- Rajshahi University Web Page
advertisement
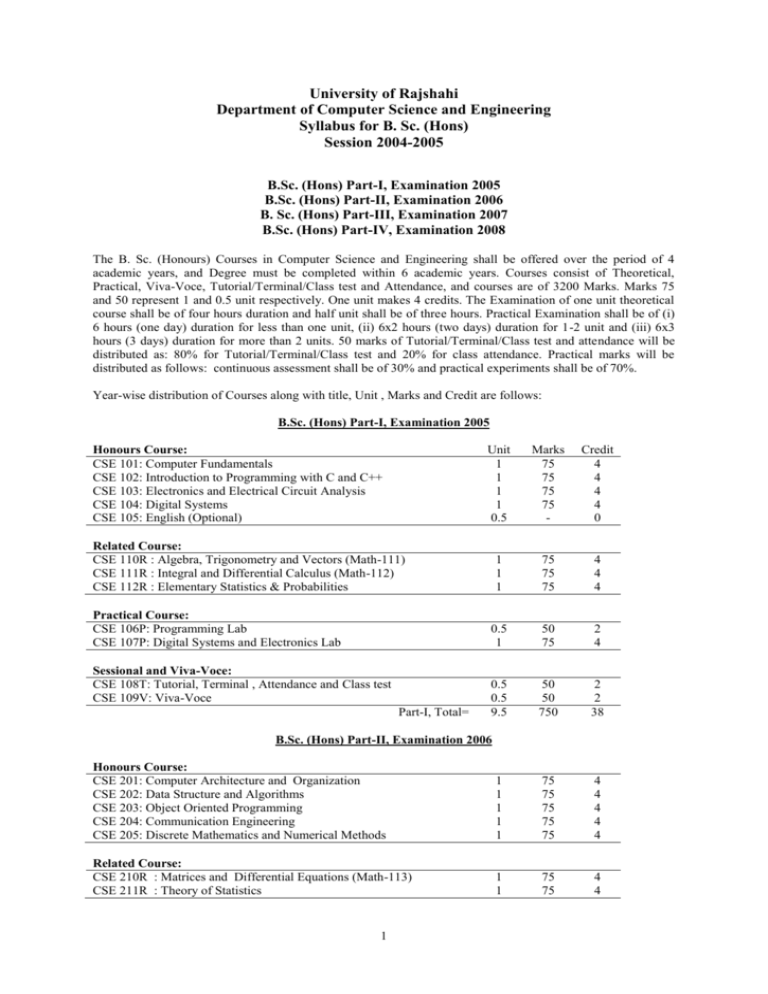
University of Rajshahi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Syllabus for B. Sc. (Hons) Session 2004-2005 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-I, Examination 2005 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-II, Examination 2006 B. Sc. (Hons) Part-III, Examination 2007 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-IV, Examination 2008 The B. Sc. (Honours) Courses in Computer Science and Engineering shall be offered over the period of 4 academic years, and Degree must be completed within 6 academic years. Courses consist of Theoretical, Practical, Viva-Voce, Tutorial/Terminal/Class test and Attendance, and courses are of 3200 Marks. Marks 75 and 50 represent 1 and 0.5 unit respectively. One unit makes 4 credits. The Examination of one unit theoretical course shall be of four hours duration and half unit shall be of three hours. Practical Examination shall be of (i) 6 hours (one day) duration for less than one unit, (ii) 6x2 hours (two days) duration for 1-2 unit and (iii) 6x3 hours (3 days) duration for more than 2 units. 50 marks of Tutorial/Terminal/Class test and attendance will be distributed as: 80% for Tutorial/Terminal/Class test and 20% for class attendance. Practical marks will be distributed as follows: continuous assessment shall be of 30% and practical experiments shall be of 70%. Year-wise distribution of Courses along with title, Unit , Marks and Credit are follows: B.Sc. (Hons) Part-I, Examination 2005 Honours Course: CSE 101: Computer Fundamentals CSE 102: Introduction to Programming with C and C++ CSE 103: Electronics and Electrical Circuit Analysis CSE 104: Digital Systems CSE 105: English (Optional) Unit 1 1 1 1 0.5 Marks 75 75 75 75 - Credit 4 4 4 4 0 1 1 1 75 75 75 4 4 4 0.5 1 50 75 2 4 0.5 0.5 9.5 50 50 750 2 2 38 Related Course: CSE 110R : Algebra, Trigonometry and Vectors (Math-111) CSE 111R : Integral and Differential Calculus (Math-112) CSE 112R : Elementary Statistics & Probabilities Practical Course: CSE 106P: Programming Lab CSE 107P: Digital Systems and Electronics Lab Sessional and Viva-Voce: CSE 108T: Tutorial, Terminal , Attendance and Class test CSE 109V: Viva-Voce Part-I, Total= B.Sc. (Hons) Part-II, Examination 2006 Honours Course: CSE 201: Computer Architecture and Organization CSE 202: Data Structure and Algorithms CSE 203: Object Oriented Programming CSE 204: Communication Engineering CSE 205: Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods 1 1 1 1 1 75 75 75 75 75 4 4 4 4 4 Related Course: CSE 210R : Matrices and Differential Equations (Math-113) CSE 211R : Theory of Statistics 1 1 75 75 4 4 1 Practical: CSE 206P: Data Structure and Algorithms Lab and Object Oriented Programming Lab CSE 207P: Computer Architecture and Communication Lab Sessional and Viva-Voce: CSE 208T: Tutorial, Terminal, Attendance and Class test CSE 209V: Viva-Voce Part-II, Total= 1 75 4 0.5 25+25 2 0.5 0.5 9.5 50 50 750 2 2 38 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-III, Examination 2007 Honours Course: CSE 301: Microprocessor and Computer Interfacing CSE 302: Operating System and System Programming CSE 303: Database Management Systems CSE 304: Computer Networks CSE 305: Automata Theory and Compiler Design CSE 306: System Analysis and Design CSE 307: Artificial Intelligence and Neural Computing CSE 308: Computer Graphics and Multimedia System 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 75 75 75 75 75 75 75 75 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 Practical: CSE 309P: Operating Systems, Microprocessor and Interfacing Lab CSE 310P: DBMS, Computer Graphics and Computer Network Lab CSE 311P: Compiler Design and Artificial Intelligence Lab 0.5 0.5 0.5 50 50 50 2 2 2 Sessional and Viva-Voce: CSE 312T: Tutorial, Terminal , Attendance and Class test CSE 313V: Viva-Voce Part-III, Total= 0.5 0.5 10.5 50 50 850 2 2 42 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 75 75 75 75 75 75 75 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0.5 50 2 0.5 50 2 0.5 50 2 1 75 4 0.5 0.5 10.5 40 50 50 850 3200 2 2 42 160 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-IV, Examination 2008 Honours Course: CSE 401: Software Engineering CSE 402: Parallel Processing and Distributed System CSE 403: Digital Signal and Image Processing CSE 404: Cryptography and Network Security CSE 405: VLSI Design CSE 406: Computer Simulation and Modelling CSE 407: E-Commerce Practical: CSE 408P: E-Commerce, Software Engineering and Cryptography and Network Security Lab CSE 409P: Parallel Processing and Distributed System and VLSI Design Lab CSE 410P: Simulation and Modelling and Digital Signal and Image Processing Lab Project: CSE 411J: Project Sessional and Viva-Voce: CSE 412T: Tutorial, Terminal , Attendance and Class test CSE 413V: Viva-Voce Part-IV, Total= Grand Total = 2 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-I CSE 101: Computer Fundamentals Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Computer Basics: Introduction to Studying Computers, History and development of Computers, Generation of Computers, Types of Computers, Impact of Computers on Society. Computer Hardware and Peripherals: Basic Units of Computer Hardware, Keyboard, Mouse and Different types of Monitors, Different parts of system unit, Internal structure of CPU, Functions of RAM, ROM and Cache memory, Basic functional mechanism of FDD, HDD and CD-ROM, Impact and Non-impact printers, Modem, Power supply stability, Handling of computer cards and chips, Typical Computer specifications. Information & data processing: Data organization, types of data processing, data processing cycle, data processing system, database concepts Software: Classifications, System software, Operating system concepts and importance, components and basic functions of DOS, Windows/Windows-NT/Windows-XP and UNIX and LINUX, X-window system operating system, Application software’s and Utility programs, Computer Virus, Software troubleshooting and maintenance. Applications: Computer networks and its goals, Basic concept on LAN, MAN, WAN and Internet systems, Internet services, E-mail, E-Commerce, M-Commerce ,WAP, WWW, Multimedia system. Books Recommended 1. Warford 2. L. Rosch 3. P. Norton, 4. Subramanian 5. P. Norton 6. V. K. Jain : Computer Science : Hardware Bible, Braddy Publishing, Indianapolis : Inside the PC : Introduction to Computers : Introduction to Computer : Switching theory and Digital Electronics. CSE 102: Introduction to Programming with C and C++ Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Programming Preliminaries: Problem solving techniques, Algorithm, Flowchart, debugging, documentation, Classifications of programming Languages, Compiler