Meiosis
advertisement

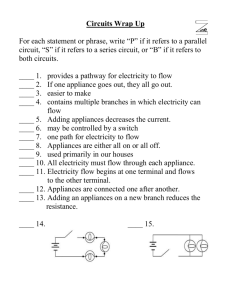
IS9 Unit 6: Electricity & Magnetism During this unit the outlines will be handed out each period and turned in the next period. Outlines will not always have a screencast. Reading – Ch. 14 (pg. 418-440) Ch. 15 (pg. 448-465) Date Homework Assigned 2-5 Outline Part I (Day 1 review: Charge W Interactions) 2-7 F 2-11 T Outline Part II (Day 2 review) 2-13 Th Outline Part IV (Day 4 review) 2-19 W Outline Part V (Day 5 review) 2-21 F 2-25 T No Homework 2-27 Th 3-3 M Outline Part VII (Day 8 review) Outline Part III (Day 3 review) Outline Part VI (Day 7 review) Outline Part VIII (Day 9 review) In-Class Parts of an atom review, Charge and force activities, Making an Electroscope, Electrostatic Charge Lab Quiz #1 on Part I, Static Electricity, Van de Graaff generator, Electric Discharge, Quiz #2 on Part II, The Flow of Electricity, What is a battery?, Comparing: voltage, current and resistance Quiz #3 on Part III, The math behind electricity: Ohm’s Law (amps, volts and ohms) Quiz #4 on Part IV, Light the bulb, Current Direction: AC vs. DC, What makes a good insulator? Electric Circuits-Series and Parallel, Household Circuits, Circuits and Safety A Crude Awakening Video with Guide Quiz #5 on Part V, Electric Power-Watt is it all about?, The apple battery, Electricity-It’s in your DNA! Quiz #6, Electricity and Magnetism, Make a DC Motor Generating Electricity: from nuclear to biomass, Energy Transformations, Transformers: more than meets the eye! Hydropower Lab 3-5 Complete hydropower lab W 3-7 Complete Study Guide Review for test! F 3-11 Relax Test T Vocabulary – Charge (positive/negative) Resistance Van de Graaff Static electricity Series circuit Transformer Atom Parallel circuit Grounding Proton Magnetism Conductor Neutron Charge by Induction Insulator Electron Charge by Friction Electric Fields Current Charge by Conduction Transistor Voltage Multimeter & Voltmeter Semiconductor Ohm’s law Fuses Electromagnet Amps (ampere) Resistor Learning Targets: A. Electric Charge 1. Name the three principles subatomic particles (protons, neutrons and electrons) 2. Describe the nature of unlike charges and like charges 3. Define and electric field B. Static Electricity 1. Define and explain static electricity 2. Compare friction, conduction and induction 3. Explain the differences between insulators and conductors 4. Explain what causes lightening 5. Describe the structure and use the electroscope C. The Flow of Electricity 1. Define electric current and state the units in which it is measured 2. Describe the structure and uses of dry cells and wet cell batteries 3. Define voltage, state the in which it is expressed and name the device used to measure it 4. Define resistance and state the unit in which it is measured 5. State and apply Ohm’s law 6. Contrast direct current and alternating current D. Electric Circuits 1. Define electric circuit 2. State the parts of a circuit and their functions 3. Compare series and parallel circuits 4. Explain the use and operation of fuses and circuit breakers E. Electric Power 1. Define electric power. Be able to state and apply the formula as it relates to voltage and current. 2. State the units of power and electric energy 3. Calculate electric energy, given power and time 4. State six important safety rules relating to electricity