Diversity, Culture & Leadership: Exhibits & Comparisons
advertisement
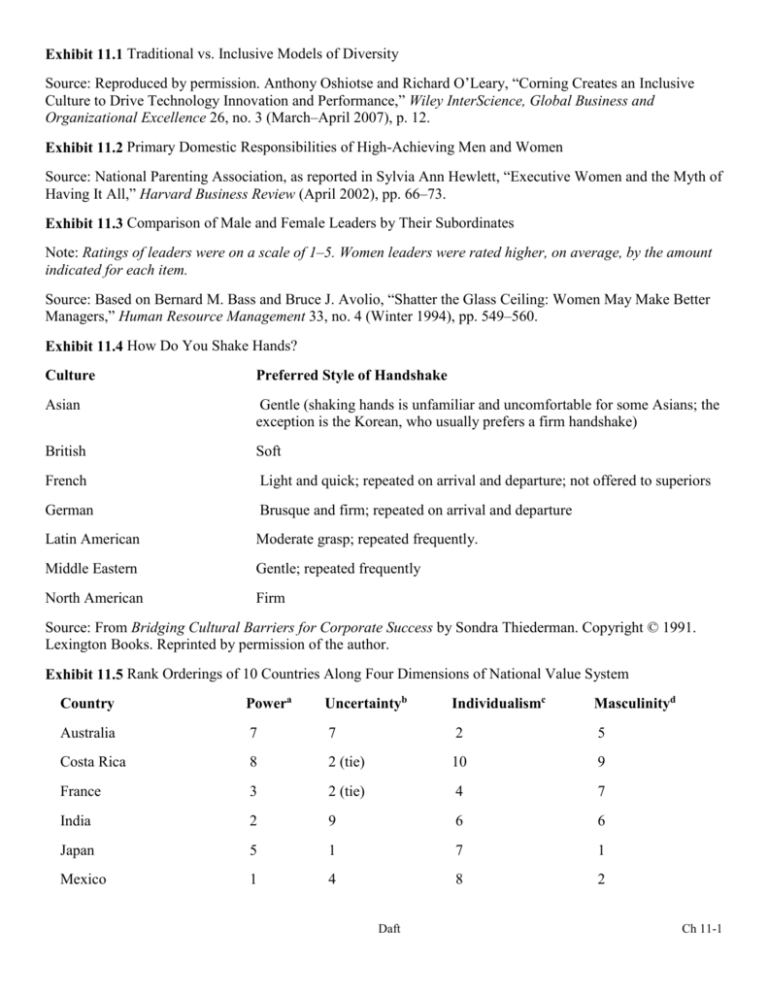
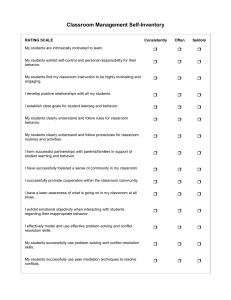
Exhibit 11.1 Traditional vs. Inclusive Models of Diversity Source: Reproduced by permission. Anthony Oshiotse and Richard O’Leary, “Corning Creates an Inclusive Culture to Drive Technology Innovation and Performance,” Wiley InterScience, Global Business and Organizational Excellence 26, no. 3 (March–April 2007), p. 12. Exhibit 11.2 Primary Domestic Responsibilities of High-Achieving Men and Women Source: National Parenting Association, as reported in Sylvia Ann Hewlett, “Executive Women and the Myth of Having It All,” Harvard Business Review (April 2002), pp. 66–73. Exhibit 11.3 Comparison of Male and Female Leaders by Their Subordinates Note: Ratings of leaders were on a scale of 1–5. Women leaders were rated higher, on average, by the amount indicated for each item. Source: Based on Bernard M. Bass and Bruce J. Avolio, “Shatter the Glass Ceiling: Women May Make Better Managers,” Human Resource Management 33, no. 4 (Winter 1994), pp. 549–560. Exhibit 11.4 How Do You Shake Hands? Culture Preferred Style of Handshake Asian Gentle (shaking hands is unfamiliar and uncomfortable for some Asians; the exception is the Korean, who usually prefers a firm handshake) British Soft French Light and quick; repeated on arrival and departure; not offered to superiors German Brusque and firm; repeated on arrival and departure Latin American Moderate grasp; repeated frequently. Middle Eastern Gentle; repeated frequently North American Firm Source: From Bridging Cultural Barriers for Corporate Success by Sondra Thiederman. Copyright © 1991. Lexington Books. Reprinted by permission of the author. Exhibit 11.5 Rank Orderings of 10 Countries Along Four Dimensions of National Value System Country Powera Uncertaintyb Individualismc Masculinityd Australia 7 7 2 5 Costa Rica 8 2 (tie) 10 9 France 3 2 (tie) 4 7 India 2 9 6 6 Japan 5 1 7 1 Mexico 1 4 8 2 Daft Ch 11-1 Sweden 10 10 3 10 Thailand 4 6 9 8 United States 6 8 1 4 a 1 = highest power distance; 10 = lowest power distance b c 1 = highest uncertainty avoidance; 10 = lowest uncertainty avoidance 1 = highest individualism; 10 = highest collectivism d 1 = highest masculinity; 10 = highest femininity Source: From Dorothy Marcic, Organizational Behavior and Cases, 4th ed. (St. Paul, MN: West, 1995). Based on Geert Hofstede, Culture’s Consequences (London: Sage Publications, 1984); and Cultures and Organizations: Software of the Mind (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1991). Exhibit 11.6 Stages of Personal Diversity Awareness Source: Based on M. Bennett, “A Developmental Approach to Training for Intercultural Sensitivity,” International Journal of Intercultural Relations 10 (1986), pp. 179–196. Ch 11-2 Daft