and Interpreter, Loader and Linker, Source and Object programs, Modular programming techniques. Programming Language C : Program creating, Compiling, Debugging and Running; Data types, Variables and Constants, Data Input and Output, Statements and Operators, Control Structures, Arrays, Record/Structure, Procedure and Functions, Recursive function, User-Defined data types, Pointers, External File handling, Uses of Graphics functions. Introduction to GUI programming, editing, compiling, linking and running programs on Windows and UNIX platforms, make files. Introduction to C++: Overview of Object Oriented Programming; Encapsulation, Polymorphism and Inheritance; Object and Classes; Base Class, Derived Class, Virtual Function and Classes, Function Overloading and exception handling. Books Recommended 1. Kernighan and Ritchie 2. Gotfreid 3. M. Keller 4. D.E. Knuth: 5. H. Schieldt 6. E. Balagurusamy 7. H. Schieldt 8. H. Schieldt 9. N. Barkakati : The C Programming Language : Programming with C, Schaum's Outline Series, TMH : Afirst Course on Computer Programming using Pascal, McGraw-hill, 1987 : The Art of Computer Programming : The complete reference, Turbo C/C++ : Programming with ANSI C : Teach yourself C : Teach yourself C++ : Object Oriented Programming with C++ 3 CSE 103: Electronics and Electrical Circuit Analysis Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction: N-type and P-type Semiconductors; P-N Junction Diodes and their V-I Characteristics; Zener Diode; Ideal Rectifier Concept; P-N Junction Diode as a Rectifier; Half-wave and Full-wave Rectifier; Voltage Regulator Using Zener Diode. Transistor: PNP and NPN Junction Transistor; V-I Characteristics; CB, CE and CC Configurations; Bias Stabilization; Different Types and Biasing; Operating Point; Transistor an amplifier, Transistor as an high speed switch, DC and AC Load Lines; JFET; MOSFET. Amplifiers: Transistor DC amplifiers, CE, CB and CC amplifiers and their equivalent circuits and computation of current, voltage and power Gains, class A, class B and class C amplifiers, Feed back amplifiers and Oscillators, Operational amplifiers. Micro-Electronics: Microelectronic Technology; Planer Process; Introduction to VLSI; Bipolar Transistor, ; FET and IC Fabrication Technique; CMOS Technology; Monolithic Diodes; Metal-Semiconductor Contract; IC Resistor and Capacitor; IC Packaging; Characteristics of IC Components; Micro-Electronic Circuit Layout; Printed Circuit Board. Circuit analysis: Concepts of Electrical Networks; Kirchhoff’s law; Thevenin’s and Norton’s Theorems; Superposition Theorem; Maximum Power Transfer Theorem; Equivalence of Pi, T, Star, Delta Conversions; Lattice Networks; Constant K-Type Low Pass, High Pass, Band Pass and Band-Elimination Filters. Books Recommended 1. Mottershed, A 2. Milman and Helkias 3. Theraja, B L 4. Grobe, Bernard 5. Mehta, V K 6. Illiot 7. John D. Rider 8. Theraja, B. L. : Electronic Devices and Circuits : Integrated Electronics : Basic Electronics : Basic Electronics : Principles of Electronics : Microelectronics Fabrication Technology : Network Lines and Fields : Basic Electricity and Magnetism CSE 104: Digital Systems Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Fundamentals of Digital Logic System: Number Systems and Codes, Logic Gates and Boolean Algebra, Logic Circuit Design, Minimization Techniques: Algebraic Simplification, Karnaugh Map Method, Quine-McCluskey method, Consensus method. Switching Devices: Switching concepts of Diodes, Transistors and FETs. Flip-Flops and related Devices: Transistor Latch, NAND gate latch, NOR gate latch, D latch. Clock signals and Clocked F.Fs: Clocked S-C, J-K and D Flip-Flops. F.F timing considerations, Master/Slave F.Fs. F.F T-F.F. applications, Frequency division and counting. Schmitt Trigger devices, Monostable and Astable Multivibrators. SSI Logic Circuits: BCD to decimal decoders, BCD to 7 segment decoder/drivers. Encoders, Multiplexers and their applications. Demultiplexers. Trouble shooting case studies. Analog to digital conversion, digital ramp, successive approximation, flash and tristate ADC. digital to analog conversion: circuits, specifications, applications, Sample and hold circuits. Analog multiplexers. Data acquisition, digital voltmeter. Integrated Circuit Logic Families: DTL & TTL logic family, standard TTL series characteristics, other TTL series, TTL loading rules, TTL open-collector outputs, tristate TTL. The ECL family. Digital MOSFET circuits, characteristics, CMOS circuits, CMOS tristate logic, TTL driving CMOS, CMOS driving TTL. Introduction to sequential circuits: formal representation of sequential circuits, Moore and Mealy models, analysis and synthesis of synchronous and asynchronous sequential circuits. Counters and Registers: Asynchronous (Ripple) up and down counters, Synchronous up and down Counters. Counters with MOD 4 number <2N. Propagation delay in Ripple counters. Presettable counters. The 74193 counter. Counter applications. Shift registers. IC shift-registers, shift-register counters. Books Recommended 1. R.J. Tocci 2. D.V. Hall 3. F.P. Prosser and D.E. Einkel 4. V. K. Jain 5. Moris Manno : Digital Principles, 5th ed., PHI : Digital Circuits and systems, McGraw-Hill, 1989 : The Art of Digital Design, Prentice-Hall : Switching theory and Digital Electronics : Digital Logic and Computer Design 5 Related Course: CSE 105: English (Optional) Basic Terminologies of Physical Sciences CSE 110R : Algebra, Trigonometry and Vectors Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 1. a) Algebra of sets, De Morgan's rule, Relation and Function. b) Determinants : Properties and Crammer's rule. 2. 3. Theory of Equations: a) Theorems, Relation between roots and coefficients. b) Solution of cubic Equations. a) De Moiver's Theorem. b) Deduction from De Moiver's Theorem. 4. a) Functions of Complex Arguments. b) Gregory's Series. 5. a) Summation of Series. b) Hyperbolic Functions. 6. Vector Addition, Multiplication and Differentiation. 7. Vector Differential Operator - Grad., Div. and Curl. Books Recommended 1. Barnside and Panton 2. Bernard and Child 3. Hall and Knight 4. Das and Mukherje 5. Spigel : Theory of Equations : Higher Algebra : Higher Algebra : Higher Trigonometry : Vector Analysis CSE 111R : Integral and Differential Calculus Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Functions: Domain, Range, Inverse Function and Graphs of Function; Limits, Continuity and Indeterminate Form. Ordinary Differentiation: Differentiability, Differentiation and Leibnitz Theorem. a) Expansions of Functions: Rolle's Theorem, Mean Value Theorem, Taylor's and Maclaurin's Formulae. b) Maxima and Minima of Functions of one variable. a) Partial Differentiation: Euler's Theorem, Tangents and Normals. b) Asymptotes. 