse noise) of .01 sec occurs. 17. What is Nyquist's equation for channel capacity? 18. What is Shannon's equation for channel capacity? 19. Why is the Eb/No ratio important? 20. What is the equation for power ratios in dB? voltage ratios? 21. What is the equation for dBW? dBmV? Ch. 4 Transmission Media 1. What type of media is most often found in buildings for carrying voice and data? 2. Describe a coax cable. How does it differ from a fiber optics cable? 3. How does rain affect frequencies in the upper microwave region of the spectrum? 6. What is meant by transponder? What is a VSAT system? What are they used for? 7. What is the difference between broadcast radio and microwave? What is meant by line-of-sight transmission? 8. What are the advantages of infrared communications? Ch. 5 Data Encoding 1. Define the following terms: (Table 5.1) a. data rate b. signaling rate (modulation rate) 2. What are the classic definitions of mark and space? 3. What is meant by the bit error rate (BER)? In general what happens to the BER when a. data rate increases? b. SNR increases? 4. In general what is the relationship between bandwidth and data rate? 5. List five ways to evaluate and compare encoding schemes? 6. Describe non-return to zero (NRZ) encoding formats NRZL and NRZI.. 7. In general, what is differential signaling? 8. What is meant by multilevel binary signals? How are bipolar-AMI and pseudoternary defined? How does multilevel binary encoding compare to NRZ? 9. What are the bi-phase encoding formats, Manchester and Differential Manchester? How do they perform when compared to NRZ. 10. How does your author define the “modulation rate” D in baud? 11. What is the purpose of “scrambling techniques” used with bi-phase encoding? 12. Briefly describe ASK, BFSK, and PSK. 13. Explain how a single pair of wires can be used for full-duplex operation using FSK. 14. What is QPSK? 15. What is meant by the transmission bandwidth? What are the general equations for BT for ASK and MPSK? 16. What is a codec? 17. State the sampling theorem? 18. Describe PAM and PCM. 19. What is quantization? quantization noise? 20. What is the general equation for SNR dB as a function of n, the number of bits in the digitization process. 21. What is companding? How is it related to nonlinear quantization? 22. What is delta modulation? 23. Why is PCM used when it tends to require a very large transmission bandwidth?