European History Unit 7 Questions
advertisement

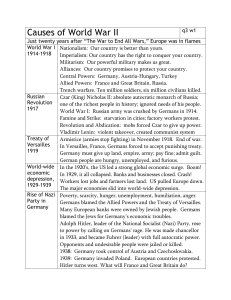
European History Unit 7: World War I Questions Part 1, Pg. 769-773 1. Why did the goals of the Serbians create tensions in the Balkan Peninsula? 2. Who assassinated Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand and what was his background? 3. How did the Austrian government want to make use of the assassination? Why did the Austrians seek the support of the Germans? 4. What was the “blank check?” 5. What actions did the Austrians take between July 23-28,1914? 6. Why did Czar Nicholas order the partial mobilization of the Russian army? Why did he change the order to full mobilization? 7. How did the Germans react to the mobilization of the Russian army? 8. Explain the Schlieffen Plan. 9. What brought Belgium, France and Great Britain into the war? Part 2 Pg. 773-783 1. What caused the German’s Schlieffen Plan to fail? What happened soon after the Battle of the Marne? 2. What happened to the Russian invasion of Germany? 3. What happened to Austria in 1914 and 1915? What successes did the Germans and Austrians enjoy later in 1915? 4. How did the military leaders try to win the war in the west in 1916-1917? Why did the offensives always fail? 5. How did the British and the Germans make use of their navies after World War I began? Why did the Germans resort to unrestricted submarine warfare in 1917? 6. What resulted from Germany’s policy of unrestricted submarine warfare? What setbacks did the Allies suffer in 1917? 7. How did new innovations in technology change the way war was fought during WWI? 8. How was WWI a total war? 9. Why was it necessary for governments to expand their powers during WWI? 10. What did Woodrow Wilson mean when he said that the men and women “who remain to till the soil and man the factories are no less a part of the army than the men beneath the battle flags.”? Part 3 Pg. 783-788 1. How was Germany’s mobilization for total war different than most other countries? Why? 2. What were the special challenges that France faced in organizing a total war economy? 3. What were the major sources of internal opposition to the war during 1916 and 1917 and what did activists hope for. 4. Why did governments turn to more authoritarian measures and expand their police powers as public opposition to the war increased? 5. What other methods did governments use to change morale and arouse enthusiasm for the war? Were these methods successful? 6. What were some of the benefits to labor as a direct result of the war? 7. How did women benefit directly from the war? How significant were these benefits and to what extent did they continue after the war? 8. Who benefited most from the impact of the war? 9. Were there any measures to equalize the economic impact of the war on society? Part 4 Pg. 795-800 1. What gamble did the Germans take in 1918? What was the result? 2. What proposals were included in Wilson’s Fourteen Points? 3. What motives determined the behavior of David Lloyd George and Georges Clemenceau? What did Clemenceau want in particular? 4. What compromises were reached at Versailles? 5. What aspect of the Versailles Treaty angered the Germans the most? 6. What were the main military and territorial provisions of the treaty? (pertaining to Germany) 7. How was the map of Eastern Europe altered after World War I? 8. What happened to the Ottoman Empire after the war? (What was a mandate?)