5. Indefinite Integral: Methods of Substitutions, Integration by Parts, Special Trigonometric Functions and Rational Fractions. 6. Definite Integral: Fundamental Theorem, General Properties, Evaluation of Definite Integral and Reduction Formulas. 7. Multiple Integral: Determination of Length, Areas, and Volumes. Books Recommended: 1. Ayres, F 2. Das and Mukherjee 3. Das and Mukherjee 4. Edwards : Calculus : Differential Calculus : Integral Calculus : Differential Calculus 6 CSE 112R : Elementary Statistics and Probabilities Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Statistics: Meaning & Scope, Variables and Attributes, Collection and presentation of Statistical data, Frequency Distribution and Graphical Representation. Analysis of Statistical Data: Location, Dispersion and their measures. Skewness, Kurtosis and their measures. Moment and cumulants. Elements of Probabilities: Concept of probality, Sample Space, Events. Union and Intersection of Events. Probability of Events. Laws of probability. Conditional Probabilities. Bose Einstein Statistics. Bays probability. Chebysec's Inequality. Random Variables and Probality Distribution: Basic concepts. Discrete and continuous Random variables. Density and distribution functions. Mathgematical Expectation and variance. Conditional Expectation and conditional variance. Expected values and variances of the density distributions. Moments and Cumulant generating functions. Characteristic function. Study of Binomial, Poisson, Normal. Geometric, Negative Binomial, Hypergeometric, Multinomial, uniform, exponential, Log normal, Logirithmic, Beta and Gamma, cauchy and Weibul distributions. Books Recommended: 1. Anderson, A. J. B. 2. Cramer, H. 3. Hoel, P. 4. Lindley, D. V. 5. Lipschutz, S 6. Mosteller, Rourke and Thomas 7. Wolf, F. L. 8. Wonnacot, T. H. and Wonnacot, R. J. 9. Yule, G.U. and Kendall M. G. : Interpreting Data. Chapman and Hall, London. : The Elements of Probability Theory. Wiley, N. Y. : Introductory Statistics, Wiley and Sons, N. Y. : Introduction to Probalility and Statistics. Vol-1 C. U. P. London : Probalility, McGraw-Hill, N. Y. : Probability With Statistical Applications. 2nd Ed. AddisonWesley : Elements of Probability, and Statistics McGraw-Hill, N. Y. : Introductory Statistics, 3rd Ed. Wiley and Sons. N. Y. : An Introduction to the Theory of Statistics. Fourteenth Ed. Charles Griffin, London 7 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-II CSE 201: Computer Architecture and Organisation Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 The evolution of computers: The nature of computer, the first generation, the latter generation, recent development. Processor Design: Introduction: Processor organization, information representation, number formats; Fixed Point Arithmetic: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division; ALU Design: Basic ALU organization, floating point arithmetic. Control Design: Hardwired control: Design methods, multiplier control unit, CPU control unit; Basic concept of Microprogrammed Control, Control memory optimization. Memory Devices and its Organization: Different types of semiconductor memory, magnetic memory, optical memory, virtual memory, memory hierarchies; High-speed Memories: Interleaved memories, caches, associative memories. System Organization: Communications: Introduction, bus control; IO Systems: Programmed IO, DMA and interrupts, IO processors. Parallel Processing: Basic Concepts: Introduction to parallel processing. RISC processor, introduction, data dependency, addressing modes, condition codes, register sets, brief study of standard RISC processor. Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. V. Hamacher, Z. Vranesic and S. Zaky J.P. Hayes K. Hwang and F.A. Briggs W. Stallings : Computer Organization. 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill, 1988. : Computer Architecture and Organization, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, 1992. : Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing, McGraw-Hill, 1986. : Computer Organization and Architecture. CSE 202: Data Structure and Algorithms Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 The design and analysis of efficient algorithms for important computational problems. Emphasis on the relationships between algorithms and data structures and on measures of algorithmic efficiency. Arrays: Maximization, ordered lists, sparse matrices, representation of arrays. Stacks, Queues and Recursion: Fundamentals of different types of stacks and queues: Circular, dequeues, etc; evaluation of expressions, multiple stacks and queues; Recursion: Direct and indirect recursion, depth of recursion; Simulation of Recursion: Removal of recursion; Towers of Hanoi. Links Lists: singly linked lists, linked stacks and queues, the storage pool, polynomial addition, equivalence relations, sparse matrices, doubly linked lists and dynamic storage management, generalised lists, garbage collection and compaction. Trees: Basic terminology, binary trees, binary tree representations, binary tree traversal; Extended binary trees: 2-trees, internal and external path lengths, Huffman codes/algorithms; threaded binary trees, binary tree representation of trees; Application of Trees: Set representation, decision trees, games trees: Counting binary trees. Graphs: Introduction, definitions and terminology, graph representations, traversals, connected components and spanning trees, shortest path and transitive closure, activity networks, topological sort and critical paths, enumerating all paths. 8 Internal Sorting: Searching, bubble sort, shell sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, heap sort, 2-way merge sort, How fast can we sort? Sorting on several keys, practical considerations for internal sorting. External Sorting: General idea; Sorting with Disks: K-way merging, buffer handling for parallel operation, run generation; sorting with Tapes: Balanced merge sorts, polyphase merge, sorting with fewer than 3 tapes. Symbol Tables: static tree tables, dynamic tree tables; Hash Tables: Hashing functions, overflow handling, theoretical evaluation of overflow techniques. Files: file, queries and sequential organisations: Indexing Techniques: Cylinder-surface indexing hashed indexes, tree indexing-B-trees; Tree indexing. Books Recommended 1. E. Horowitz and S. Sahni 2. Reingold 3. Robert L. Kruse 4. Niklaus Wirth 5. Lipshultz 6. E. Horowitz and S. Sahni 7. Goodman and Hedetnie : Fundamentals of Data Structures, Galgotia, 1985. : Data Structures. : Data Structures and Program Design, 3rd Edition. : Algorithms-Data Structures-Programs, Prentice Hall of India, 1992. : Data Structures, Schaum's Outline Series, 1987. : Computer Algorithms, Galgotia, 1985. : Introduction to Design and