Anatomy & Physiology
advertisement

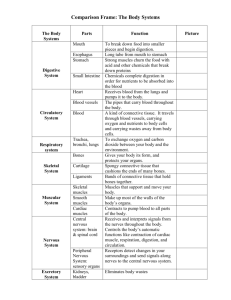
Anatomy & Physiology FINAL EXAM REVIEW KEY SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Describe the 2 portions of the skeleton? The axial skeleton consists of the bony and cartilaginous parts that support and protect the organs of the head, neck and trunk. These include: skull, hyoid bone, vertebral column, thoracic cage (ribs and sternum). The appendicular skeleton consists of the upper and lower limbs and the bones that anchor them to the axial skeleton. These include: pectoral girdle (scapula & clavicle), upper limbs, pelvic girdle, lower limbs. 2. List the functions of the skeletal system: Protection, movement, storage, blood cell production, support 3. What is the difference between the skeletal system of an adult and baby? Babies: more bones, more cartilage because ossification has not occurred yet in all. 4. What is the difference between a complete fracture and an open fracture? (Kids Complete – fully broken Open – bone sticks through skin 5. Describe a “greenstick” fracture. Who is more likely to get this—adult or child—and why? Bone is bent, not completely broken through. Children’s bones are more flexible, so they are more likely to get this than an adult. 6. List the pairs of ribs and how many of each (cephalic to caudal). 12 pairs – 7 true, 3 false attached, 2 floating 7. List the bones in your arm from shoulder to finger tips. Humerus, ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges 8. List the bones in your leg from proximal to distal. Femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges 9. How are muscles connected to bones? How are bones connected to each other? Tendons connect muscles to bones; ligaments connect bones to bones 10. Name the types of joints with an example of each. Ball and socket – hip Condyle – between phalanges and metacarpals Plane/gliding – wrist Hinge – elbow Pivot – between radius and ulna Saddle – between carpal and metacarpal of thumb AMUSCLE SYSTEM Use the key below to answer the following questions. Letters may be used more than once and answers may have more than one! a. cardiac muscles b. skeletal muscles c. smooth muscles ___AB__ 1. These have striations. ___C__ 2. These are found in the viscera. ___A__ 3. These are found in the heart. ___AC__ 4. These are involuntary. ___B__ 5. These are voluntary. ___B__ 6. These are attached to the bone. ___B_ 7. These provide movement, transportation, and posture. Match Column A with Column B. A B __A__ 8. Extension __C___ 9. Flexion a. Increase an angle b. Immoveable end of muscle __B___ 10. Origin c. Decrease an angle __D___ 11. Insertion d. Movable end of muscle 12. Explain what is meant by “muscle insertion” and “muscle origin.” Origin – immovable end of muscle Insertion – movable end of muscle 13. List the major functions of muscle tissue: Skeletal: contract to pull bones or other muscles; attached to bones or other muscles Smooth: move substances through cardiovascular system and digestive system; line blood vessels and digestive tract Cardiac: pump blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulatory loops; make up the heart 14. The mechanical force of contraction (shortening) is generated by ___. a. shortening of the thick filaments b. shortening of the thin filaments c. the sliding of thin filaments past thick ones d. the “accordion-like” folding of thick and thin filaments 15. The sites where the motor nerve impulse is transmitted from the nerve endings to the skeletal muscle cell membranes are the ___. a. neuromuscular junctions b. sarcomeres c. myofilaments d. Z lines NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. List the three major functions of the nervous system. Sensory input, integration, motor output 2. Explain both the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system. Include in your explanation the subdivisions of each. CNS – brain and spinal cord PNS – cranial nerves and spinal nerves (everything outside of CNS) PNS is further broken down into somatic and autonomic systems Autonomic is further broken down into sympathetic and parasympathetic 3. Label the neuron and describe nerve impulse transmission either on the diagram or below: Use the key below to answer the following questions. Letters may be used more than once and more than one letter may be used at one time. 4. a. integration b. sensory input c. motor output 5. ___B__ This is the first step in information processing of the central nervous system. 6. ___ABC__ This is a step of information processing within the CNS. 7. ___C__ This causes muscles or glands to respond to a received stimulus. 8. ___B__ This involves the PNS receiving stimuli. 9. ___B__ This generally involves unipolar and bipolar neurons. 10. Describe what happens at a synapse: neurotransmitters released from axon terminal; move across synaptic gap; attach to receptor protein on effector cell ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: 1. What does the endocrine system regulate? The body's growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function 2. Name the endocrine glands. Pituitary, pineal, hypothalamus, parathyroid, thyroid, adrenals, thymus, ovaries, testes, pancreas 3. What is the function of hormones? Growth & development, metabolism, sexual function, reproduction & mood 4. What is homeostasis? Maintenance of the internal environment 5. How is homeostasis regulated within the body? Negative feedback 6. How does endocrine system communication differ from nervous system communication in the body? Nervous system – rapid electrochemical transmission Endocrine system – specific cell receptors for chemical (hormone) transmission 7. What is stress? A normal physical response to events that make you feel threatened or upset your balance in some way 8. What is the “stress response” also known as? Fight or flight reaction 9. Name 4 body responses to stress. Stress hormones are released: adrenaline & cortisol; heart pounds faster; blood pressure rises; breath quickens; senses become sharper; reaction time is faster; speed & stamina increas 10.What is the “master gland?” Pituitary gland DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is “peristalsis?” Involuntary contraction of smooth muscles lining digestive tract to move substances through from esophagus to anus 2. You eat a pizza with mozzarella cheese, tomatoes, and fresh basil. Describe how and each location as this is digested and absorbed—explaining both mechanical and chemical digestion. Mouth: mechanical (chewing/mastication to increase surface area) and chemical (saliva – water and amylase to breakdown carbs and macromolecule bonds) Esophagus: movement to stomach Stomach: mechanical and chemical (HCl and pepsin) to breakdown proteins Duodenum (beginning of small intestine): receives bile from gall bladder (produced in liver) and pancreatic enzymes for breakdown of fat (bile), proteins and nucleic acids (pancreatic enzymes) Small intestine: further digestion and absorption of nutrients via villi/microvilli to bloodstream Large intestine: compaction of wastes; absorption of water and minerals, production of vitamin K REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. How long is the average female cycle and when does ovulation occur (on average)? 28 days; 14th day 2. Where does fertilization occur? Fallopian tube 3. What is spermatogenesis? At what age do males produce gametes? Production of sperm, adding flagellum Puberty till death 4. What are the female gonads? What are the male gonads? Female: ovaries Male: testes 5. At what age does menarche occur? Menopause? When do eggs form? When do they mature? Around age 12; around 48-52 years old Eggs form before birth; one matures every month from puberty until menopause 6. Define the term ‘contraception’ and give three examples. Contraception: PREVENTING fertilization 1. Abstinence 2. Mechanical barriers – male or female condom, diaphragm, cervical cap or sponge 3. Chemical barriers – nonoxynol 9 spermacide (liquid, gel, foam) 7. What is the best way to avoid an STD (sexually transmitted disease)? What is the second best way? BEST: abstinence 2nd best: spermacide