Ch16.1 worksheet-Solved
advertisement

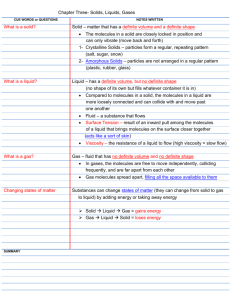
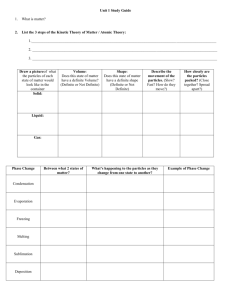
Q1) Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Matter that has a definite volume and a definite shape is a ____. a. Gas c. plasma b. Liquid d. solid 2. Matter in which atoms are tightly held in place is a ____. a. Gas c. plasma b. Liquid d. solid 3. A gas-like mixture with no definite volume or shape that is made up of positively and negatively charged particles is a ____. a. Gas c. plasma b. Liquid d. solid 4. Matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape is a ____. a. Gas c. plasma b. Liquid d. solid 5. Matter in which the particles are free to move in all directions until they have spread evenly throughout their container is a ____. a. Gas c. plasma b. liquid d. solid 6. Most matter ____ when heated. a. condenses c. expands b. contracts d. solidifies 7. The amount of energy needed to change a material from a solid to a liquid is called the heat of ____. a. Condensation c. fusion b. Evaporation d. vaporization Page 1 of 6 8. The amount of energy needed to change a material from a liquid to a gas is called the heat of ____. 9. a. Condensation c. fusion b. Evaporation d. vaporization Matter in which particles are arranged in repeating geometric patterns is a ______. a. Solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 10. Matter with no definite volume and no definite shape is a ______. a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 13. Matter in which the particles are free to move in all directions until they have spread evenly throughout their container is a ______. a. solid b. liquid c. buoyant d. gas 14. As a sample of matter is heated, its particles ______. a. stop moving c. move more quickly b. move more slowly d. are unaffected 15. The most common state of matter in the universe is ______. a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 16. The particles that make up a solid move ______ than do the particles that make up a gas. a. more slowly c. in the same way b. more quickly d. more quickly and farther 17. The attraction between particles gives solids a definite ______. a. shape and volume c. shape and position b. shape and color d. flow and radius 18. ______ is the term used to explain how hot or cold an object is. a. Mass b. Weight c. Temperature d. Volume 19. Ice is an example of matter in the ______ state. a. solid Page 2 of 6 b. liquid c. gaseous d. plasma 20. The temperature at which a solid begins to liquefy is its ______ point. a. freezing b. boiling c. melting d. mass 21. The kinetic energy of particles in a liquid is ______ the kinetic energy of particles in a solid. a. more than b. less than c. the same as d. none of these Q2) Use the terms definite, not definite, close together, and spread apart to complete the table below. State Gas Shape Indefinite Volume Indefinite Particles movement Far apart and free to move Liquid Indefinite Definite Tightly packed but far apart enough so they slide over another Solid Definite Definite Tightly packed and vibrating very slowly Plasma Indefinite Indefinite Far apart and free to move Q3) Use the labels heat of vaporization, heat of fusion, stronger, and broken to complete the concept map about energy and changes the state. a- heat fusion Page 3 of 6 b- stronger c- heat of vaporization d- broken Q4) Where you might find plasma? SUN, Lightning, Aurora, Neon tube Q5) Explain why do gases fill the container they are in, rather than staying in just one part of it? …Gases have enough Kinetic energy and they are far apart and can move freely. So gases do not have fixed volume or shape, Q6) why should you never leave spray cans near a heat source? …because spray is a gas under pressure, and with heat it will gain kinetic energy and temperature will increase then will explode Q7) What are the three assumptions of the kinetic theory? 1- All matters are composed of small particles…………… 2- Particles are random and constant motion 3- these particles are colliding with each other and with wall in Elastic collision Q8) Define thermal energy? total energy of a material’s particles, -including kinetic and potential—resulting from forces that act within or between particles. Q9) How are kinetic energy and temperature related? 1-Temperature is the average kinetic energy of particles in matter. 2- When kinetic energy increases the temperature increase Page 4 of 6 Q10) Using the below graph, describe the energy changes that are occurring when water goes from -20°C to 100°C. Temperature increases as Heat added, At 0 Co, the ice is melting and the temperature keeps constant till all the ice melts Then the temperature increases again till it reaches 100 0 Co the boiling point of water, then the temperature will keep constant Page 5 of 6 Q11) Compare between melting point and boiling point? Melting point Temperature at which a solid begins to liquefy Boiling point Temperature at which the pressure of the vapor in the liquid is equal to the external pressure Q12) Distinguish between heat fusion and heat of vaporization? Heat Fusion Heat Vaporization The amount of energy required to Amount of energy required for the change a substance from the solid liquid at its boiling point to become a phase to the liquid phase at its melting gas. point Q13) Compare between evaporation and boiling. Evaporation Boiling 1- Happens at the surface 1- Happens throughout the liquid 2- Happens at any temperature above 2- Happens at specific Temperature melting point Q14) Explain why diffusion in gases is faster than in liquids/ solids Because they move fast and they are far apart Q15) Explain why amorphous solids melts over a temperature range ……because there is no specific geometric arrangement ( no ordered structure) Q16) List some examples of amorphous solids. ……Plastic, wax, Glass and volcanic glass ( obsidian) Page 6 of 6