Analysis of Algorithms, McGraw-Hill, 1985 CSE 203: Object Oriented Programming Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction to object oriented programming, C++ as an object oriented language: Declaration and constants, expression and statements, data types, operator, Functions. Classes: Base, Derived virtual class, Inheritance, encapsulation, Operator and function overloading (Run-time and compile time polymorphism), Template, streams, tiles, C++ binary functions. Exception handling, Function overriding, Virtual function An Introduction to Java. The Java Programming Environment, Fundamental Programming Structures in Java, Object and classes, Inheritance. Interfaces and Inner Classes Graphics Programming, User Interface Components with swing, Applets, Exceptions and Debugging, Streams and Files. Controlling Program Flow, Intitialization & Cleanup, Hiding the implementation. Ressing classes, Polymorphism, Interfaces & Inner Classes, Holding your objects, error handling with exceptions, The Java I/O system, Run-time type Identification, Creating windows & Applets, Multiple Threads, Distributed Computing, Enterprise Java frame work, application model, multi-tier application, Java servelets, Java server pages and Beans. Books Recommended 1. H. Schidt 2. N. Barkakati 3. B. Stroustrap 4. H. M. Deitel P. J. Deitel 5. Sun Press 6. Ivor Horton 7. H. Schildt : Teach yourself C++ : Object Oriented Programming with C++ : The C++ programming language, 2nd ed. : Java How To Program : Core Java(Vol-1&2) : Beginning Java 2, Wrox : Java 2 Complete Reference, Jessey CSE 204: Communication Engineering Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction: Data communication concept, queuing theory, Analog and digital data, spectrum and bandwidth, Transmission impairments, Data rate and channel capacity, Asynchronous and synchronous data transmission techniques, Error detection and correcting codes, Data compression algorithms, interfacing with serial and parallel ports. Transmission Media: Characteristics and applications of Twisted pairs coaxial cables and optical fibres, Geostationary and low-orbit Satellites, VSAT, Radio waves. 9 Optical Fiber communication: Transmission principles and internal structure of Optical Fiber, Transmission characteristics of optical fiber, LED and Laser as optical sources, Photodiode and Phototransistor as optical detectors, Optical fiber connections, Signal degradation in optical fiber. Practical Implementation of fiber com. Optical fiber amplifier, Optical fiber measurements, Applications and future developmnt Wireless Communication, Cellular Radio, Mobile Technology. Data Encoding: Data and signal, RZ, NRZ, Manchester and differential Manchester encoding, Bi-phase mark, ASK, FSK, PSK, QPSK, modems, sampling theorem, pulse Code modulation techniques, Delta modulation. Error control mechanism (Backward and forward), Flow control mechanism, BISYNC, and HDLC. Data transmission technique: Frequency division multiplexing, time division multiplexing, wavelength division multiplexing, Circuit switching, Packet switching, Hybrid switching, ATM, Frame Relay. Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. W. Stallings, Macmillan John M. Senior Kaiser F. Halsall, Addison Wesly, 1993 3rd edition : : : : 5. A.S. Tanenbaum, Prentice Hall, 1996 : Data and Computer Communications, 1996 4th edition, Optical Fiber Communications 2nd edition Optical Fiber Communication Data Communication Computer Network and open systems Computer Networks CSE 205: Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Method Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Mathematical Logic: Connectives, normal Forms, theory of inference for proposition calculus, predicate calculus, inference theory of predicate calculus, method of proof, mathematical induction. Sets: Basic concept of set theory, operation of sets, ordered pairs and n-tuples. Relation and ordering: Relations, properties of Binary relation in a set, composition of binary relation, relation matrix and graph of a relation, partial ordering, path in relation and di-graph. Functions: definition, composition of function, inverse function, binary and array operation. Ordered relation and structure: partially ordered set, external element of P.O. set, Lattice, finite Boolean algebra, function on Boolean algebra, Boolean function as Boolean polynomial. Graph: Introduction to graph, graph terminology, representing graph and graph isomorphism, paths, reachability, connectivity, Euler and Hamilton path, shortest path problems, graph colouring, matrix representation of graph. Trees: Introduction of trees, application of trees, tree traversal, labelling trees, trees and sorting, spanning trees, minimal spanning tree, undirected trees. Algebraic structure: Algebraic system, general properties, some simple algebraic system. Semigroup and monoids: Homomorphism of semigroups and monoid, Grammars and languages, Formal definition of a language. Group: Definition and examples, homomorphism, product and quotients of group. Numerical Methods: Solutions of polynomials and transcendental equations; Interpolation and polynomial approximation; Least square approximation; Solutions of systems of linear equations gauss elimination technique; Gauss-siedel iteration technique; Numerical Differentiation and Integration; Numerical Solutions of Ordinary Differential Equations. 10 Books Recommended 1. Lipshutz 2. Kuo, S. S. 3. C.L. Liu, 4. Sharon Ross 5. S. S. Sastry 6. K.H. Rosen 7. Chopra : Theory and Problems of Discrete Mathematics, Schaum's outline series. : Computer Application of Numerical Methods. : Elements of Discrete Mathematics, 2nd Ed, McGraw-Hill, 1985. : Descrete Mathematical Structure. : Introductory methods of Numerical Analysis. : Discrete Mathematics and its Applications : Numerical Methods for Engineers. Related Course: CSE 210R : Matrices and Differential Equations Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Algebra of matrices, Adjoint, Inverse and Rank of a matrix-definition, properties and evaluation. Elementary transformation-echelon, canonical and normal forms. Solution of systems of linear equationsconsistency and solution of homogeneous system by matrix method, and reduction to equivalent system. Characteristics equation, eigenvalues, eigenvectors and Caley-Hamilton theorem. Similar matrices and diagonalization. Solution of first order and first degree, and first order and higher degree equations. Solution of higher-order linear differential equations. Series solutions of linear differential equations. Books Recommended 1. F Ayres 2. McDuffe 3. Khanna, M L 4. Ross, S L 5. Ayres, F 6. Sharma, B D : Theory and problems of Matrices : Theory of Matrices : Matrices : Introduction to Ordinary Diff. Equations : Differential Equations : Differential Equations CSE 211R: Theory of Statistics Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Sampling Distributings: Fisher's Lemma. Study of 2 Distribution, T-Distribution and F-Distribution, Propertices, uses & Applications. Distribution of sample correlation coefficient in the null case. Sampling Distribution of the Medians and Range. Elements of Point Estimations: Basic Concepts. consistent estimates. Unbiased estimates. Mean and variance of estimates. Ideas of Efficiency. Principle of Maximum Likelihood. Illustration from Bionomial, poission & Normal Distributions. Decision Rules: Statistical decisions; Statistical hypothesis; Critical region, Best critical region; Two types of errors; procedure of Test of hypothesis; Most powerful test, standard Errors. Test of Significance: Test of single mean & single variance. Comparison of two sample Means, proportions and Variances. Bartlett's test for homogeniety of variances. Test for correlation and Regression coefficients. Exact test for 2*2 tables. Test for r*c tables. Three-Way contingency tables. Large Sample Test of Significance. Nonparametric Test, One Sample and two Sample Sign Test. Run Test and Rank Sum Test. Books Recommended 1. 2. Anderson R. L., Bancroft T. A. Beaumont, G. : Statistical Theory in Reseatch, McGraw-Hill N. Y. Banctoft, T. A. : Intermediate Mathematical Statistics, Third Ed. Chapman and Hill, 11 1. Anderson R. L., Bancroft T. A. : 3. Gutman, Wilks and Hunter : 4. Hoel, P. G. : 5. Hogg. R. V. and Graig, A. T. : 6. Kendall M. G. and Stuart A. : 7. 8. 9. Lindgren, B. W. Mood, Graybill and Boes Weatheril, G. B. : : : Statistical Theory in Reseatch, McGraw-Hill N. Y. Banctoft, T. A. London Introductory Engineering Statistics Fourth Ed. John Wiley and Sons, N. Y. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics, Fifth Ed. John Wiley and Sons, N. Y. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics Fourth Ed. Collier Macmilan, N. LY. The Advanced Theory of Statistics Vol. 1, Fourth Ed. Charles Griffin and Co. London. Statistical Theory, Third ed. Collier-Macmillan Co; N. Y. Introduction to the Theory of Statistics, Third ed. McGraw-Hill, N. Y. Intermediate Statistics Mithods, Chapman and Hall, London 12 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-III CSE 301: Microprocessor and Computer Interfacing Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Microprocessors and Microcomputers, Evolution of microprocessors, Microprocessors applications. Intel 8086 Microprocessor: Internal architecture, register structure, programming model, addressing modes, instruction set, assembly language programming, condition tests, branches; control structures; subroutine and parameter passage; macros/O. Control signals; I/O port organization and accessing; 8086 family of chips, interrupts and interrupt Handling; Coprocessors. System design using 8086; on overview of Intel 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium microprocessors. RISC processors, 6800 and 68000 processors. Basic Interfacing Techniques: Review of computers signals used for interfacing, Address Decoding techniques, DI/DO Registers design and interface with the computer, p controlled and external device controlled interfacing techniques, PPI, DMA controller, interrupt controller, programmable interval timer, interfacing with memory, monitor, printers, keyboard; design of computer controlled system using serial and parallel ports. Interfacing with real world: Signal conditioning techniques, interfacing with sensors, transducer, measurement of different electrical quantities- voltage current etc., interfacing with ADC and DAC to control real world devices, stepper motor, motor speed control, smart data acquisition card design, temp control. Books Recommended 1. Rafiquzzaman 2. D. V. Hall 3. Y. Liu and G. A. Gibson 4. Artwick 5. Ramesh Goanker 6. James E. Powell : Microprocessor and Microcomputer based system design : Microprocessors and Interfacing, McGraw-Hill, 1987. : Microcomputer Systems: 8086/8088 Family, Prentice-Hall, 1991. : Microcomputer Interfacing : Microcomputer Interfacing :Designing User Interfaces CSE 302: Operating Systems and System Programming Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction, evolution, goals and components of OS. Process management, process states and state transition, process control blocks, job and process scheduling, scheduling levels, objective and criteria, CPU scheduling algorithms, process co-ordination, critical section problems, semaphores, language constructs classical problems of process co-ordination, interposes communication, message and mailbox etc. I/O programming. Device management techniques. Interrupt processing. Parallel processing. Deadlock, deadlock prevention, avoidance, detection and recovery. Memory management, memory allocation schemes, paging and segmentation, virtual memory, page replacement strategies, working sets, demand paging. Secondary storage management, disk scheduling algorithms. File management: file system functions, file organization, logical and physical file maps, tree structured file systems, space allocation, file catalogues, file access control mechanisms, operating systems security. Time sharing and virtual machines. Main Features of MS-DOS, Windows-NT, UNIX, Linux, VMS and VSE. Distributed System. Assembler-general Design procedure, Table processing, Macro language and Microprocessor, Compiler, Loader, Linker, Translator Design, System call, Remote procedure call, Interprocess communication, Unix socket, Multithreading. Books Recommended 1. Tanenbaum 2. Madnick and J. Donovon 3. Peterson and Silberchaltz 4. B. Hausen 5. Donovan 6. M. MilenKovic 7. Terrence : Operating Systems, Prentice-Hall, 1987. : Operating systems, McGraw-Hill, 1986. : Operating Systems Concepts. : Operating System Principles, Prentice-Hall of India, 1986. : Systems Programming, McGraw-Hill, 1987. : Operating System Concept and Design. : Unix System Programming in C++ 13 CSE 303: Database Management Systems Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Overview: Definition of DBMS, types of DBMS, advantage & disadvantages of DBMS, applications. Entity relationship model, Relational model, Relational query language, Structure Query Language (SQL), Relational database design, Object Relational database design, Storage and file structure, Query process, Concurrency control, Recovery system, Database system architecture, Distributed database. Oracle: Introduction to SQL Plus, PL /SQL, Triggers, Forms, Reports, Query, Procedures, and Project builder. Case study: MS SQL server, MySQL server. Books Recommended 1. A. Silberschatz 2. James Martin 3. Uillman 4. Abey : Database System Concepts. : Principles of Data_Base Management. : Database Management systems. : Oracle 8i a Beginners Guide CSE 304: Computer Networks Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction: Introduction to Computer Networks, Network Goals and Applications, Network Architectures, OSI reference model, TCP/IP model and terminology, Connectionless and Connection Oriented services, Network Topologies, Service primitives, Public Networks, The ARPANET, SNA. Physical Layer: Circuit switching and Packet switching, X-25 protocol, ISDN, BISDN, Frame relay and Cell relay. Medium Access Sublayer: Static and Dynamic channel allocation in LAN and MAN, LAN Cables, Pure and slotted ALOHA, Persistent and Non persistent CSMA, CSMA with collision detection and collision free protocols, IEEE standard 802.3 and Ethernet, Token Bus and Token Ring, FDDI, Fibernet II, DATAKIT. Data Link Layer: Service provided to the network layer, Framing, Flow control, Error detecting and Correcting Codes, Stop-and-Wait protocol, Sliding Window protocol, Go Back n protocol, Selective Repeat protocol, Performance of Stop-and Wait and Sliding Window protocol, Data Link layer in Public network and ARPANET. Network Layer: Service provided to the Transport layer, Internal organization of Network layer, Routing algorithms, Internetworking, Router, Bridge, Gateway, Network layer in Public network and ARPANET. Transport Layer: Services provided to the Session layer, Quality of service, Transmission Controls protocols, Connection management, Addressing, Establishing and Releasing Connection, Flow control and Buffering, Multiplexing, Transport layer in Public network and ARPANET. Session Layer: Services provided to the Presentation layer, Data exchange, Synchronization, Dialog and Activity management, OSI session service primitives. Presentation Layer: Data Compression techniques, Frequency Dependent Coding, Context Dependent Encoding, Cryptography, Traditional Cryptography, Data Encryption Standard, Public key cryptography, MIT algorithm. Application Layer: File transfer Access and management, Electronic Mail, Virtual Terminal, Client Server, Other applications, OSI service elements. Internet: Introduction to internet and intranets, internet protocols, Internet services and goals, Domain Name System (DNS) and Addresses, FTP, Gopher and Telnet, World Wide Web (WWW), Internet Relay Chat (IRC), USENET, DHCP and BOOTP. 14 Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A.S. Tanenbaum G. H. Cady, Pat McGregor Barry Nance W. Stallings, Macmillan F. Halsall, Addison wesley Sydni Feit : : : : : : Computer Networks Mastering The Internet Introduction to Networking Data and Computer Communications Data Communications, Computer Networks and Open Systems TCP/IP CSE 305: Automata Theory and Compiler Design Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction to compiler, compiler and translator, The structure of a compiler. Notation and concepts for languages and Grammars, sets and string, Discussion and classification of Grammars, Scanner regular expression, regular definition, finite autometa, LL and LR Grammars, ambiguous grammar. Basic parsing technique, parsers, shift reduce parsing, operator-precedure parsing, top-down parsing, bottom up parsing, predictive parsing. Syntax directed translation, intermediate code generation, polish notation, parse tree and syntax trees, quadruples, triples, boolean expression. Perspective and motivation of symbol table. Symbol table content, operation on symbol table, organization of symbol table. Code optimization, sources of optimization, basic blocks, folding, loop optimization, flowgraph, induction variable elemination, reduction in strength, code motion. Compile time error handling, error detection, error recovery, error repair. Code generation, object programs, problems in code generation, a machine model, a simple code generator, register allocation and assignment peephole optimization. Books Recommended 1. A.J. Holub 2. Trembly and Sorensen 3. Aho and D. Ullman 4. Hopcroft and Ulman 5. Adamek : Compiler design in C, Prentice-Hall of India, 1993. : Theory and Practices of Compiler Writing : Compiler Design. : Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages and Computation : Automata and Algebra CSE 306: System Analysis and Design Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction to information systems, general design consideration of information systems. Overview: system concepts and the information systems environment, information needs, the concepts of MIS, the system development life cycle, the role of the systems analysis. Systems Analysis: Systems planning and the initial investigation, information gathering, the tools of structured analysis, feasibility study, cost benefit analysis. Systems Design: The process and stages of systems design, input/output and forms design, file organization and data base design. System Implementation: system testing and quality assurance, implementation and software maintenance, hardware/software selection, project scheduling and software, Security, disaster/recovery, and ethics in system development. Case studies of various information systems such as: Library management system, inventory system, voter identity management system, payroll system, etc. 15 Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. : : : 4. E.M. Awad P. Rdwards J.G. Burch Jr., F.R. Strater and G. Grundnitski G. Scott. 5. A. Daniels and D. Yeates : : System analysis and Design Galgotia Publication Ltd, 1994. System Analysis & Design, McGraw-Hill, 1993. Information systems: Theory and Practice, 5 th Ed., John Wiley & Sons. Principles of Management Information Systems, McGraw-Hill, 1986. Basic system analysis, Galgottia, 1990. CSE 307: Artificial Intelligence and Neural Computing Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Problems and Search: Overview of AI; AI techniques; Underlying Assumption; Problems, Problem spaces and Search, Different Heuristic Search techniques. Knowledge representation: Knowledge Representation Issues, Knowledge Representation using Predicate logic, Knowledge Representation using Rules, Symbolic Reasoning under Uncertainties, probabilistic reasoning, structured knowledge, object oriented representation. Knowledge representation using semantic nets, conceptual graph, frames etc. Introduction to selected topics in AI: Game Playing, Planning, Understanding, Natural language processing, Expert system, Genetic algorithm, robotics and Fuzzy logic. Neural Networks: Basic concept and structure of neural networks, Learning rules, Back propagation rule, Hopfield network, neural network as an object classifier. An Overview on Artificial Intelligence Programming Languages: Prolog, Visual Prolog, LISP etc. Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dan W. Patterson E. Rich and K. Knight H. Schildt C.F. Chabris and T. Jackson Books on Prolog, Lisp etc. : : : : Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems. Artificial Intelligence, Tata-McGraw-Hill Publication Co. Ltd, 1992. Artificial Intelligence Using C, Osborne-Mc-Graw-Hill, 1987. An Introduction to Neural Computing, Adam Hilger Pub, 1990. CSE 308: Computer Graphics and Multimedia System Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction: A survey of Computer Graphics, Overview on basic components of Computer Graphics, Graphics Input devices, Architecture of Graphics display devices, Video memory. Fundamental Graphics Algorithms: Scan Conversion of Points and Lines, Line drawing algorithm, DDA algorithm, Bresenham’s Line algorithm, Bresenham’s circle drawing algorithm, Loading the frame buffer, circle generating algorithm, Midpoint circle algorithm, Ellipse generating algorithm, Midpoint Ellipse algorithm, pixel addressing, Region Filling algorithms. Clipping Operations: Point clipping, line clipping, polygons clipping, curve clipping, text clipping Implementation of Computer Graphics: Co-ordinates Transformations, Two and Three dimensional Transformation, Viewing and Clipping, Projections, 3D object representations, Curves and Surface Design, Elimination of Hidden surfaces, Z-buffer algorithm, Painters algorithm, scan-line algorithm, Vector mathematics method, Raster graphics systems, Image synthesis methods, Ray tracing, Shadow mapping, color and shading models. Multimedia systems – introduction; Coding and compression standards; Architecture issues in multimedia; Operating systems issues in multimedia – real-time OS issues, synchronization, interrupt handling; Database issues in multimedia – indexing and storing multimedia data, disk placement, disk scheduling, searching for a multimedia document; Networking issues in multimedia – Quality-of-service guarantees, resource reservation, 16 traffic specification, haping and monitoring, admission control; Multicasting issues; Session directories; Protocols for controlling sessions; Security issues in multimedia – digital water-marking, partial encryption schemes for video streams; Multimedia applications – audio and video conferencing, video on demand, voice over IP. Books Recommended 1. Steven Haringtron 2. Hearn and Baker 3. F. S. Hill 4. Plastock and Kalley 5. Zhigang Xiang & Roy Plastock 6. John Villamil-Casanova, Louis Molina 7. John Villamil-Casanova, Leony Fernandez-Elias 8. John Villamil-Casanova, Louis Molina : Computer Graphics a Programming Approach, Second Edition, 1987. : Computer Graphics. : Fundamentals of Computer Graphics. : Computer Graphics. : Computer Graphics. : Multimedia. An Introduction : Multimedia. Graphics : Multimedia Sound & Video 17 B.Sc. (Hons) Part-IV CSE 401 : Software Engineering Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 The product, the process, managing software projects, project management concepts, software myths, software process models. Software process and project metrics. size-oriented metrics and function oriented metrics. Software project estimation. Risk management, software risk vs problem. Risk assessment RMMM. Scheduling, Degree of rigor. Software quality assurance, cost of quality. Formal technical reviews. Statistical quality assurance. Analysis modeling, requirement analysis, FAST. Data modeling, DFD, Behavioral modeling, Data dictionary. Software architecture. Design concepts and principle. Design methods. Software testing, write-box testing, black-box testing, basic-path testing, control-structure testing, alpha-testing, beta-testing. Object oriented concepts, operation, methods, and services, messages encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, OOP metrics and estimation, object-oriented analysis, OO design and testing. Formal method. CASE STUDY: Rational rose, Visual modeler (UML) etc. Books Recommended 1. Roger S. Pressman 2. Richard Fairley 3. Robert N. Charette 4. Wrox Publisher 5. Wrox Publisher : Software Engineering, A practitioner's Approach, Second Edition : Software Engineering Concepts. : Software Engineering Environments : UML in a Nutshell : Instant UML CSE 402: Parallel Processing and Distributed System Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Introduction: Trends towards Parallel processing, Parallel processing mechanism, Multiprogramming and Time sharing, Parallel Computer Structures, Parallelism and Pipelining, Parallel processing applications, Speedup Performance Laws, Parallel Random Access Machines (PRAM) and VLSI model. Hardware Technology: Advanced processor Technology, Superscalar and Vector processor, Shared memory organization, Design of Linear and Non linear Pipeline processor, Multiprocessor System Interconnects. Pipelining and Vector Processing: Principles of Pipelining, Classification of pipelined processors, Instruction and Arithmetic pipeline design, Vector Processing principles, Vector processing requirements, Designing Pipelined processors, Compound Vector processing, Recent Vector processors, Vectorization and Optimization methods. Parallel Programming: Parallel Programming models, Parallel Languages and Compilers, Code Optimization and Scheduling, Loop Parallelization and Pipelining, Parallel Programming Environments, Shared-variable program structures, mapping programs onto Multicomputers. Distributed Processing: Introduction, Function distribution, Hierarchical and Horizontal distributed system, Strategies for distributed data processing, Data distribution, Conflict analysis, Distributed Database and applications. Transaction and distributed transaction, concurrency control, security in distributed system. Books Recommended 1. Kai Hwang (Senior Consulting Edition) : 2. 3. 4. Kai Hwang, Faye A. Briggs R. J. Cypser James Martin : : : Advanced Computer Architecture Parallelism, Scalability, Programmability Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Communication Architecture for distributed system Design and Strategy for distributed data processing 18 CSE 403: Digital Signal and Image Processing Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Digital Signal Processing: Digital signal processing model, Discrete time signal and system, Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT),; Separability, Convolution and Correlation properties of DFT, Convolution theorem, Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), Z-Transform, Sampling theorem, Different types of window, Digital Filter design. Fundamentals of Image processing: Digital Image representation, Elements of image processing system, Problems and Applications of image processing, Mathematical model of image, Image sampling and quantization, two dimensional image transformation, Binary and Gray level images, Photographic film. Image enhancement: Enhancement in spatial and frequency domains, some simple Intensity transformations, Histogram equalization, Histogram specification, Image subtraction, Image average, Filtering in frequency domain. Image Analysis: Image compression- fundamentals and models, Image segmentation- edge detection, thresholding and region oriented segmentation, Morphological image processing. Image processing on remote sensing data. Books Recommended 1. Defatta 2. Rafeal C. Gonzalez & Richard E. Woods 3. Gordon E. Carlson : Digital Signal Processing : Digital Image Processing. : Signal and Linear System Analysis CSE 404: Cryptography and Network Security Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Overview, Terminology, Substitution and Transposition ciphers, One time pads, Symmetric Ciphers, classical Encryption Technique, Block Ciphers and the Data Encryption Standard, Introduction to Finite Fields, Advanced Encryption Standard, Contemporary, Symmetric Ciphers Confidentiality Using Symmetric Encryption Public, Key Encryption, One way functions and Hash Functions, Introduction to Number Theory, Prime number generation, Public-Key Cryptography and RSA, Key Management, Key exchange algorithm; Other Public-key Cryptosystems, Message Authentication and Hash Functions, Hash Algorithms, MD5, SHA, Digital Signatures and Authentication Protocols, DSA, Kerberos, Network Security Practice, Authentication Digital certificates and Public key infrastructure, X.500, Application Electronic Mail Security, IP Security, Web Security, System Security, Intruders, Malicious Software, Firewalls. Books Recommended 1. 2. Bruce Schneier Dieter Gollmann : : 3. Edward Amoroso : 4. Stallings W. : 5. E.Biham and A. Shamir : 6. 7. D.Denning N.Kobliz : : Applied Cryptography, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Computer Security; ISBN: 0-471-97844-2; Edition: 1999; Publisher: John Wiley and Son Ltd. Fundamentals of Computer Security Technology; ISBN: 0-13-108929-3; Publisher: Prentice Hall. Cryptography and Network Security Principles and Practice, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1999. Diffential Crypt analysis of the data encryption standard, Springer Verlag, 1993. Cryptography and data security, Addison Wesley, 1982. A course on Number theory and Cryptography, Springer Verlag, 1994. CSE 405: VLSI Design Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 VLSI design methodology: top-down design approach, technology trends, introduction to MOS technology, operation of MOS transistor as a switch and amplifier, MOS, NMOS, CMOS inverters, pass transistor and pass gates: DC and transient characteristics. Brief overview of fabrication process: NMOS, CMOS, Bi-CMOS process. NMOS and CMOS layout, stick diagram, and design rules. CMOS circuit characteristics and performance estimation: resistance and capacitance, rise and fall time, power estimation. Buffer circuit design. Introduction to Bi-CMOS circuits. Shifter, adder, counter, multipliers. Data Path and memory structures. Design style: FPGA and PLDs. 19 Introduction to HDL: basic digital design using VHDL. Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. Basic VLSI design: System & Circuit R. K. Brayton et al. F. Lombardi C. A. Mead and L. A. Conway : K. Eshraghian & D. A. Pucknell - Prentice Hall : : : Logic Minimization Algorithems for VLSI Synthesis. Testing and diagnosable Design of VLSI and ULSI. Introduction to VLSI Systems. CSE 406: Computer Simulation and Modelling Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 Simulation methods: Introduction to Simulation, Random number generator, analogue simulation of continuous system, Discrete system simulation, Simulation of a pert network, Statistical analysis of result, Validation and verification techniques, Application of simulation to problems e.g. business, operation research, operating system, Computer design, Introduction to simulation packages, Computer animation. Modelling :- Introduction to modelling techniques, Problems, models and systems, Modelling concepts, Logic for (conceptual) modelling, Logic programming for conceptual modelling, Concepts of relational modelling and its practice. Some practical modelling e.g. Relational Database modelling, Different methods for Curves and surface modelling, Fractals, Polyhedral modelling with Euler’s formula, Advanced modelling, Procedural models. Case Study: Simulation and Modeling software: SimScript. Books Recommended 1. J. A. Spriet 2. R. S. Lehman 3. G. Cordon 4. James D. Foley Andries van Dam : Computer Aided Modeling & Simulation. : Computer Simulation and Modeling. : System Simulation. : Computer Graphics. CSE 407: E-Commerce Lecture: 60, Unit: 1, Marks: 75, Credit: 4 E-Commerce Basics: E-Commerce Definition, Internet History and E-Commerce Development, Business-toBusiness E-Commerce, Business-to-Consumer E-Commerce, E-Commerce Stages and Processes, E-Commerce Challenges, E-Commerce Opportunities . E-Commerce Options: Internet Access Requirements, Web Hosting Requirements, Entry-Level Options, Storefront and Template Services, E-Commerce Software Packages, E-Commerce Developers, E-Business Solutions. Marketing Issues: Online and Offline Market Research, Data Collection, Domain Names, Advertising Options, E-Mail Marketing, Search Engines, Web Site Monitoring, Incentives. Planning and Development: Web Site Goals, International Issues, Planning Stages, Resource Allocation, Content Development, Site Map Development, Web Site Design Principles, Web Site Design Tools, Web Page Programming Tools, Data-Processing Tools. E-Commerce Components: Navigation Aids, Web Site Search Tools, Databases, Forms, Shopping Carts, Checkout Procedures, Shipping Options. . Payment Processing: Electronic Payment Issues, E-Cash, Credit Card Issues, Merchant Accounts, Online Payment Services, Transaction Processing, Taxation Issues, Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce). Security Issues: Security Issues and Threats, Security Procedures, Encryption, Digital Certificates, SSL and SET Technologies, Authentication and Identification, Security Providers, Privacy Policies, Legal Issues. Customer Service: Customer Service Issues, E-Mail Support , Telephone Support , Live Help Services, Customer Discussion Forums, Value-Added Options. 20 Books Recommended 1. Jeffrey F., Rayport, Bernard J. Jaworsk 2. David Kosiur 3. Jeffrey F. Rayport, et al. 4. Debra Cameron 5. Charles Trepper 6. SAMS Publisher : E-Commerce, Mc Graw-Hill, ISBN-0072465212, 1st Edition. : Understanding Electronic Commerce, Microsoft Press. : Introduction to E-Commerce, Mc Graw-Hill, 1st Edition Aug13,2001. : E-Commerce Security Strategies: Protection the Enterprise,, Computer Technology Research Corp. Aug-1998. : E-Commerce Strategies : Web programming A desktop Reference 21